Abstract
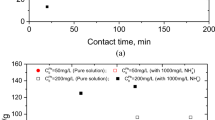
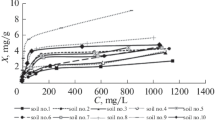
Nickel is a toxic heavy metal among trace elements which has a detrimental impact on living organisms. There is growing need of finding an economic and effective solution for Ni(II) immobilization in environments. Chinese loess was selected as adsorbent to remove Ni(II) from aqueous solution. Adsorbent dosage, reaction time, solute concentration, temperature, and solution pH also have influences on efficiency of Ni(II) removal. The monolayer adsorption capacity of loess towards Ni(II) is determined to be about 15.61 mg/g. High temperature and pH favor the removal of Ni(II) using Chinese loess soil and the optimal dosage of loess is determined to be 10 g/L. The kinetics and adsorption isotherms of the adsorption process can be best-fitted with the pseudo second order kinetics and Langmuir isothermal model, respectively. The thermodynamic analysis reveals that the adsorption process is spontaneous, endothermic and the system disorder increases with duration. Nickel ions can be removed with the removal efficiency of 98.5% at pH greater than or equal to 9.7. Further studies on loess and Ni(II) laden loess (using X-Ray diffraction, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy) and Ni(II) species distribution at various pH have been conducted to discuss the adsorption mechanism. Loess soils in China have proven to be a potential adsorbent for Ni(II) removal from aqueous solutions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
KADIRVELU K, THAMARAISELVI K, NAMASIVAYAM C. Adsorption of nickel(II) from aqueous solution onto activated carbon prepared from coirpith [J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2001, 24(3): 497–505.
VIJAYARAGHAVAN K. Biosorption of nickel from synthetic and electroplating industrial solutions using a green marine Algae Ulva reticulate [J]. CLEAN-Soil, Air, Water, 2008, 36(3): 299–305.
WANG X S, REN J J, LU H J, ZHU L, LIU F, ZHANG Q Q, XIE J. Removal of Ni(II) from aqueous solutions by nanoscale magnetite [J]. CLEAN-Soil, Air, Water, 2010, 38(12): 1131–1136.
CHU Guang, ZHAO Si-jia, YANG Tian-zu. Extraction of Nickel from molybdenum leaching residue of metalliferous black shale by segregation roasting and acid leaching [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2012, 19(2): 340–346.
BOUJELBEN N, BOUZID J, ELOUEAR Z. Adsorption of nickel and copper onto natural iron oxide-coated sand from aqueous solutions: Study in single and binary systems [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2009, 163(1): 376–382.
NAMASIVAYAM C, RANGANATHAN K. Removal of Pb(II), Cd(II) and Ni(II) and mixture of metal ions by adsorption onto waste Fe(III)/Cr(III) hydroxide and fixed bed studies [J]. Environmental Technology, 1995, 16(9): 851–860.
NOURI L, GHODBANE I, HAMDAOUI O, CHIHA M. Batch sorption dynamics and equilibrium for the removal of cadmium ions from aqueous phase using wheat bran [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2007, 149(1): 115–125.
SHUKLA A, ZHANG Y H, DUBEY P, MARGRAVE J L, SHUKLA S S. The role of sawdust in the removal of unwanted materials from water [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials B, 2002, 95(1/2): 137–152.
ZHU S J, HOU H B, XUE Y J. Kinetic and isothermal studies of lead ion adsorption onto bentonite [J]. Applied Clay Science, 2008, 40(1/2/3/4): 171–178.
MUSSO T B, PAROLO M E, PETTINARI G, FRANCISCA E M. Cu(II) and Zn(II) adsorption capacity of three different clay liner materials [J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2014, 146: 50–58.
JULICH D, GATH S. Sorption behavior of copper nanoparticles in soils compared to copper ions [J]. Goederma, 2014, 235: 127–132.
MAHMOUD M E, ABDEL-FATTAH T M, OSMAN M M, AHMED S B. Chemically and biologically modified activated carbon sorbents for the removal of lead ions from aqueous media [J]. Journal of Environmental Science and Health Part A-Toxic/Hazardous Substances & Environmental Engineering, 2012, 47(1): 130–141.
SRIVASTAVA V C, MALL I D, MISHRA I M. Adsorption of toxic metal ions onto activated carbon: Study of sorption behaviour through characterization and kinetics [J]. Chemical Engineering and Process, 2008, 47(8): 1275–1286.
EI-KAMASH A M, ZAKI A A, EI GELEEL M A. Modeling batch kinetics and thermodynamics of zinc and cadmium ions removal from waste solutions using synthetic zeolite A [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2005, 127(1/2/3): 211–220.
KOCAOBA S, ORHAN Y, AKYUZ T. Kinetics and equilibrium studies of heavy metal ions removal by use of natural zeolite [J]. Desalination, 2007, 214(1/2/3): 1–10.
GRAFE M, EICK M J, GROSSL P R. Adsorption of arsenate(V) and arsenite(III) on goethite in the presence and absence of dissolved organic carbon [J]. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 2001, 65(6): 1680–1687.
ZHU J, HUANG Q Y, PIGNA M. Competitive sorption of Cu and Cr on goethite and goethite-bacteria complex [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2012, 179: 26–32.
OSTERGREN J D, TRAINOR T P, BARGAR J R, BROWN G E, PARKS G A. Inorganic ligand effects on Pb(II) sorption to goethite (a-FeOOH): I. Carbonate [J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2000, 225(2): 466–482.
MUSTAFA G, SINGH B, KOOKANA R S. Cadmium adsorption and desorption behaviour on goethite at low equilibrium concentrations: Effects of pH and index cations [J]. Chemosphere, 2004, 57(10): 1325–1333.
ÖZCAN A S, GÖK Ö, ÖZCAN A. Adsorption of lead(II) ions onto 8-hydroxy quinoline-immobilized bentonite [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2009, 161(1): 499–509.
NASEEM R, TAHIR S S. Removal of Pb(II) from aqueous/acidic solutions by using bentonite as an adsorbent [J]. Water Research, 2001, 35(16): 3982–3986.
ADEBOWALE K O, UNUABONAH I E, OLU-OWOLABI B I. Adsorption of some heavy metal ions on sulfate-and phosphatemodified kaolin [J]. Applied Clay Science, 2005, 29(2): 145–148.
BHATTACHARYYA K G, SEN GUPTA S. Adsorption of a few heavy metals on natural and modified kaolinite and montmorillonite: A review [J]. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 2008, 140(2): 114–131.
BHATTACHARYYA K G, SEN GUPTA S. Kaolinite and montmorillonite as adsorbents for Fe(III), Co(II) and Ni(II) in aqueous medium [J]. Applied Clay Science, 2008, 41(1/2): 1–9.
SEN T K, MAHAJAN S P, KHILAR K C. Adsorption of Cu2+ and Ni2+ on iron oxide and kaolin and its importance on Ni2+ transport in porous media [J]. Colloids and Surfaces A-Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2002, 211(1): 91–102.
BARBIER F, DUC G, PETIT-RAMEL M. Adsorption of lead and cadmium ions from aqueous solution to the montmorillonite/water interface [J]. Colloids and Surfaces A-Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2000, 166(1/2/3): 153–159.
KOZAK O, PRAUS P, MACHOVIC V, KLIKA Z. Adsorption of zinc and copper ions on natural and ethylenediamine modified montmorillonite [J]. Ceramics–Silikaty, 2010, 54(1): 78–84.
LIN S H, JUANG R S. Heavy metal removal from water by sorption using surfactant-modified montmorillonite [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2002, 92(3): 315–326.
LAKSHTANOV L Z, STIPP S LS. Experimental study of nickel(II) interaction with calcite: Adsorption and coprecipitation [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2007, 71(15): 3686–3697.
UYGUR V, RIMMER D L. Reactions of zinc with iron-oxide coated calcite surfaces at alkaline pH [J]. European Journal of Soil Science, 2000, 51(3): 511–516.
CARVALHO W A, VIGNADO C, FONTANA J. Ni(II) removal from aqueous effluents by silylated clays [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2008, 153(3): 1240–1247.
CHANG P P, WANG X K, YU S M, WU W S. Sorption of Ni(II) on Na-rectorite from aqueous solution: Effect of pH, ionic strength and temperature [J]. Colloids and Surfaces A-Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2007, 302(1/2/3): 75–81.
ECHEVERRIA J, INDURAIN J, CHURIO E, GARRIDO J. Simultaneous effect of pH, temperature, ionic strength, and initial concentration on the retention of Ni on illite [J]. Colloids and Surfaces A-Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2003, 218(1/2/3): 175–187.
TANG X W, LI Z Z, CHEN Y M. Behaviour and mechanism of Zn(II) adsorption on Chinese loess at dilute slurry concentrations [J]. Journal of Chemical Technology and Biotechnology, 2008, 83(5): 673–682.
TANG X W, LI Z Z, CHEN Y M, WANG Y. Removal of Cu(II) from aqueous solution by adsorption on Chinese Quaternary loess: Kinetics and equilibrium studies [J]. Journal of Environmental Science and Health Part A-Toxic/Hazardous Substances & Environmental Engineering, 2008, 43(7): 779–791.
LI Z Z, TANG X W, CHEN Y M, WANG Y. Sorption behavior and mechanism of Pb(II) on Chinese loess [J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering-ASCE, 2009, 135(1): 58–67.
WANG Y, TANG X W, CHEN Y M, ZHAN L T, LI Z Z, TANG Q. Adsorption behavior and mechanism of Cd(II) on loess soil from China [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2009, 172(1): 30–37.
HO Y S. Citation review of Lagergren kinetic rate equation on adsorption reactions [J]. Scientometrics, 2004, 59(1): 171–177.
HO Y S, MCKAY G. A comparison of chemisorption kinetic models applied to pollutant removal on various sorbents [J]. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 1998, 76(B4): 332–340.
ZHOU L M, WANG Y P, LIU Z R, HUANG Q W. Characteristics of equilibrium, kinetics studies for adsorption of Hg(II), Cu(II), and Ni(II) ions by thiourea-modified magnetic chitosan microspheres [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2009, 161(2/3): 995–1002.
GILES C H, SMITH D A. A general treatment and classification of the solute sorption isotherms. I. Theoretical [J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 1974, 47(3): 755–765.
DO D D. Adsorption analysis: Equilibrium and kinetics [M]. London: Imperial College Press, 1998: 32–191.
KILISLIOGLU A, BILGIN B. Thermodynamic and kinetic investigations of uranium adsorption on amberlite IR-118H resin [J]. Applied Radiation and Isotopes, 2003, 58(2): 155–160.
ÖZCAN A, ÖNCÜ E M, ÖZCAN A S. Kinetics, isotherm and thermodynamic studies of adsorption of Acid Blue 193 from aqueous solutions onto natural sepiolite [J]. Colloids and Surfaces A-Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2006, 277(1/2/3): 90–97.
MATTIGOD S V, RAI D, FELMY A R, RAO L F. Solubility and solubility product of crystalline Ni(OH)2 [J]. Journal of Solution Chemistry, 1997, 26(4): 391–403.
ROBERTS D R, SCHEIDEGGER A M, SPARKS D L. Kinetics of mixed Ni-Al precipitate formation on a soil clay fraction [J]. Environmental Science and Technology, 1999, 33(21): 3749–3754.
ELZINGA E J, SPARKS D L. Reaction condition effects on nickel sorption mechanisms in illite-water suspensions [J]. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 2001, 65(1): 94–101.
BISWAS M, MASUDA J D, MITRA S. Hydrothermal synthesis, crystal structure and magnetic properties of a new one-dimensional polymer [{Cu(4,4'-bipy)(CH3COO)2}·3H2O]n [J]. Structural Chemistry, 2007, 18(1): 9–13.
SEN G UPTA B, CURRAN M, HASAN S, GHOSH T K. Adsorption characteristics of Cu and Ni on Irish peat moss [J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2009, 90(2): 954–960.
SCHEIDEGGER A M, LAMBLE G M, SPARKS D L. Investigation of Ni sorption on pyrophyllite: An XAFS study [J]. Environmental Science and Technology, 1996, 30(2): 548–554.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: Projects(51179168, 51308310) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project(LQ13E080007) supported by Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Tang, Xw. & Wang, Hy. Characteristics and mechanisms of Ni(II) removal from aqueous solution by Chinese loess. J. Cent. South Univ. 22, 4184–4192 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-015-2966-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-015-2966-z