Abstract
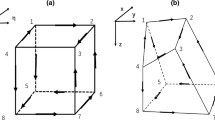
A modeling tool for simulating three-dimensional land frequency-domain controlled-source electromagnetic surveys, based on a finite-element discretization of the Helmholtz equation for the electric fields, has been developed. The main difference between our modeling method and those previous works is edge finite-element approach applied to solving the three-dimensional land frequency-domain electromagnetic responses generated by horizontal electric dipole source. Firstly, the edge finite-element equation is formulated through the Galerkin method based on Helmholtz equation of the electric fields. Secondly, in order to check the validity of the modeling code, the numerical results are compared with the analytical solutions for a homogeneous half-space model. Finally, other three models are simulated with three-dimensional electromagnetic responses. The results indicate that the method can be applied for solving three-dimensional electromagnetic responses. The algorithm has been demonstrated, which can be effective to modeling the complex geo-electrical structures. This efficient algorithm will help to study the distribution laws of 3-D land frequency-domain controlled-source electromagnetic responses and to setup basis for research of three-dimensional inversion.
摘要
大规模三维电磁数据的定量解释需要发展高效、 稳定的三维正反演算法。 正演是反演的前提和基础, 本文对正演问题开展深入研究, 实现了适用于陆地电磁勘探的频率域可控源电磁三维正演。 首先, 基于麦克斯韦方程组推导得到关于电场的亥姆霍兹方程, 通过伽辽金法建立了基于棱边元的有限元方程。 控制方程经过矢量有限元离散化后得到大型、 对称、 稀疏复线性方程组, 为了实现高效求解该线性方程组, 选用了不完全 Cholesky 分解预处理的迭代解法进行求解。 其次, 通过对均匀半空间模型的矢量有限元模拟计算, 数值结果与解析解的对比验证了本文算法的正确性。 最后, 对电性三维地电模型进行数值模拟, 计算的电磁响应均能反应出异常体的存在, 进一步说明本文算法能够对频率域可控源电磁三维进行有效模拟。 因此, 本文矢量有限元算法的成功实现可用于三维电磁响应的分析计算, 并有助于研究陆地三维频率域可控源电磁响应的分布规律, 同时也能为三维频率域可控源电磁法反演研究奠定基础。
Similar content being viewed by others
References
WHITE D, BOERNER D, WU J, LUCAS S, BERRER E, HANNILA J, SOMERVILLE R. Mineral exploration in the Thompson nickel belt, Manitoba, Canada, using seismic and controlled-source EM methods [J]. Geophysics, 2000, 65(6): 1871–1881.
CONSTABLE S, SRNKA L J. Special section-marine controlled-source electromagnetic methods an introduction to marine controlled-source electromagnetic methods for hydrocarbon exploration [J]. Geophysics, 2007, 72(2): WA3–WA12.
MACGREGOR L, SINHA M, CONSTABLE S. Electrical resistivity structure of the Valu Fa Ridge, Lau Basin, from marine controlled-source electromagnetic sounding [J]. Geophysical Journal International, 2001, 146(1): 247–236.
AVDEEV D B, KUVSHINOV A V, PANKRATOV O V, NEWMAN G A. Three-dimensional induction logging problems, Part 1: An integral equation solution and model comparisons [J]. Geophysics, 2002, 67(2): 413–426.
HURSAN G, ZHDANOV M S. Contraction integral equation method in 3-D electromagnetic modeling [J]. Radio Science, 2002, 37(6): 1089.
LIU Jian-xin, JIANG Peng-fei, TONG Xiao-zhong, XU Ling-hua, XIE Wei, WANG Hao. Application of BICGSTAB algorithm with incomplete LU decomposition preconditioning to two-dimensional magnetotelluric forward modeling [J]. Journal of Central South University: Science and Technology, 2009, 40(4): 485–490. (in Chinese)
ZHDANOV M S, LEE S K, YOSHIOKA K. Integral equation method for 3Dmodeling of electromagnetic fields in complex structures with inhomogeneous background conductivity [J] Geophysics, 2006, 71(6): G333–G345.
HABER E, ASCHER U, ARULIAH D, OLDENBURG D. Fast simulation of 3D electromagnetic problems using potentials [J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 2000, 163(1): 150–171.
HAN N, NAM M J, KIM H J, SONG Y, SUH J H. A comparison of accuracy and computation time of threedimensional magnetotelluric modelling algorithms [J]. Journal of Geophysics and Engineering, 2009, 6(2): 136–145.
MEHANEE S, ZHDANOV M. A quasi-analytical boundary condition for three-dimensional finite difference electromagnetic modeling [J]. Radio Science, 2004, 39(6): RS6014.
NEWMAN G A, ALUMBAUGH D L. Frequency-domain modeling of airborne electromagnetic responses using staggered finite differences [J]. Geophysical Prospecting, 1995, 43(8): 1021–1042.
STREICH R. 3D finite-difference frequency-domain modeling of controlled-source electromagnetic data: Direct solution and optimization for high accuracy [J]. Geophysics, 2009, 74(5): F95–F105.
WEISS C J, CONSTABLE S. Mapping thin resistors and hydrocarbons with marine EM methods, part II-modeling and analysis in 3D [J]. Geophysics, 2006, 71(6): G321–G332.
BÖRNER R U, ERNST O G, AND SPITZER K. Fast 3-D simulation of transient electromagnetic fields by model reduction in the frequency domain using Krylov subspace projection [J]. Geophysical Journal International, 2008, 173(3): 766–780.
da SILVA N V, MORGAN J V, MACGREGOR L, WARNER M. A finite element mutifrontal method for 3D CSEM modeling in the frequency domain [J]. Geophysics, 2012, 77(2): E101–E115.
MUKHERJEE S, EVERETT M E. 3Dcontrolled-source electromagnetic edge-based finite element modeling of conductive and permeable heterogeneities [J]. Geophysics, 2011, 76(4): F215–F226.
NAM M J, KIM H J, SONG Y, LEE T J, SON J S, SUH J H. 3D magnetotelluric modelling including surface topography [J]. Geophysical Prospecting, 2007, 55(2): 277–287.
UM E, HARRIS J M, ALUMBAUGH D L. 3D time-domain simulation of electromagnetic diffusion phenomena: A finiteelement electric-field approach [J]. Geophysics, 2010, 75(4): F115–F126.
FARQUHARSON C G, MIENSOPUST M P. Threedimensional finite-element modelling of magnetotelluric data with a divergence correction [J]. Journal of Applied Geophysics, 2011, 75(4): 699–710.
JIN J M. The finite element method in electromagnetics [M]. 2nd ed. New York: John Wiley & Sons, 2002.
SAAD Y. Iterative methods for sparse linear systems [M]. 2nd ed London: Cambridge University Press, 2002.
KAUFMAN A A, KELLER G V. Frequency and Transient Soundings (Methods in Geochemistry and Geophysics) [M]. Elsevier Science Press, 1983.
CAI Hong-zhu, XIONG Bin, MICHAEL Z. Threedimensional marine controlled-source electromagnetic modeling in anisotropic medium using finite element method [J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2015, 58(8): 2839–2850. (in Chinese)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: Projects(41674080, 41674079) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Jx., Liu, Pm. & Tong, Xz. Three-dimensional land FD-CSEM forward modeling using edge finite-element method. J. Cent. South Univ. 25, 131–140 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-018-3723-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-018-3723-x
Key words
- three-dimensional model
- frequency-domain electromagnetic method
- horizontal electric dipole
- forward modeling
- edge finite-element