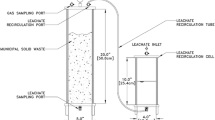
Abstract
Municipal solid waste (MSW) and its disposal are gaining significant importance in geotechnical and geoenvironmental engineering. However, conventional research is primarily focused on fresh MSW or MSW that is compacted under its own weight in the landfill. In this work, a series of tests to study the properties of a densified MSW after ground treatment were presented. The tests involved oedometer test, simple shear test, triaxial shear test, and permeability test, which were conducted to investigate the compressibility, shear strength, creep behavior and permeability of the MSW. The results show that the compressibility modulus of the MSW increases as the dry density increases. However, the influence of density on modulus decreases once the density reaches a certain value. Like most soils, the stress-strain curve of the densified MSW can be approximated by a hyperbola in the triaxial shear test. Fibrous components provide additional cohesion for MSW, but have a relatively smaller effect on friction angle. Permeability is also found to be closely related to the dry density of the MSW, i.e., MSW with a higher dry density has a smaller permeability. The permeability coefficient may be less than 10-7 cm/s if the density is high enough.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
BRAY J D, ZEKKOS D, KAVAZANJIAN J E, ATHANASOPOULOS G A, RIEMER M F. Shear strength of municipal solid waste [J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, ASCE, 2009, 135(6): 709–722.
GABR M A, VALERO S N. Geotechnical properties of municipal solid waste [J]. Geotechnical Testing Journal, 1995, 18(2): 241–251.
GABR M A, HOSSAIN M S, BARLAZ M A. Shear strength parameters of municipal solid waste with leachate recirculation [J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, ASCE, 2007, 133(4): 478–484.
LANDVA A O, CLARK J I. Geotechnics of waste fills [C]// Geotechnics of Waste Fills-Theory and Practice, ASTM STP 1070. 1990: 86–107.
LANDVA A O, CLARK J I. Geotechnical testing of waste fill [C]// Proceedings of Canadian Geotechnical Conference. Ottawa, Ontario, 1990: 371–385.
MACHADO S L, CARVALHO F M, VILAR O M. Constitutive model for municipal solid waste [J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, ASCE, 2002, 128(11): 940–951.
STARK T D, HUVAJ-SARIHAN N, LI G C. Shear strength of municipal solid waste for stability analyses [J]. Environment Geology, 2009, 57: 1911–1923.
ZHAN L T, CHEN Y M, LING W A. Shear strength characterization of municipal solid waste at the Suzhou landfill, China [J]. Engineering Geology, 2008, 97: 97–111.
RICHARDSON G, REYNOLDS D. Geosynthetics consideration in a landfill on compressible clays [C]// Proceedings of Geosynthetics 91. Atlanta, GA, 1991, 2: 507–516.
WITHIAM J L, TARVIN P A, BUSHELL T D, SNOW R E, GERMAN H W. Prediction and performance of municipal landfill slope [C]// Geoenvironment 2000. New Orleans, Louisiana: Geotechnical Special Publication. 1995, 46: 1005–1019.
LI X Y, XU R J. Probability characteristic of parameters of municipal solid waste in Beijing [C]// Proceedings of 1st Conference on Geoenvironment and Geosynthetics. Hangzhou, China, 2002: 177–180. (in Chinese)
WANG Z H. Engineering properties and stability analysis of municipal solid waste [D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 1999. (in Chinese).
KOCKEL R, JESSBERGER H L. Stability evaluation of municipal solid waste slopes [C]// Proceedings of the 11th European Conference on Soil Mechanics and Foundation Engineering. Copenhagen, 1995: 267–272.
KOCKEL R, KÖNIG D, SYLLWASSCHY O. Three basic topics on waste mechanics [C]// Proceedings of 14th International Conference on Soil Mechanics and Foundation Engineering. Hamburg, 1997: 1831–1837.
JESSBERGER H L, KOCKEL R. Determination and assessment of the mechanical properties of waste materials [C]// Proceedings of Sardinia 93, 4th International Landfill Symposium. San Margherita di Pula, CISA, Cagliari, Italy, 1993: 1383–1392.
BORGATTO A V A, MAHLER C F, IZZO R L S, BAUER J. Influence of soft plastic on MSW geomechanical behavior [C]// 3th International Workshop on Hydro-Physico-Mechanics of Landfill. Braunschweig, Germany, 2009: 1–10.
CHEN Y M, ZHAN L T, WEI H Y, KE H. Aging and compressibility of municipal solid wastes [J]. Waste Management, 2009, 29: 86–95.
CHEN Y M, KE H, FREDLUND D G, ZHAN L T, XIE Y. Secondary compression of municipal solid wastes and a compression model for predicting settlement of municipal solid waste landfills [J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, ASCE, 2010, 136(5): 706–717.
CHEN R H, CHEN K S, LIU C N. Study of the mechanical compression behavior of municipal solid waste by temperature-controlled compression tests [J]. Environment Earth Science, 2010, 61: 1677–1690.
GANDOLLA M, ACAIA C, DECKA I. Prediction of surface subsidence of a MSW landfill [C]// Proceedings of Italian-Brazilian Congress S.I.B.E.S.A. Gramado, Brasil, 1995: 1–10. (in Italian)
HOSSAIN M S, GABR M A, ASCE F. The effect of shredding and test apparatus size on compressibility and strength parameters of degraded municipal solid waste [J]. Waste Management, 2009, 29: 2417–2424.
KANG S T, SHIN H S, LEE C Y, LEE N H. 1997. Relationship between biological decomposition and landfill settlement at various leachate recirculation rates [C]// Proceeding of 7th Kais-Ntu-Ku Tri-laterial Seminar/Workshop on Environmental Engineering. Kyoto, Japan, 1997: 29–31.
RAO S K, MOULTON L K, SEALS R K. Settlement of refuse landfills [C]// Proceedings of the Conference on Geotechnical Practice for Disposal of Solid Waste Materials. Michigan, 1977: 574–598.
SWATI M, JOSEPH K. Settlement analysis of fresh and partially stabilised municipal solid waste in simulated controlled dumps and bioreactor landfills [J]. Waste Management, 2008, 28: 1355–1363.
WARDWELL R E, NELSON J D. Settlement of sludge landfill with fiber decomposition [C]// Proceeding of 10th International Conference for Soil Mechanics and Foundation Engineering. Stokholm, Sweden, 1981: 397–401.
AL-KHAFAJI W N, ANDERSLAND O B. Compressibility and strength of decomposing fibre-clay soils [J]. Geotechnique, 1981, 31(4): 497–508.
CODUTO D P, HUITRIC R. Monitoring landfill movements using precise instruments [C]// Geotechnics of Waste Fills-Theory and Practice, ASTM STP 1070. Philadephia, 1990: 358–370.
WALL D K, ZEISS C. Municipal landfill biodegradation and settlement [J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering, 1995, 121(3): 214–224.
PARK Y I I, LEE S R, DO N Y. Evaluation of decomposition effect on long-term settlement prediction for fresh municipal solid waste landfills [J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, 2002, 128(2): 107–118.
HAO X N. An experimental study on bioreactor landfill disposal of municipal solid waste [D]. Beijing: Beijing University of Chemical Technology, 2005. (in Chinese)
KONG X J, SUN X L, ZHOU D G, LOU S L. Study on relationship between volume reduction of municipal solid waste due to biodegradation and time [J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2006, 28(12): 2060–2065. (in Chinese)
CHEN T H, CHYNOWETH D P. Hydraulic conductivity of compacted municipal solid waste [J]. Bioresource Technology, 1995, 51: 205–212.
CHEN Y M, KE H. 2002. Engineering properties of municipal solid waste and filling technique [C]// Proceedings of 1st Conference on Geoenvironment and Geosynthetics. Hangzhou, China, 2002: 47–60. (in Chinese)
JANG Y S, KIM Y W, LEE S I. Hydraulic properties and leachate level analysis of Kimpo metropolitan landfill, Korea [J]. Waste Management, 2002, 22: 261–267.
OWEIS I S, SMITH D A, ALLWOOD R B, GREENE D S. Hydraulic characteristics of municipal refuse [J]. Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, ASCE, 1990, 116(4): 539–553.
QIAN X D, GUO Z P. Modern landfill engineering in USA [J]. Advances in Science and Technology of Water Resources, 1995, 15(6): 27–31. (in Chinese)
QIAN X D, KOERNER R M, GRAY D H. Geotechnical aspects of landfill design and construction [M]. New Jersey: Prentice-Hall Inc., 2002.
DUNCAN J M, CHANG C Y. Nonlinear analysis of stress and strain in soils [J]. Journal of the Soil Mechanics and Foundations Division, ASCE, 1970, 96(5): 1629–1653.
ZHU J G, SHI J Y. Test on strength properties of municipal solid waste [C]// Proceedings of 1st Conference on Geoenvironment and Geosynthetics. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University Press, 2002: 192–196. (in Chinese)
FENG S J, ZHOU Z F, CHEN Y M, ZHAN L T. Shear strength parameters on municipal solid waste [J]. Journal of Zhejiang University: Science and Technology, 2005, 9(7): 987–991. (in Chinese)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: Project(50979047) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project(2010CB732103) supported by the National Basic Research Program of China; Project(2012-KY-02) supported by the State Key Laboratory of Hydroscience and Engineering (Tsinghua University), China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jie, Yx., Xu, Wj., Dunzhu, D. et al. Laboratory testing of a densified municipal solid waste in Beijing. J. Cent. South Univ. 20, 1953–1963 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-013-1695-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-013-1695-4