Abstract
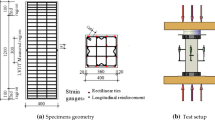
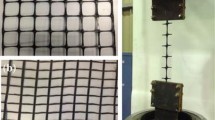
In order to investigate the size effect and other effects on the stress-strain relationship of confined concrete, 42 specimens with different sizes and section shapes were placed under axial compression loading. Effects of key parameters such as size of specimens, tie configuration, transverse reinforcement ratio, and concrete cover were studied. The results show that for specimens with the same configuration and the same volumetric ratio of the transverse reinforcement, along with the increasing specimen size, the peak stress, peak strain and deformation of the post-peak show a down trend, however, the volumetric ratio of the transverse reinforcement is lowered, the decreasing of the peak stress is accelerated, but the decreasing of the deformation is slow down. For specimens with the same volumetric ratio but different configurations of transverse reinforcement, though the transverse reinforcement configuration becomes more complicated, the peak stress of the large size specimen does not improve more than that of the small size. However, the deformation occurs before the stress declines to 85% of peak stress, and the improvement with the grid pattern tie configuration is much greater due to size effect.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
SIM J II, YANG K H, KIM H Y, CHOI B J. Size and shape effects on compressive strength of lightweight concrete [J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2013, 38: 854–864.
YI S T, YANG E I, JOONG-CHEOL C. Effect of specimen sizes, specimen shapes, and placement directions on compressive strength of concrete [J]. Nuclear Engineering and Design, 2006, 236(2): 115–127.
del VISO J R, CARMONA J R, RUIZ G. Shape and size effects on the compressive strength of high-strength concrete [J]. Cement and Concrete Research, 2008, 38(3): 386–395.
KIM J E, PARK W S, EOM N Y. Size effect on compressive strength and modulus of elasticity in high performance concrete [J]. Advanced Materials Research, 2013, 634–638(1): 2742–2745.
WANG Yuan-feng, WU Han-liang. Size effect of concrete short columns confined with aramid FRP jackets [J]. Journal of Composites for Construction, 2011, 15(4): 535–544.
MOTAZ M E, KRAUTHAMMER T. Dynamic size effect in normal and high-strength concrete cylinders [J]. ACI Materials Journal, 2005, 102(2): 77–85.
LIU Hong-yi, ZHANG Jin-quan, CHENG Shou-shan. Study on compressive strength of concrete core samples [J]. Concrete, 2012 (2): 36–38. (in Chinese)
NEVILLE A M. Influence of size of concrete test cubes on mean strength and standard deviation [J]. Magazine of Concrete Research, 1956, 8(23): 101–110.
BAŽANT Z P, KWON Y W. Failure of slender and stocky reinforced concrete columns: Tests of size effect [J]. Materials and Structures, 1994, 27(2): 79–90.
TANG Xin-wei. Study on damage and fracture behavior of concrete based on macro and meso mechanics [D]. Beijing: Tsinghua University, 2008. (in Chinese)
CHE Yi, BAN Sheng-long, CUI Jian-yu, CHEN Geng, SONG Yu-pu. Effect of specimen shape and size on compressive strength of concrete [J]. Advanced Materials Research, 2011, 163/177(2): 1375–1379.
DU Xiu-li, FU Jia, ZHANG Jian-wei. The experimental study on size effect of the large-size reinforced concrete column under axial loading [J]. China Civil Engineering Journal, 2010, 43: s1–s8. (in Chinese)
SENER S, BARR B I G, ABUSIAF H F. Size effect in axially loaded reinforced concrete columns [J]. Journal of Structural Engineering, 2004, 130(4): 662–670.
SHEIKH S A, TOKLUCU M T. Reinforced concrete columns confined by circular spiral and hoops [J]. ACI Structure Journal, 1993, 90: 542–553.
GB 50010-2010. Code for design of concrete structure [S]. (in Chinese)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: Project(50838001) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Zb., Song, J., Du, Xl. et al. Size effect of confined concrete subjected to axial compression. J. Cent. South Univ. 21, 1217–1226 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-014-2056-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-014-2056-7