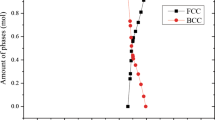
Abstract
Because of the mixed grain and coarse grain structure, the long heat treatment cycle and large energy conservation in the heavy cylinder heat treatment process, the up ladder type and terraced type normalizing heat treatment of heavy cylinder after rolling were put forward. The microstructure and mechanical properties of 2.25Cr1Mo0.25V steel after the up ladder type normalizing, terraced type normalizing and isothermal type normalizing were studied. Experimental results show that: 1) For the grain refinement, the twice terraced type normalizing is better than the up ladder type and isothermal type normalizing, and the average grain size is 18 μm; 2) The yield strength, tensile strength and -30 °C charpy impact energy after twice terraced type normalizing are 681 MPa, 768 MPa and 181 J, respectively, and the mechanical properties are better than those of the up ladder type and isothermal type normalizing; 3) Compared with the isothermal type normalizing, the holding time of terraced type normalizing can be shortened by 30%, which greatly reduces the energy consumption.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
PEI X H, ZHOU L P, LIU X W. Analysis of edge microstructure characteristics and stamping formability of low carbon pickled steel sheets [J]. Baosteel Technical Research, 2014, 8(2): 36–40.
GUAN Y P, WANG Z H, WU B, WANG W X, FU W T. Mechanism and inhibition of grain coarsening of Al-Mg-Si alloy in hot forming [J]. Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology (New Series), 2013, 20(3): 67–74.
LI Q, LIU Z D, TANG G B, TIAN Z I, SICILIAN O F. Mathematical model of microstructure evolution of X60 line pipe steel during CSP hot rolling [J]. Journal of Iron Steel Research (International), 2010, 17(1): 70–78.
YUAN Guo, WANG Guo-dong, WANG Ri-qing, WANG Li-jun, WANG Zhao-dong. Development and application of steel plate heat treatment technology and facilities [J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 2009, 21(5): 1–7. (in Chinese)
AKIO F, KAZUO O. JEF steel’s advanced manufacturing technologies for high performances steel plates [J]. JEF Technical Report, 2005, 10(5): 10–15.
LIU Y R, YE D, YONG Q L. Effect of heat treatment on microstructure and property of Cr13 super martensitic stainless steel [J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 2011, 18(11): 60–66.
PAN Jian-sheng, GU Jian-feng, WANG Jing. Discussion of heat treatment development strategy in China [J]. Heat Treatment of Metals, 2013, 38(1): 4–14. (in Chinese)
HE Xi-kou, BAI Tian, LIU Zheng-dong, LIN Zhao-jie. Effect of heating rate and cooling model on austenite grain size of 508-3 steel [J]. Hot Working Technology, 2013, 42(20): 204–205. (in Chinese)
ZHOU Wei-hai, ZHANG Wen-hui, WANG Cun-yu, CHUI Zhan-quan. Effect of heat treatment process on the cryogenic toughness of steel 2.25Cr-1Mo-0.25V [J]. China Metallurgy, 2015, 15(9): 46–48. (in CHinese)
HU Guang-qi, WANG Zhi-gang, HU Tian-jiang. Test study of domestic 2.25Cr-1Mo-0.3V steel heat treatment process [J]. Petro-Chemical Equipment, 2012, 41(2): 23–26. (in Chinese)
WANG Yue-xiang, ZHOU Ping, MA Heng, LI Yong-qiang. Influence of heat treatment process on microstructure and properties of the low-temperature pressure vessel steel [J]. Transactions of Materials and Heat Treatment, 2012, 33(Supplement): 77–80.
O’BRIEN J M, HOSFORD W F. Spheroidization cycles for medium carbon steels [J]. Metall Mater Trans A, 2002, 33A(4): 1255–1261.
YANG Hong-bo, WANG Kuai-she, WANG Qing-juan, ZHU Fu-xian. Spheroidizing growth mechanism of C cementite in GCr15 bearing steel [J]. Transactions of Materials and Heat Treatment, 2012, 33(8): 79–83.
YOU Y, YAN M F, ZHANG C S. Phase field simulation for grains evolution of 17-4PH steel during cyclic heat treatment [J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2013, 26(2): 183–187.
JING Qin, MOU Jun, KANG Da-tao, ZHU Ya-gang, LI Fan-ying. Structure heredity of high harden ability steels and its elimination [J]. Iron and Steel, 1998, 33(7): 41–43. (in Chinese)
SONG Chuan-bao, JIN Jia-yu, LIU Zhi-ying, GUO Pei-liang. Research of heat treatment process of grain refinement and homogenization on steam turbine low pressure rotor [J]. Heavy Casting and Forging, 1998(4): 34–37. (in Chinese)
GUO Jian. Microstructure and mechanical properties of 2.25Cr-1Mo-0.25V steel [D]. Qinhuangdao: Yanshan University, 2004. (in Chinese)
YI Hai-hong, SUN Ming-xue, XU Yang, LIU Zhen-yu. Effect of rolling process on low temperature impact energy for a Q690 construction machinery steel [J]. Transactions of Materials and Heat Treatment, 2013, 34(10): 34–37. (in Chinese)
ZHONG Quan-peng, ZHAO Zhi-hua. Fractography [M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2006. (in Chinese)
WANG Y F, MA S G, CHEN X H, SHI J Y, ZHANG Y, QIAO J W. Optimizing mechanical properties of AlCoCrFeNiTix high-entropy alloys by tailoring micristructures [J]. Acta Metall Sin, 2013, 26(3): 277–284.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: Project(51305388) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project(BJ2014055) supported by the Youth Talent Projects of Colleges in Hebei Province, China; Project(2016M590211) supported by China Postdoctoral Science Foundation
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, Jl., Peng, Y., Qiu, Cw. et al. Comparison of up ladder type and terraced type normalizing heat treatments of heavy cylinder. J. Cent. South Univ. 23, 2777–2783 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-016-3340-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-016-3340-5