Abstract
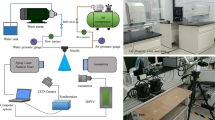
In order to enhance the atomization efficiency of atomizer, a new type of wind-spray dust controller combining the rotary-atomization and colliding broken of droplets was designed by the method of opening the water circulation within the blades. The experiment test for dust controller was conducted by adjusting the following parameters: rotating speed, diversion hole-exit diameter, and colliding tooth angle. Results show that the atomization efficiency increases firstly then decreases with them. And the optimal parameters are obtained with rotating speed 1500-2200 r/min, diversion hole-exit diameter 2-2.5 mm and colliding tooth angle 30°-40°, and under these conditions the corresponding atomization efficiency tops to 95%. Then, the atomization situation under the optimal parameters is held from the aspect of simulation internal flow field and the results of droplet size (30-80 µm) are got, which indicates that the conclusion on the optimized parameters of dust controller is reasonable. The collecting efficiencies of different dust concentrations are determined, ranging from 85% to 98.4%, which shows that the designed dust controller can obtain a good atomizing effect and achieve well dustfall efficiency for the wetting dust control of coal mine.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
FIFE J P, OZKAN H E, DERKSEN R C, GREWAL P S. Effects of pumping on entomopathogenic nematodes and temperature increase within a spray system [J]. Applied Engineering in Agriculture, 2007, 23: 405–412.
WU Chao. Fault tree analysis of dust suppression mechanism in a spray system with wetting agent [J]. Journal of Central South University of Technology, 2000, 7(3): 117–123.
XIE J L, GAN Z W, DUAN F. Characterization of spray atomization and heat transfer of pressure swirl nozzles [J]. International Journal of Thermal Sciences, 2013, 68: 94–102.
STECKEL H, ESKANDAR F. Factors affecting aerosol performance during nebulization with jet and ultrasonic nebulizers [J]. European Respiratory Journal, 2003, 19: 443–455.
LIU Qiu-zu, KOU Zi-ming, HAN Zhen-nan. Numerical simulation of dynamic process for liquid film spreading by lattice Boltzmann method and its experimental verification [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2014(8): 3247–3253.
MA Su-ping, KOU Zi-ming. Study on mechanism of reducing dust by spray [J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2005(3): 297–300. (in Chinese)
LI Qing-zhao, LIN Bai-quan, ZHAO Shuai, DAI Hua-ming. Surface physical properties and its effects on the wetting behaviors of respirable coal mine dust [J]. Powder Technology, 2013, 233: 137–145.
XAVIER S, DENIS B, SANDRINE C, DOMINIQUE T, ROLAND R. Consequences of high transitory airflow flows generated by segmented pulse-jet cleaning of dust collector filter bags [J]. Powder Technology, 2010, 201: 37–43.
ZHEN J Q, LUO Y Q, ZHANG J, LONG H L, The experiment of best gas-consumption rate on the Pneumatic atomizing [J]. Journal of Agricultural Machinery, 2007, 38: 195–120.
JIANG X, SIAMAS G A, JAGUS K, KARAYIANNIS T G. Physical modelling and advanced simulations of gas-liquid two-phase jet flows in atomization and sprays [J]. Progress in Energy and Combustion Science, 2010, 36: 131–167.
NARAYANAN S, BHAVE P, SRINIVASAN K, RAMAMURTHI K, SUNDARARAJAN T. Spectra and directivity of a Hartmann whistle [J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2009, 321: 875–892.
MA Z F, YAN Z B, CHEN J X. CFD numerical simulation and experiment of the water-air rotating jet flow dust-controlling system on the comprehensive mechanized mining faces [J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2011, 36: 818–822. (in Chinese).
ZHAO Zhi-guo, XIE Mao-zhao. Numerical simulation about interaction between pressure swirl spray and hot porous medium [J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2008, 49: 1047–1055.
YIN J L, JIAO L, QIU X Q. Numerical and experimental investigation of flow in swirling nozzle [J]. Journal of Zhejiang University: Engineering Science, 2009, 43: 968–972. (in Chinese)
LIU Jun-xiang, YU Qing-bo, GUO Qiang. Experimental investigation of liquid disintegration by rotary cups [J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2012, 73: 44–50.
HADEF R, LENZE B. Measurements of droplets characteristics in a swirl-stabilized spray flame [J]. Experimental Thermal and Fluid Science, 2005, 30: 117–130.
EJIM C E, RAHMAN M A, AMIRFAZLI A, FLECK B A. Effects of liquid viscosity and surface tension on atomization in two-phase, gas/liquid fluid coker nozzles [J]. Fuel, 2010, 89: 1872–1882.
JULIÁ N P, JULIO H, PABLO G, CLAUDIO Z, JOAQUÍN L. Experimental study of splashing patterns and the splashing/deposition threshold in drop impacts onto dry smooth solid surfaces [J]. Experimental Thermal and Fluid Science, 2013, 44: 571–582.
LIU D, HE Q, EVANS G M. Penetration behaviour of individual hydrophilic particle at a gas-liquid interface [J]. Advanced Powder Technology, 2009, 21: 401–411.
ZHENG H E, GAO Y, GU X, WANG G. Investigating a droplet wall impact model [J]. Journal of University Engineering Harbin, 2009, 30 (3): 267–272. (in Chinese)
ZHOU G, CHENG W M, WANG G, CUI X F. Experiment research of the coupling relationship between dust field and droplet field about fully mechanized and roof caving workface [J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2010, 35(10): 1660–1667.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: Project(U1261107) supported by the Joint Funds of the National Natural Science Foundation of China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kou, Bf., Liu, Qz., Cao, Sc. et al. Experimental investigation on atomization and collecting efficiency of wind-spray dust controller and its parameters optimization. J. Cent. South Univ. 22, 4213–4218 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-015-2969-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-015-2969-9