Abstract
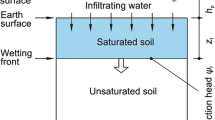
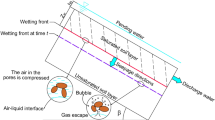
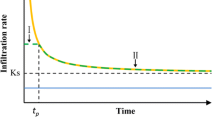
For fully understanding the hydrological dynamics of an infinite terraced slope, the infiltration process was studied by employing the Green and Ampt infiltration model. The limit equilibrium method and the Mohr-Coulomb failure criterion were adopted to derive a stability model for the infinite terraced slope subjected to an intense rainfall. Numerical simulation was performed for verifying its applicability. The results of numerical simulation indicate that a set of stepped wetting fronts are found during infiltration, and the infiltration of terraced slope covered by coarse-textured soils can be approximated as one-dimensional infiltration. The potential sliding surfaces from the numerical method are all parallel to the slope line, and the proposed model and framework can provide an approximate method of estimating how the infiltration affects the stability of an infinite terraced slope.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
GASMO J M, RAHARDJO H, LEONG E C. Infiltration effects on stability of a residual soil slope [J]. Computers and Geotechnics, 2000, 26(2): 145–165.
HARRIS S J, ORENSE R P, ITOH K. Back analyses of rainfall-induced slope failure in Northland Allochthon formation [J]. Landslides, 2012, 9(3): 349–356.
SUNG E C. Infiltration analysis to evaluate the surficial stability of two-layered slopes considering rainfall characteristics [J]. Engineering Geology, 2009, 105(1/2): 32–43.
RAHIMI A, RAHARDJO H, LEONG E C. Effect of hydraulic properties of soil on rainfall-induced slope failure [J]. Engineering Geology, 2010, 114(3/4): 135–143.
KIM J, JEONG S, SHARMA J. Influence of rainfall-induced wetting on the stability of slopes in weathered soils [J]. Engineering Geology, 2004, 75(3/4): 251–262.
MATSUSHI Y, HATTANJI Y, MATSUKURA Y. Mechanisms of shallow landslides on soil-mantled hillslopes with permeable and impermeable bedrocks in the Boso Peninsula, Japan [J]. Geomorphology, 2006, 76(1/2): 92–108.
CHEN H, LEE C F, LAW K T. Causative mechanism of rainfall-induced fill slope failures [J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, ASCE 2004, 130(6): 593–602.
LU N, GODT J. Infinite slope stability under steady unsaturated seepage conditions [J]. Water Resources Research, 2008, 44(11): W11404.
TRAVIS Q B, HOUSTON S L, MARINHO F A M, SCHMEECKLE M. Unsaturated infinite slope stability considering surface flux conditions [J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, ASCE 2010, 136(7): 963–974.
CROSTA G B, DAL NEGRO P, FRATTINI P. Soil slips and debris flows on terraced slopes [J]. Natural Hazards and Earth System Sciences, 2003, 3(1/2): 31–42.
ZHANG M, LIU J. Controlling factors of loess landslides in western China [J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2010, 59(8): 1671–1680
XU L, DAI F C, GONG Q M, THAM L G, MIN H. Irrigation-induced loess flow failure in Heifangtai Platform, North-West China [J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2011, 66(6): 1–7
CORRADO C, MARCO M, TIZIANA A. Rainfall, infiltration, and groundwater flow in a terraced slope of Valtellina (Northern Italy): Field data and modeling [J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2011, 65(4): 1191–1202.
CAMPBELL R H. Soil slips, debris flows, and rainstorms in the Santa Monica Mountains and vicinity, southern California, USGS, Prof [P]. 1975: 851.
CROSTA G B, FRATTINI P. Rainfall-induced landslides and debris flows [J]. Hydrological Processes, 2008, 22(4): 473–477.
CROSTA G B, FRATTINI P. Rainfall thresholds for triggering soil slips and debris flow [C]// Proc 2nd Plinius Conference on Mediterranean Storms. Siena, Italy: PCMS, 2002: 16–18.
LESSCHEN J P, CAMMERAAT L H, NIEMAN T. Erosion and terrace failure due to agricultural land abandonment in a semi-arid environment [J]. Earth Surface Processes and Landforms, 2008, 33(10): 1574–1584.
van ASCH T W J, BUMA J, VAN BEEK L P H. A view on some hydrological triggering systems in landslides [J]. Geomorphology, 1999, 30(1): 25–32.
WON TAEK OH, VANAPALLI SAI K. Influence of rain infiltration on the stability of compacted soil slopes [J]. Computers and Geotechnics, 2010, 37(5): 649–657.
GREEN W H, AMPT C A. Studies on soil physics: Flow of air and water through soils [J]. Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 1911, 4(1): 1–24.
WANG Quan-jiu, LAI Jian-bing, LI Yi. Comparison of Green-Ampt model with Philip infiltration model [J]. Tran sactions of the CSAE, 2002, 18(2): 13–16. (in Chinese)
MEIN R G, FARREL D A. Determination of wetting front suction in the Green-Ampt equation [J]. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 1974, 38(6): 872–876.
van VGENUCHTEN MTH. A closed-form equation for predicting the hydraulic conductivity of unsaturated soils [J]. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 1980, 44(5): 892–898.
FREDLUND D G, MORGENSTERN N R, WIDGER R A. The shear strength of unsaturated soils [J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal, 1978, 15(3): 313–321.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: Project(51178423) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, Sg., Han, Tc., Xu, Rq. et al. Effects of intense rainfall on stability of infinite terraced slope. J. Cent. South Univ. 21, 1534–1545 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-014-2094-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-014-2094-1