Abstract
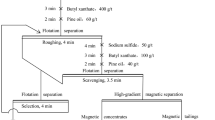
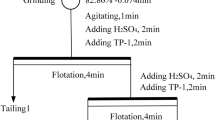
An effective flotation approach is proposed for improving the recovery of molybdenite fines from a finely-disseminated molybdenum ore. To maximize the flotation recovery of molybdenum, process mineralogy of raw ore, contrast tests, optimization of operation conditions and particle size analysis were systematically investigated. Process mineralogy suggests that in the raw ore, 61.63% of molybdenite particles distribute in the <20 μm size fraction, and intergrow with muscovite and pyrite as the contained and disseminated type. Contrast tests indicate that conventional flotation responds to poor collection efficiency for particles less than 25 μm. Oil agglomerate flotation (OAF) process demonstrates an obvious superiority in improving the flotation recovery of molybdenite fines. Furthermore, the flotation results of OAF process reveal that the dosage of transformer oil plays a critical role on the average size of collected mineral particles (d p50 ), agglomerates (d a50 ) and the molybdenum recovery. In addition, industrial tests illustrate that compared with the Mo-S bulk flotation approach, OAF process not only increases Mo recovery and grade of molybdenum concentrate by 22.75% and 17.47% respectively, but also achieves a sulfur concentrate with a superior grade of 38.92%.
摘要
本文提出了一种从细粒浸染状钼矿中有效回收辉钼矿的浮选方案。为了最大限度地提高辉钼矿 的回收率,系统地开展了原矿工艺矿物学、对比试验、工艺条件优化及颗粒尺寸分析等研究。工艺矿 物学研究表明,原矿中61.63%的辉钼矿的粒度分布在小于20 μm 粒级中,且它们与云母、黄铁矿共 生呈包含状结构及微细粒浸染状结构。对比试验结果表明,常规浮选工艺对粒径小于25μm 的颗粒回 收效果不佳,而油团聚浮选工艺对微细粒辉钼矿的回收具有明显优势。油团聚浮选工艺利用变压器油 作团聚油,团聚油用量变化对捕获的辉钼矿颗粒平均尺寸( (d p50 )、团聚体平均尺寸(d a50 ) 及辉钼矿回收 率影响显著。工业试验结果表明,与钼-硫混合浮选工艺相比,油团聚浮选工艺不仅使钼精矿的钼回 收率提高22.75%,钼品位提升17.47%,而且还获得含硫38.92%的合格硫精矿。
Similar content being viewed by others
References
LINCE J R, FRANTZ P. Anisotropic oxidation of MoS2 crystallites studied by angle-resolved X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy [J]. Tribology Letters, 2000, 9(3, 4): 211–218. DOI: 10.1023/A:1018869107511.
ZANIN M, AMETOV I, GRANO S, ZHOU L, SKINNER W. A study of mechanisms affecting molybdenite recovery in a bulk copper/molybdenum flotation circuit [J]. International Journal of Mineral Processing, 2009, 93(3, 4): 256–266. DOI: 10.1016/j.minpro.2009.10.001.
SONG Shao, ZHANG Xin, YANG Bing, LOPEZ-MENDOZA A. Flotation of molybdenite fines as hydrophobic agglomerates [J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2012, 98: 451–455. DOI: 10.1016/j.seppur.2012. 06.016.
LIN Qing, GU Guo, WANG Hui, LIU You, FU Jian, WANG Chong. Flotation mechanisms of molybdenite fines by neutral oils [J]. International Journal of Minerals, Metallurgy and Materials, 2018, 25(1): 1–10. DOI: 10.1007/s12613-018-1540-8.
LIN Qing, GU Guo, WANG Hui, LIU You, WANG Chong, FU Jian, ZHAO Jun, HUANG Luo. Recovery of molybdenum and copper from porphyry ore via iso-flotability flotation [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2017, 27(10): 2260–2271. DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(17)60252-8.
SIVAMOHAN R. The problem of recovering very fine particles in mineral processing–A review [J]. International Journal of Mineral Processing, 1990, 28(3, 4): 247–288. DOI: 10.1016/0301-7516(90)90046-2.
MIETTINEN T, RALSTON J, FORNASIERO D. The limits of fine particle flotation [J]. Minerals Engineering, 2010, 23(5): 420–437. DOI: 10.1016/j.mineng.2009.12.006.
SHAHBAZI B, REZAI B, KOLEINI S J. Bubble-particle collision and attachment probability on fine particles flotation [J]. Chemical Engineering and Processing: Process Intensification, 2010, 49(6): 622–627. DOI: 10.1016/j.cep. 2010.04.009.
QIN Wen, REN Liu, WANG Pei, YANG Cong, ZHANG Yan. Electro-flotation and collision-attachment mechanism of fine cassiterite [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2012, 22(4): 917–924. DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(11)61265-X.
REN Liu, ZHANG Yi, QIN Wen, BAO Shen, WANG Jun. Collision and attachment behavior between fine cassiterite particles and H2 bubbles [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2014, 24(2): 520–527. DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(14)63091-0.
CHOI J, LEE E, CHOI S Q, LEE S, HAN Y, KIM H. Arsenic removal from contaminated soils for recycling via oil agglomeration flotation [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2016, 285: 207–217. DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2015.09.105.
SUBRAHMANYAM T V, FORSSBERG K S E. Fine particles processing: Shear-flocculation and carrier flotation-a review [J]. International Journal of Mineral Processing, 1990, 30(3, 4): 265–286. DOI: 10.1016/0301-7516(90)90019-U.
CEBECI Y. Investigation of kinetics of agglomerate growth in oil agglomeration process [J]. Fuel, 2003, 82(13): 1645–1651. DOI: 10.1016/S0016-2361(03)00095-4.
VALDERRAMA L, RUBIO J. Unconventional column flotation of low-grade gold fine particles from tailings [J]. International Journal of Mineral Processing, 2008, 86(1–4): 75–84. DOI: 10.1016/j.minpro.2007.11.003.
ZHANG Qin, XIE Jun, CHEN Jian, CHENG Wei. Separation of azodicarbonamide from surface of diatomite by froth flotation [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2018, 25(1): 29–37. DOI: 10.1007/s11771-018-3714-y.
FU Jian, CHEN Kai, WANG Hui, GUO Chao, LIANG Wei. Recovering molybdenite from ultrafine waste tailings by oil agglomerate flotation [J]. Minerals Engineering, 2012, 39: 133–139. DOI: 10.1016/j.mineng. 2012.07.006.
AKTAS Z. Some factors affecting spherical oil agglomeration performance of coal fines [J]. International Journal of Mineral Processing, 2002, 65(3, 4): 177–190. DOI: 10.1016/S0301-7516(01)00074-6.
GENCE N. Coal recovery from bituminous coal by aggloflotation with petroleum oils [J]. Fuel, 2006, 85(7, 8): 1138–1142. DOI: 10.1016/j.fuel.2005.11.001.
SAHINOGLU E, USLU T. Amenability of Muzret bituminous coal to oil agglomeration [J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2008, 49(12): 3684–3690. DOI: 10.1016/j.enconman.2008.06.026.
SAHINOGLU E, USLU T. Role of recovery sieve size in upgrading of fine coal via oil agglomeration technique [J]. Fuel Processing Technology, 2015, 138: 21–29. DOI: 10.1016/j.fuproc.2015.04.030.
NETTEN K V, MORENO-ATANASIO R, GALVIN K P. A kinetic study of a modified fine coal agglomeration process [J]. Procedia Engineering, 2015, 102: 508–516. DOI: 10.1016/j.proeng.2015.01.201.
SEN S, SEYRANKAYA A, CILINGIR Y. Coal-oil assisted flotation for the gold recovery [J]. Minerals Engineering, 2005, 18(11): 1086–1092. DOI: 10.1016/j.mineng.2005. 03.007.
DUZYUL S, OZKAN A. Effect of contact angle, surface tension and zeta potential on oil agglomeration of celestite [J]. Minerals Engineering, 2014, 65: 74–78. DOI: 10.1016/j.mineng.2014.05.015.
AZEVEDO M A D, MILLER J D. Agglomeration and magnetic deinking for office paper [J]. Technical Association of the Pulp and Paper Industry Journal, 2000, 83(3): 66–72. https://utah.pure.elsevier.com/en/publications/agglomerationand-magnetic-deinking-for-office-paper.
KANG S K, SHIN H D. Method for selective recovery and dewatering sewage sludge by using sludge-coal-oil co-agglomeration: US, 7087171 [P]. 2006–08–08. http://patents.com/us-7087171.html.
HWANG I H, NAKAJIMA D, MATSUTO T, SUGIMOTO T. Improving the quality of waste-derived char by removing ash [J]. Waste Management, 2008, 28(2): 424–434. DOI: 10.1016/j.wasman.2006.11.015.
HE Ting, WAN He, SONG Nian, GUO Lin. The influence of composition of nonpolar oil on flotation of molybdenite [J]. Minerals Engineering, 2011, 24(13): 1513–1516. DOI: 10.1016/j.mineng.2011.07.003.
XU Tao, SUN Chun. Aerosol flotation of low-grade refractory molybdenum ores [J]. International Journal of Minerals, Metallurgy and Materials, 2012, 19(12): 1077–1082. DOI: 10.1007/s12613-012-0673-4.
DU Shu, LUO Zhen. Flotation technology of refractory low-grade molybdenum ore [J]. International Journal of Mining Science and Technology, 2013, 23(2): 255–260. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijmst.2013.04.010.
YIN Wan, ZHANG Li, XIE Feng. Flotation of Xinhua molybdenite using sodium sulfide as modifier [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2010, 20(4): 702–706. DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(09)60201-6.
CEBECI Y, SONMEZ I. The investigation of coalpyrite/lignite concentration and their separation in the artificial mixture by oil agglomeration [J]. Fuel, 2002, 81(9): 1139–1146. DOI: 10.1016/S0016-2361(02)00028-5.
ABAKAY H, AYHAN F D, KAHRAMAN F. Selective oil agglomeration in Sirnak asphaltite beneficiation [J]. Fuel, 2004, 83(14, 15): 2081–2086. DOI: 10.1016/j.fuel.2004. 05.001.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: Project(2016zzts103) supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, China; Project(51374249) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project(2015BAB12B02) supported by the National Key Technology R&D Program of China; Project(2013B090800016) supported by Guangdong Provincial Science and Technology Plan, China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, Qq., Gu, Gh., Wang, H. et al. An effective approach for improving flotation recovery of molybdenite fines from a finely-disseminated molybdenum ore. J. Cent. South Univ. 25, 1326–1339 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-018-3829-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-018-3829-1