Abstract
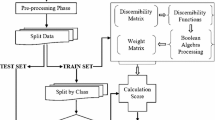
With development of web services technology, the number of existing services in the internet is growing day by day. In order to achieve automatic and accurate services classification which can be beneficial for service related tasks, a rough set theory based method for services classification was proposed. First, the services descriptions were preprocessed and represented as vectors. Elicited by the discernibility matrices based attribute reduction in rough set theory and taking into account the characteristic of decision table of services classification, a method based on continuous discernibility matrices was proposed for dimensionality reduction. And finally, services classification was processed automatically. Through the experiment, the proposed method for services classification achieves approving classification result in all five testing categories. The experiment result shows that the proposed method is accurate and could be used in practical web services classification.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
RINDERLE-MA S, REICHERT M, JURISCH M. On utilizing web service equivalence for supporting the composition life cycle [J]. International Journal of Web Services Research, 2011, 8(1): 41–67.
ZULKERNINE F H, MARTIN P. An adaptive and intelligent SLA negotiation system for web services [J]. IEEE Transactions on Services Computing, 2011, 4(1): 31–43.
WU Bin, DENG Shui-guang, LI Ying, WU Jian, YIN Jian-wei. AWSP: An automatic web service planner based on heuristic state space search [C]// Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Web Services (ICWS’11), Washington, DC, USA: IEEE Press, 2011: 403–410.
CHINNICI R, MOREAU J, RYMAN A, WEERAWARANA S. Web services description language (WSDL) Version 2.0 Part 1: Core Language (W3C Recommendation) [EB/OL]. http://www.w3.org/TR/wsdl20. 2007-06-26.
MITRA N, LAFON Y. SOAP Version 1.2 Part 0: Primer (Second Edition) (W3C Recommendation 2007-04-27) [EB/OL]. http://www.w3.org/TR/soap12-part0.
Universal Description Discovery and Integration (UDDI) Technical White Paper [EB/OL]. [2011-06-08]. http://uddi.xml.org.
UNSPSC (United Nations Standard Products and Services Code) [EB/OL]. [2011-10-20]. http://www.unspsc.org.
NAICS (North American Industry Classification System) [EB/OL]. [2011-12-15]. http://www.census.gov/eos/www/naics.
HE A, KUSHMERICK N. Automatically attaching semantic metadata to web services [C]// Proceedings of Workshop on Information Integration on the Web (IIWeb’03) at the 18th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence (IJCAI’03). Acapulco, Mexico, 2003: 111–116.
HE A, JOHNSTON E, KUSHMERICK N. ASSAM: A tool for semi-automatically annotating semantic web services [C]// Proceedings of the 3rd International Semantic Web Conference (ISWC’04), Lecture Notes in Computer Science 3298. Hiroshima, Japan, 2004: 320–334.
BRUNO M, CANFORA G, DI PENTA M, SCOGNAMIGLIO R. An approach to support web service classification and annotation [C]// Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on e-Technology, e-Commerce and e-Services (EEE’05). Hong Kong, China: IEEE Press, 2005: 138–143.
PATIL A A, OUNDHAKAR S, SHETH A, VERMA K. METEOR-S Web service annotation framework [C]// Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on World Wide Web (www’04). Manhattan, NY, USA, 2004: 553–562.
OLDHAM N, THOMAS C, SHETH A P, VERMA K. METEOR-S Web service annotation framework with machine learning classification [C]// Proceedings of the 1st International Workshop on Semantic Web Services and Web Process Composition (SWSWPC’04) at International Semantic Web Conference (ISWC’04). San Diego, CA, USA, 2004: 137–146.
HUA Jian-ping, TEMBE W D, DOUGHERTY E R. Performance of feature-selection methods in the classification of high-dimension data [J]. Pattern Recognition. 2009, 42(3): 409–424.
YANG Jian-bo, ONG Chong-jin. Feature selection for support vector regression using probabilistic prediction [C]// Proceedings of ACM SIGKDD the 16th International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining (KDD’10). Washington, DC, USA: ACM, 2010: 343–352.
GHEYAS I A, SMITH L S. Feature subset selection in large dimensionality domains [J]. Pattern Recognition, 2010, 43(1): 5–13.
PAWLAK Z, SKOWRON A. Rough sets: Some extensions [J]. Information Sciences. 2007, 177(1): 28–40.
PAWLAK Z, SKOWRON A. Rudiments of rough sets [J]. Information Sciences, 2007, 177(1): 3–27.
SKOWRON A, RAUSZER C. The discernibility matrices and functions in information system [M]// Intelligent Decision Support: Handbook of Applications and Advances of the Rough Sets Theory. Netherlands: Kluwer Academic Publishers, 1992, 331–362.
BUCKLEY C, SALTON G, ALLAN J. The effect of adding relevance information in a relevance feedback environment [C]// Proceedings of ACM SIGIR the 17th Annual International Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval (SIGIR’94). New York, NY, USA: ACM, 1994: 292–300.
KLUSCH M, KAPAHNKE P, FRIES B, KHALID M A, VASILESKI M. OWL-S Test Collection Version 4 [EB/OL]. [2012-03-03]. http://semwebcentral.org/projects/owls-tc.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: Projects(9140A0605, 0409JB8102) supported by Weaponry Equipment Pre-Research Foundation of PLA Equipment Ministry of China; Project(2009JSJ11) supported by Pre-Research Foundation of PLA University of Science and Technology, China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, L., Zhang, Y., Song, Zl. et al. Automatic web services classification based on rough set theory. J. Cent. South Univ. 20, 2708–2714 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-013-1787-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-013-1787-1