Abstract
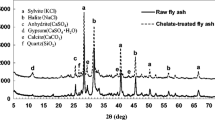
The mechanism of removing phosphate by MSWI (municipal solid waste incineration) fly ash was investigated by SEM (scanning electron microscopy) with EDS (energy dispersion spectrum), XRD (X-ray diffraction), FT-IR (Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy), BET (specific surface area), and BJH (pore size distribution). The results indicate that the removal rate of phosphate (100 mg/L) in 50 mL phosphorus wastewater reaches at 99.9% as the dosage of MSWI fly ash being 0.9000 g under room temperature. The specific surface area of MSWI fly ash is less than 6.1 m2/g and the total pore volume is below 0.021 cm3/g, suggesting that the absorption capacity of calcite is too weak to play an important role in phosphate removal. SEM images show that drastic changes had taken place on its specific surface shape after reaction, and EDS tests indicate that some phosphate precipitates are formed and attached onto MSWI fly ash particles. Chemical precipitation is the main manner of phosphate removal and the main reaction is: 3Ca2++2 PO4 3−+xH2O→Ca3(PO4)2↓·xH2O. Besides, XRD tests show that the composition of MSWI fly ash is complex, but CaSO4 is likely to be the main source of Ca2+. The soluble heavy metals in MSWI fly ash are stabilized by phosphate.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
TIAN Shu-lei, WANG Qi, WANG Qun-hui, JIN Jing, HU Xiao-ying, LI Run-dong. Characteristics of heavy metals during melting and solidification of MSWI fly ash [J]. Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology, 2008, 40(10): 1576–1580. (in Chinese)
ZHNG Fu-shen, HIDEAKI I. Extraction of metals from municipal solid waste incinerator fly ash by hydrothermal process [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2006, 136: 663–670.
JIANG Yong-hai, XI Bei-dou, LI Xiu-jin, ZHANG ling, WEI Zi-min. Effect of water-extraction on characteristics of melting and solidification of fly ash from municipal solid waste incinerator [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2009, 161(2/3): 871–877.
SHI Hui-sheng, KAN Li-li. Leaching behavior of heavy metals from municipal solid wastes incineration (MSWI) fly ash used in concrete [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2009, 164: 750–754.
JIANG Jian-guo, ZHAO Zhen-zhen, WANG Jun, ZHANG Yan, DU Xue-juan. Study on cement solidification technology in treating with fly ash [J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2006, 26(2): 230–235.
BAYUSENO A P, SCHMAHL W W, MÜLLEJANS T. Hydrothermal processing of MSWI Fly Ash-towards new stable minerals and fixation of heavy metals [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2009, 167(1/2/3): 250–259.
GAO Xing-bao, WANG Wei, YE Tun-min, WANG Feng, LAN Yu-xin. Utilization of washed MSWI fly ash as partial cement substitute with the addition of dithiocarbamic chelate [J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2008, 88(2): 293–299.
WANG Qi, TIAN Shu-lei, WANG Qun-hui, HUANG Qi-fei, YANG Jie. Melting charateristics during the vitrification of MSWI fly ash with a pilot-scale diesel oil furnace [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2008, 160: 376–381.
CAI Ke-bing, PENG Xiao-chun, YANG Ren-bin, WU Yan-yu, HU Xiao-ying. Progress of disposal and utilization of fly ash from MSW incineration [J]. Environmental Science and Management, 2012, 37(4): 30–34. (in Chinese)
ZHANG Xian-zhong, ZHANG Zhi, WEI Hu-bing. Process an practice of phosphorus containing wastewater treatment [J]. Technology of Water Treatment, 2007, 33(8): 85–87.
JIANG Hai-ming, LUO Sheng-jun, SHI Xiao-shuang, DAI Meng, GUO Rong-bo. A system combining microbial fuel cell with photobioreactor for continuous domestic wastewater treatment and bioelectricity generation [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2013, 20(2): 488–494.
HE Qiang, ZHANG Ting-ting, CHAI Hong-xiang, YANG Shi-wei, ZHOU Jian, DU Guo-jun. Pretreatment of hypersaline mustard wastewater with integrated bioreactor [J]. Journal of Central South University, 2012, 19(6): 1673–1678.
DAVOR D, KREŠIMIR K, BARBARA V. RO/NF treatment of wastewater from fertilizer factory-removal of fluoride and phosphate [J]. Desalination, 2011, 265: 237–241.
WANG Jun, JIANG Jian-guo, SUI Ji-chao, YANG Shi-jian, ZHANG Yan. Fundamental properties of fly ash from municipal solid waste incineration [J]. Environmental Science, 2006, 27(11): 2283–2287. (in Chinese)
WANG Wei, ZHENG Lei, WANG Feng, WAN Xiao, YIN Ke-qing, GAO Xing-bao. Release of elements from municipal solid waste incineration fly ash [J]. Frontiers of Environmental Science & Engineering in China, 2010, 4(4): 482–489.
CHEN Jian-gang, Kong Hai-nan, WU De-yi, CHEN Xue-chu, ZHANG Da-lei, SUN Zhen-hua. Phosphate immobilization from aqueous solution by fly ashes in relation to their composition [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2007, 139: 293–300.
LU Sheng-gao, BAI Shi-qiang, ZHU Lei, SHANG Hong-dan. Removal mechanism of phosphate from aqueous solution by fly ash [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2009, 161(1): 95–101.
YUAN Dong-hai, ZHANG Meng-qun, GAO Shi-xiang, YI Da-qiang, Wang Lian-sheng. The abilities and mechanisms of absorption phosphorus in some clay minerals and soils [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2005, 24(1): 17–10. (in Chinese)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: Projects(51108100, 50808184) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project(100Z007) supported by the Ministry of Education of China; Project(200103YB020) supported by Foundation of Guangxi Educational Committee, China; Project supported by Guangxi Normal University Education Development Foundation for Young Scholars, China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhong, S., Gao, H., Kuang, W. et al. Mechanism of high concentration phosphorus wastewater treated by municipal solid waste incineration fly ash. J. Cent. South Univ. 21, 1982–1988 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-014-2146-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-014-2146-6