Abstract
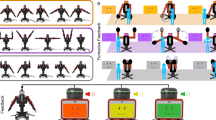
r-learning, which is based on e-learning and u-learning, is defined as a learning support system that intelligent robots serve verbal and nonverbal interactions on ubiquitous computing environment. In order to guarantee the advantages of r-learning contents with no limits of time and place and with nonverbal interaction which are not in e-learning contents, in recent years, assessment criteria for r-learning contents are urgently required. Therefore, the reliable and valid assessment criteria were developed for nonverbal interaction contents in r-learning, and its detailed research content is as follows. First, assessment criteria for nonverbal interaction in r-learning contents will be specified into gesture, facial expression, semi-verbal message, distance, physical contact and time. Second, the validity of the developed assessment criteria will be proved by statistics. Consequently, the assessment criteria for nonverbal interaction contents will be helpful when choosing the better r-learning content and producing the better r-learning content, and the reliability of school education is improved ultimately.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Paro Robots Intelligent System. Seal-type therapeutic robot. [EB/OL]. [2010-10-01] http://www.paro.jp.
KIESLER S, GOETZ J. Mental models and cooperation with robotic assistants [C]// Conference on Human Factors in Computing System, CHI 02. Mineapolis, MN: CHI 2002: 20–25.
KANDA T, HIRANO T, EATON D, ISHIGURO H. Interactive robots as social partners and peer tutors for children [J]. A Field Trial, Human Computer Interaction, 2004, 19: 61–84.
HAN J, JO M, PARK S, KIM S. The educational use of home robots for children [C]// Proceedings of the 14th IEEE International Workshop on Robot and Human Interactive Communication (RO-MAN2005), Nashville, TN, USA: IEEE, 2005: 378–383.
KIM Byeong-jun, HAN Jeong-hye. Analysis on psychological and educational effects in children and home robot interaction [J]. Journal of Korea Association of Information Education, 2005, 9(3): 387–395.
JEONG Jaeg-yeong, CHOI Jong-hong, HAN Jeong-hye. Analysis on Children’s response depending on teaching assistant robots’ styles [J]. Journal of Korea Association of Information Education, 2007, 11(2): 195–203.
LEE Seung-min, HAN Jeong-hye. Development of elementary English learning contents using a hybrid intelligent robot and their application [J]. Journal of Korea Association of information Education, 2004, 8(2): 97–119.
KIM Geonhui, LEE Hyosin, JANG Sujeong, GU Hyeonjin. The reaction of children labeled with autism through interactions with robot [J]. Journal of Emotional & Behavioral Disorders, 2010, 26(10): 331–353.
CHENG Z, SUN S, KANSEN M, HUANG T, HE A. A personalized ubiquitous education support environment by comparing learning instructional requirement with learner’s behavior [C]// AINA 2005. 19th International Conference Taipei; IEEE 2005: 567–573.
HAN Jeong-hye, JO Mi-heon. Robot-Assisted Learning in r-learning [J]. Journal of Korea Association of Information Education, 2009, 13(4): 497–508.
LIM Jaeh-yeon, KIM Chi-su, JUN Byeong-ho, LEE Se-jin, KIM Won-hyeong, KIM Yong. A study on the quality management of educational contents [R]. Research Paper of Korea Education & Research Information Service, 2005.
TOSHIKI I, NEC. Analysis on children’s images of robots in terms of clinical psychology-how children perceive robots changes in children’s images of robots after their Interaction with Robots? [R]. Tokyo: NEC, 2003.
LITTLEJOHN S W. Theories of human communication [M]. Long Grove, USA: Waveland Press, Inc, 2010.
LIM Chilseong. Interpersonal relations and Communication [M]. Seoul: Jimmundang Press, 1995.
BIDWHISTELL R L. Kinesics and context: essays on body motion communication [M]. Seoul: University of Pennsylvania Press, 1970.
LEE Changdeok, LIM Chilseong, SIM Yeongtaek, Won Jinsuk. Life and Speech [M]. Philadelphia Bagijeong Press, 2010.
MEST. 2007’s Revised Korean Language Curriculum Guide for middle school [M]. Seoul: Daehan Printing & Publishing Co., Ltd, 2007.
STWART J, LOGAN C E. Together: Communication interpersonally [M]. NY: Mcgraw Hill, 1998.
CHAN L K, COLE P G. Teaching Principles and Practice [M]. NY: Prentice Hall, 1987.
ADLER P B, ASLER ROSENFELD L B, PROCTOR R F. Interplay: The process of interpersonal communication [M]. NY: Oxford University Press, 2012.
LEE Changdeok, MIN Byeonggon, PARK Changgyun, LEE Jeongu, KIM Juyeong. Teacher’s Speech [M]. Seoul: Tekeubil.Com Press, 2010.
Argyle M. Bodily Communication [M] (2nd ed.), Madison: International Universities Press, 1975.
KIM Uryong, JANG Sowon. Non-verbal Communication [M]. Seoul: Nanam Press, 2004.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: Project(2011) supported by the research grant of the Chungbuk National University, South Korea
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Choi, Jh., Lee, Jy. & Yoon, Hs. Assessment criteria for nonverbal interaction contents in r-learning. J. Cent. South Univ. 20, 2388–2398 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-013-1748-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-013-1748-8