Abstract
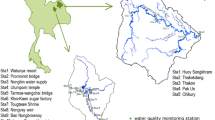
Multivariate statistical techniques, such as cluster analysis (CA), discriminant analysis (DA), principal component analysis (PCA) and factor analysis (FA), were applied to evaluate and interpret the surface water quality data sets of the Second Songhua River (SSHR) basin in China, obtained during two years (2012-2013) of monitoring of 10 physicochemical parameters at 15 different sites. The results showed that most of physicochemical parameters varied significantly among the sampling sites. Three significant groups, highly polluted (HP), moderately polluted (MP) and less polluted (LP), of sampling sites were obtained through Hierarchical agglomerative CA on the basis of similarity of water quality characteristics. DA identified pH, F, DO, NH3-N, COD and VPhs were the most important parameters contributing to spatial variations of surface water quality. However, DA did not give a considerable data reduction (40% reduction). PCA/FA resulted in three, three and four latent factors explaining 70%, 62% and 71% of the total variance in water quality data sets of HP, MP and LP regions, respectively. FA revealed that the SSHR water chemistry was strongly affected by anthropogenic activities (point sources: industrial effluents and wastewater treatment plants; non-point sources: domestic sewage, livestock operations and agricultural activities) and natural processes (seasonal effect, and natural inputs). PCA/FA in the whole basin showed the best results for data reduction because it used only two parameters (about 80% reduction) as the most important parameters to explain 72% of the data variation. Thus, this work illustrated the utility of multivariate statistical techniques for analysis and interpretation of datasets and, in water quality assessment, identification of pollution sources/factors and understanding spatial variations in water quality for effective stream water quality management.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
NGOYE E, MACHIWA J F. The influence of land-use patterns in the Ruvu river watershed on water quality in the river system [J]. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth, 2004, 29(15/16/17/18): 1161–1166.
BIERMAN P, LEWIS M, OSTENDORF B, TANNER J. A review of methods for analysing spatial and temporal patterns in coastal water quality [J]. Ecological Indicators, 2011, 11: 103–114.
BHUIYAN M A H, RAKIB M A, DAMPARE S B, GANYAGLO S, SUZUKI S. Surface water quality assessment in the central part of Bangladesh using multivariate analysis [J]. KSCE Journal of Civil Engineering, 2011, 15(6): 995–1003.
OUYANG Y, NKEDI-KIZZA P, WU Q T, SHINDE D, HUANG C H. Assessment of seasonal variations in surface water quality [J]. Water Research, 2006, 40: 3800–3810.
SHAHIDUL I M, TANAKA M. Impacts of pollution on coastal and marine ecosystems including coastal and marine fisheries and approach for management: A review and synthesis [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2004, 48(7/8): 624–649.
ORPIN A R, RIDD P V, THOMAS S, ANTHONY K R N, MARSHALL P, OLIVER J. Natural turbidity variability and weather forecasts in risk management of anthropogenic sediment discharge near sensitive environments [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2004, 49 (7/8): 602–612.
SANCHEZ E, COLMENAREJO M F, VICENTE J, RUBIO A, GARCIA M G, TRAVIESO L, BORJA R. Use of the water quality index and dissolved oxygen deficit as simple indicators of watersheds pollution [J]. Ecological Indicators, 2007, 7(2): 315–328.
DIXON W, CHISWELL B. Review of aquatic monitoring program design [J]. Water Research, 1996, 30: 1935–1948.
VEGA M, PARDO R, BARRADO E, DEBAN L. Assessment of seasonal and polluting effects on the quality of river water by exploratory data analysis [J]. Water Research, 1998, 32(12): 3581–3592.
SINGH K P, MALIK A, SINHA S. Water quality assessment and apportionment of pollution sources of Gomti River (India) using multivariate statistical techniques: A case study [J]. Analytica Chimica Acta, 2005, 35: 3581–3592.
BU H M, TAN X, LI S Y, ZHANG Q F. Water quality assessment of the Jinshui River (China) using multivariate statistical techniques [J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2010, 60(8): 1631–1639.
ALBERTO W D, PILAR D M D, VALERIA A M, FABIANA P S, CECILIA H A, ANGELES B M D L. Pattern recognition techniques for the evaluation of spatial and temporal variations in water quality. A case study: Squia River Basin (Cordoba-Argentina) [J]. Water Research, 2000, 35: 2881–2894.
SINGH K P, MALIK A, MOHAN D, SINHA S. Multivariate statistical techniques for the evaluation of spatial and temporal variations in water quality of Gomti River (India)—A case study [J]. Water Research, 2004, 38: 3980–3992.
MCNEIL V H, COX M E, PREDA M. Assessment of chemical water types and their spatial variation using multi-stage cluster analysis, Queensland, Australia [J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2005, 310 (1/2/3/4): 181–200.
PANDA U C, SUNDARAY S K, RATH P, NAYAK B B, BHATTA D. Application of factor and cluster analysis for characterization of river and estuarine water systems—A case study: Mahanadi River (India) [J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2006, 331 (3/4): 434–445.
SHRESTHA S, KAZAMA F. Assessment of surface water quality using multivariate statistical techniques: A case study of the Fuji river basin, Japan [J]. Environmental Modelling & Software, 2007, 22: 464–475.
NAJAR I A, KHAN A B. Assessment of water quality and identification of pollution sources of three lakes in Kashmir, India, using multivariate analysis [J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2012, 66: 2367–2378.
ZARE G A, SHEIKH V, SADODDIN A. Assessment of seasonal variations of chemical characteristics in surface water using multivariate statistical methods [J]. International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 2011, 8(3): 581–592.
REGHUNATH R, MURTHY T R S, RAGHAVAN B R. The utility of multivariate statistical techniques in hydrogeochemical studies: An example from Karnataka, India [J]. Water Research, 2002, 36 (10): 2437–2442.
WANG Y, WANG P, BAI Y J, TIAN Z X, LI J W, SHAO X, MUSTAVICH L F, LI B L. Assessment of surface water quality via multivariate statistical techniques: A case study of the Songhua River Harbin region, China [J]. Journal of Hydro-environment Research, 2013, 7(1): 30–40.
YAN D H, DENG W, HE Y. The responses of hydro-environment system in the Second Songhua Basin to melt water [J]. Journal of Geographical Sciences, 2002, 12(3): 289–294.
JIANG G B, SHI J B, FENG X B. Mercury pollution in China [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2006, 40(12): 3672–3678.
HELENA B, PARDO R, VEGA M, BARRADO E, FERNANDEZ J M, FERNANDEZ L. Temporal evaluation of groundwater composition in an alluvial aquifer (Pisuerga river, Spain) by principal component analysis [J]. Water Research, 2000, 34: 807–816.
MCKENNA Jr J E. An enhanced cluster analysis program with bootstrap significance testing for ecological community analysis [J]. Environmental Modelling & Software, 2003, 18(2): 205–220.
WOLFGANG K H, LÉOPOLD S. Applied multivariate statistical analysis [M]. Third edition. Belin Heidelberg: Springer, 2012: 367–382.
MASAMBA W R L, MAZVIMAVI D. Impact on water quality of land uses along Thamalakane-Boteti River: An outlet of the Okavango Delta [J]. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth, 2008, 33(8/9/10/11/12/13): 687–694.
WANG X L, LU Y L, HAN J Y, HE G Z, WANG T Y. Identification of anthropogenic influences on water quality of rivers in Taihu watershed [J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences-China, 2007, 19(4): 475–481.
LIU C W, LIN K H, KUO Y M. Application of factor analysis in the assessment of groundwater quality in a Blackfoot disease area in Taiwan [J]. The Science of the Total Environment, 2003, 313: 77–89.
ZHOU F, LIU Y, GUO H C. Application of multivariate statistical methods to water quality assessment of the watercourses in Northwestern New Territories, Hong Kong [J]. Environmental Monitoring Assessment, 2007, 132(1/2/3): 1–13.
BINI L M, THOMAZ S M, CARVALHO P. Limnological effects of Egeria najas Planchon (Hydrocharitaceae) in the arms of Itaipu Reservoir (Brazil, Paraguay) [J]. Limnology, 2010, 11(1): 39–47.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: Project(2012ZX07501002-001) supported by the Ministry of Science and Technology of China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zheng, Ly., Yu, Hb. & Wang, Qs. Application of multivariate statistical techniques in assessment of surface water quality in Second Songhua River basin, China. J. Cent. South Univ. 23, 1040–1051 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-016-0353-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-016-0353-z