Abstract
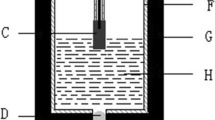
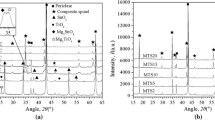
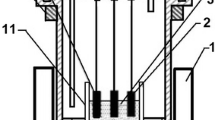
A comparative study on the corrosion resistance of NiFe2O4 ceramic inert anode for aluminum electrolysis prepared in the different sintering atmosphere was carried out in Na3AlF6–Al2O3 melt. The results show that the corrosion rates of NiFe2O4 ceramic inert anodes prepared in the vacuum and the atmosphere with oxygen content of 1×10–2 are 6.08 cm/a and 2.59 cm/a, respectively. A densification layer is formed at the surface of anode due to some reactions which produce aluminates. For the anode prepared in the atmosphere with oxygen content of 1×10–2, the thickness of the densification layer (about 50 μm) is thicker than that (about 20 μm) formed at the surface of anode prepared in the vacuum. The content of NiO and Fe(II) in Ni(II) x Fe(II)1–x Fe(III)2O4 increases with the decrease of the oxygen content of sintering atmosphere, which reduces the corrosion resistance of the material.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
PAWLEK R P. Inert anodes: An update [C] //GRANDFIELD J. Light Metals. Hoboken, NJ, USA: TMS, 2014: 1309–1313.
KVANDE H, HAUPIN W. Inert anodes for Al smelters: Energy balances and environmental impact [J]. JOM, 2001, 53: 29–33.
HALL C M. Process of reducing aluminum from its fluoride salts by electrolysis: USA, 0400664 [P]. 1889.
SADOWAY D R. Inert anodes for the Hall-Héroult cell: The ultimate materials challenge [J]. JOM, 2001, 53: 34–35.
GOUPIL G, HELLE S, DAVIS B, GUAY D, ROUÉ L. Anodic behavior of mechanically alloyed Cu–Ni–Fe and Cu–Ni–Fe–O electrodes for aluminum electrolysis in low-temperature KF-AlF3 electrolyte [J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2013, 112: 176–182.
TIAN Zhong-liang, LAI Yan-qing, LI Zhi-you, CHAI Deng-peng, LI Jie, LIU Ye-xiang. Further development on NiFe2O4-based cermet inert anodes for aluminum electrolysis [J]. JOM, 2014, 66(11): 2229–2234.
KHRAMOV A P, KOVROV V A, YU. ZAIKOV P, CHUMAREV V M. Anodic behaviour of the Cu82Al8Ni5Fe5 alloy in low-temperature aluminium electrolysis [J]. Corrosion Sci, 2013, 70: 194–202.
LI J, WANG Z G, LAI Y Q, WU Y Y, YE S L. Effect of structural parameters on the thermal stress of a NiFe2O4-based cermet inert anode in aluminum electrolysis [J]. Acta Metall Sin (Engl. Lett.) 2007, 20(2): 139–147.
DU Jin-jing, LIU Yi-han, YAO Guang-chun, LONG Xiu-li, ZHANG Xiao. Effect of MnO2 addition on early-stage sintering behavior and properties of NiFe2O4 ceramics [C]// SUAREZ C E. Light Metals. Washington, PA, USA: TMS, 2012: 1385–1388.
TIAN Zhong-liang, ZHANG Teng, LIU Kai, LAI Yin-qing, LI Jie. Effect of sintering atmosphere on composition and properties of NiFe2O4 ceramic [J]. Journal of Central South University of Technology, 2015, 22: 450–454. (in Chinese)
LAI Yan-qing, TIAN Zhong-liang, QIN Qing-wei, ZHANG Gang, LI Jie. Solubility of composite oxide ceramics in Na3AlF6-Al2O3 melts [J]. Journal of Central South University of Technology, 2003, 34(3): 245–248. (in Chinese)
OLSEN E, THONSTAD J. Nickel ferrite as inert anodes in aluminium electrolysis: Part I material fabrication and preliminary testing [J]. Journal of Applied Electrochemistry, 1999, 29: 293–299.
OLSEN E, THONSTAD J. Nickel ferrite as inert anodes in aluminium electrolysis: Part II material performance and long-term testing [J]. Journal of Applied Electrochemistry, 1999, 29: 301–311.
BLINOV V, POLYAKOV P, THONSTAD J, IVANOV V, PANKOV E. Behaviour of inert anodes for aluminium electrolysis in a low temperature electrolyte, Part I [J]. Aluminium, 1997, 73(12): 906–910.
HE Han-bing, WANG Yuan, LONG Jia-ju, CHEN Zhao-hui. Corrosion of NiFe2O4–10NiO–based cermet inert anodes for aluminium electrolysis [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2013, 23: 3816–3821.
LI Jie, DUAN Hua-nan, LAI Yan-qing, TIAN Zhong-liang, LIU Ye-xiang. Effect of NiO content on corrosion behaviour of Ni-xNiO-NiFe2O4 cermets in Na3AlF6–Al2O3 melts [J]. Transactions of the Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2004, 14(6): 1180–1186.
TIAN Zhong-liang, LAI Yan-qing, YANG Shu, LI Jie, HWANG J Y, LIU Ye-xiang. Anodic corrosion behavior of NiFe2O4-Based cermet in Na3AlF6-K3AlF6-AlF3 for aluminum electrolysis [J]. Metall Mater Trans. B, 2015, 46: 1257–1261.
ZHANG Yun-shu, WU Xiao-xia, RAPP R A. Modeling of the solubility of NiO/NiAl2O4 and FeO/FeAl2O4 in cryolite melts [C]// PAUL N. CREPEAU. Light Metals. San Diego, California, USA: TMS, 2003: 415–421.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: Projects(51474238, 51334002) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tian, Zl., Yang, K., Lai, Yq. et al. Effect of sintering atmosphere on corrosion resistance of NiFe2O4 ceramic in Na3AlF6–Al2O3 melt. J. Cent. South Univ. 24, 1929–1933 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-017-3600-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-017-3600-z