Abstract
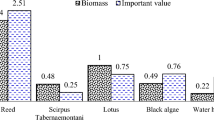
An imbedded integrating ecological entity (IIEE) was designed to combine landscaping, replenishing-water purifying and ecosystem maintaining simultaneously. With this IIEE, within 15 d experiment, simulated replenish water (SRW) with high (SRW-I) or low (SRW-II) nutrients concentration was well purified. Relative removal rates of CODCr, TP, TN, Chl-a and turbidity reached 84.87%, 84.05%, 94.76%, 188.17%, 110.93% when dealing SRW-I, and 52.62%, 90.05%, 82.44%, 166.15%, 202.99%, respectively, when dealing SRW-II. The well grew flora and fauna of IIEE benefit eco-maintaining and landscaping. Separately, the maximal root and stem length-increments of Cyperus alternifolius Linn. were 26.1 mm and 28.4 mm, while for Potamogeton crispus Linn. 18.3 mm and 25.7 mm. Mortality for both Bellamya aeruginosa and Misgurnus anguillicaudatus was both under 2.96%. The analysis of variance (ANOVA) indicated that most experimental indexes in each group performed more significantly better than those in their control. All results indicated that the IIEE is a promising technology for future urban waterscapes construction.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
BULUT Z, YILMAZ H. Determination of waterscape beauties through visual quality assessment method [J]. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 2009, 154(1/2/3/4): 459–468.
ZHU Ling-yu, LI Yong-kui. A preliminary analysis of the waterscape in face of the shortage of water [J]. Procedia Engineering, 2011, 21: 693–699.
SAKICI C. Assessing landscape perceptions of urban waterscapes [J]. Anthropologist, 2015, 21(1/2): 182–196.
HALL C M. Crisis events in tourism: Subjects of crisis in tourism [J]. Current Issues in Tourism, 2010, 13(5): 401–417.
GÖSSLING S, PEETERS P, HALL C M, CERON J P, DUBOIS G, LEHMANN L V, SCOTT D. Tourism and water use: Supply, demand, and security. An international review [J]. Tourism Management, 2012, 33(1): 1–15.
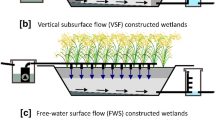
CUI Fang, YUAN Bo, WANG Ying. Constructed wetland as an alternative solution to maintain urban landscape lake water quality: Trial of Xing-Qing Lake in Xi’an City [J]. Procedia Environmental Sciences, 2011, 10: 2525–2532.
FANG Jing-jing, ZHOU Ai-guo, MA Chuan-ming, LIU Cun-fu, CAI He-sheng, GAN Yi-qun, LIU Yun-de. Evaluation of nitrate source in groundwater of southern part of North China Plain based on multi-isotope [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2015, 22(2): 610–618.
WHITE M, SMITH A, HUMPHRYES K, PAHL S, SNELLING D, DEPLEDGE M. Blue space: The importance of water for preference, effect, and restorativeness ratings of natural and built scenes [J]. Journal of Environmental Psychology, 2010, 30(4): 482–493.
ZHAO Wen-yu, YANG Guang-wen, CHEN Xiao-xing, YU Jun-yi, MA Bei-kong. Study on integrated restoration technique for eutrophic artificial lakes [J]. Advanced Materials Research, 2013, 807: 1304–1310.
LAPOINTE B E, HERREN L W, DEBORTOLI D D, VOGEL M A. Evidence of sewage-driven eutrophication and harmful algal blooms in Florida’s Indian River Lagoon [J]. Harmful Algae, 2015, 43: 82–102.
YI Li-li, JIAO Wen-tao, CHEN Xiao-ning, CHEN Wei-ping. An overview of reclaimed water reuse in China [J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2011, 23(10): 1585–1593.
State Environmental Protection Administration of China. Monitoring and analytic methods of water and wastewater [M]. 4th ed. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press, 2002. (in Chinese)
WANG Xia, LV Xian-guo, BAI Shu-ying, ZHANG Zhu-qing, YAN Bai-ru, YU Li, ZHANG Xue-lin, ZHANG Li-xian. Probability and threshold values for recognizing eutrophication in Lake Songhua [J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2006, 26(12): 3989–3997. (in Chinese)
SOLHEIM A L, REKOLAINEN S, MOE S J, CARVALHO L, PHILLIPS G, PTACNIK R, PENNING W E, TOTH L G, O’TOOLE C, SCHARTAU A K L. Ecological threshold responses in European lakes and their applicability for the water framework directive (WFD) implementation: Synthesis of lakes results from the REBECCA project [J]. Aquatic Ecology, 2008, 42(2): 317–334.
YANG Long, WANG Xiao-yan, WANG Zi-jian, WU Zai-xing, WU Jing. A eutrophication risk assessment system based on phosphorus threshold [J]. China Environmental Science, 2010, 30(Suppl): 29–34. (in Chinese)
HADWEN W L. Lake tourism: An integrated approach to lacustrine tourism systems [J]. Annals of Tourism Research, 2007, 34(2): 555–556.
BARKO J W, JAMES W F. Effects of submerged aquatic macrophytes on nutrient dynamics, sedimentation, and resuspension [M]. New York: Springer, 1998.
GEEST G J V, WOLTERS H, ROOZEN F C J M, COOPS H, ROIJACKERS R M M, BUIJSE A D, SCHEFFER M. Water-level fluctuations affect macrophyte richness in floodplain lakes [J]. Hydrobiologia, 2005, 539(1): 239–248.
ZHU Zhi-lin, LIU Yun-guo, ZHANG Ping-yang, ZENG Guang-ming, HU Xi, LI Hua-ying, GUO Yi-ming, GUO Xing-rong. Co-culture with Cyperus alternifolius induces physiological and biochemical inhibitory effects in Microcystis aeruginosa [J]. Biochemical Systematics and Ecology, 2014, 56: 118–124.
GUO Yi-ming, LIU Yun-guo, ZENG Guang-ming, HU Xin-jiang, LI Xin, HUANG Da-wei, LIU Yun-qin, YIN Yi-cheng. A restoration-promoting integrated floating bed and its experimental performance in eutrophication remediation [J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2014, 26(5): 1090–1098.
WILLIAM R B III, RELYEA R A. A new mechanism of macrophyte mitigation: How submerged plants reduce malathion’s acute toxicity to aquatic animals [J]. Chemosphere, 2014, 108: 405–410.
KARATAYEV A Y, BURLAKOVA L E, PADILLA D K. Invasive aquatic species of europe (impacts of zebra mussels on aquatic communities and their role as ecosystem engineers) [M]. Netherlands: Kluwer Academic Publishers, 2002.
CHUA L H C, TAN S B K, SIM C H, GOYAL M K. Treatment of baseflow from an urban catchment by a floating wetland system [J]. Ecological Engineering, 2012, 49(12): 170–180.
WANG Hong-bo, LI Mei, ZHANG Ke-feng, WANG Cui-yan. Study on in-situ repair technology for different water quality scenic water body [J]. Energy Procedia, 2011, 5(22): 482–486.
LI Xian-ning, SONG Hai-liang, LI Wei, LU Xi-wu, NISHIMURA O. An integrated ecological floating-bed employing plant, freshwater clam and biofilm carrier for purification of eutrophic water [J]. Ecological Engineering. 2010, 36(4): 382–390.
STEVENS Q. Artificial waterfronts [J]. Urban Design International, 2009, 14(1): 3–21.
FOREST B, FOREST P. Engineering the North American waterscape: The high modernist mapping of continental water transfer projects [J]. Political Geography, 2012, 31(3): 167–183.
WU Yong-hong, ZHANG Shan-qing, ZHAO Hui-jun, YANG Lin-zhang. Environmentally benign periphyton bioreactors for controlling cyanobacterial growth [J]. Bioresource Technology, 2010, 101(24): 9681–9687.
LIU Wen-wu, WANG Xiu-ping, TU Xue-yan, WANG Chang-yong. Treatment of pretreated coking wastewater by flocculation, alkali out, air stripping, and three-dimensional electrocatalytic oxidation with parallel plate electrodes [J]. Environmental Science & Pollution Research, 2014, 21(19): 11457–11468.
BERNARD O, MOND B R. Validation of a simple model accounting for light and temperature effect on microalgal growth [J]. Bioresource Technology, 2012, 123: 520–527.
PICARD C R, FRASER L H, STEER D. The interacting effects of temperature and plant community type on nutrient removal in wetland microcosms [J]. Bioresource Technology, 2005, 96(9): 1039–1047.
FU Wei, YE Jian-feng, GU Hong, HE Xiao-chu. Analysis on accumulation and transformation of organic matter in vertical-flow constructed wetlands [J]. Environmental Pollution & Control, 2010, 32(3): 55–59. (in Chinese)
SAEED T, SUN Guang-zhi. A comparative study on the removal of nutrients and organic matter in wetland reactors employing organic media [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2011, 171(2): 439–447.
YANG Meng-juan, LIN Jian-wei, ZHAN Yan-hui, ZHU Zhi-liang, ZHANG Hong-hua. Immobilization of phosphorus from water and sediment using zirconium-modified zeolites [J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2015, 22(5): 3606–3619.
INSEL G, EROL S, ÖVEZ S. Effect of simultaneous nitrification and denitrification on nitrogen removal performance and filamentous microorganism diversity of a full-scale MBR plant [J]. Bioprocess and Biosystems Engineering, 2014, 37(11): 2163–2173.
GUPTA V K, SADEGH H, YARI M, SHAHRYARI G R, MAAZINEJAD B, CHAHARDORI M. Removal of ammonium ions from wastewater: A short review in development of efficient methods [J]. Global Journal of Environmental Science and Management, 2015, 1(2): 149–158.
FENG Yan, YU Yan-zhen, QIU Li-ping, FENG Sheng, ZHANG Jian-wei. Domestic wastewater treatment using biological aerated filtration system with modified zeolite as biofilm support [J]. Desalination and Water Treatment, 2014, 52(25/26/27): 5021–5030.
GREGOR J, MARŠ L B. Freshwater phytoplankton quantification by chlorophyll a: A comparative study of in vitro, in vivo and in situ methods [J]. Water Research, 2004, 38(3): 517–522.
LI Fei, MAO Wen-juan, LI Xue, WANG Xiao-yu, XIAO Zhi-hua, ZHOU Yao-yu, ZENG Guang-ming. Characterization of microcystis aeruginosa immobilized in complex of PVA and sodium alginate and its application on phosphorous removal in wastewater [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2015, 22(1): 95–102.
BABA A, OLOWOYEYE O A. The hydrochemistry of Angwan Mallam and environs (PART OF KEFFI SHEET 208 NE) [J]. Journal of Applied Sciences and Environmental Management, 2013, 15(4): 675–680.
KIMBELL H S, MORRELL L J. Turbidity influences individual and group level responses to predation in guppies, Poecilia reticulata [J]. Animal Behaviour, 2015, 103: 179–185.
BAIJNATH H. A study of Cyperus alternifolius L., sens. lat. (Cyperaceae) [J]. Kew Bulletin, 1975, 30(3): 521–526.
ZHU Si-xi, GE Han-liang, GE Ying, CAO Hai-qin, LIU Dong, CHANG Jie, ZHANG Chong-bang, GU Bao-jing, CHANG Scott-X. Effects of plant diversity on biomass production and substrate nitrogen in a subsurface vertical flow constructed wetland [J]. Ecological Engineering, 2010, 36(10): 1307–1313.
SHEN Qiu-shi, ZHOU Qi-lin, SHANG Jing-ge, SHAO Shi-guang, ZHANG Lei, FAN Cheng-xin. Beyond hypoxia: Occurrence and characteristics of black blooms due to the decomposition of the submerged plant Potamogeton crispus in a shallow lake [J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2014, 26(2): 281–288.
CHEN Wang-ke, BAO Jie, NI Xi-yuan, DAI Ji-hong, YU Ye-hui, JIANG Hong-bo. Effects of temperature and sudden change on oxygen consumption rate, ammonia excretion rate and asphyxiation point of loach (Misgurnus anguillicaudatus) [J]. Journal of Shenyang Agricultural University, 2014, 45(6): 741–745. (in Chinese)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: Project(2016M590348) supported by China Postdoctoral Science Foundation; Projects(41301154, 41271332) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, Ym., Song, Bl., Liu, Yg. et al. Maintaining eco-health of urban waterscapes with imbedded integrating ecological entity: Experimental approach. J. Cent. South Univ. 23, 2827–2837 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-016-3346-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-016-3346-z