Abstract
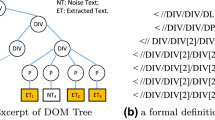
Content extraction of HTML pages is the basis of the web page clustering and information retrieval, so it is necessary to eliminate cluttered information and very important to extract content of pages accurately. A novel and accurate solution for extracting content of HTML pages was proposed. First of all, the HTML page is parsed into DOM object and the IDs of all leaf nodes are generated. Secondly, the score of each leaf node is calculated and the score is adjusted according to the relationship with neighbors. Finally, the information blocks are found according to the definition, and a universal classification algorithm is used to identify the content blocks. The experimental results show that the algorithm can extract content effectively and accurately, and the recall rate and precision are 96.5% and 93.8%, respectively.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
OU J W, DONG X B, CAI B. Topic information extraction from template web pages [J]. Journal of Tsinghua University: Science and Technology, 2005, 45(S1): 1743–1747.
SANDIP D, PRASENJIT M, C LEE G. Identifying content blocks from web documents [C]// 2005 International Symposium on Methodologies for Intelligent Systems (ISMIS 2005). New York: LNAI, 2005: 285–293.
MOHSEN A, MIR M P, AMIR M R. Main content extraction from detailed web pages [J]. International Journal of Computer Applications, 2010, 4(11): 18–21.
YI L, LIU B, LI X L. Eliminating noisy information in web pages for data mining [C]// The Eighth ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining. Washington: ACM Press, 2003: 296–305.
SUHIT G, HILA B, GAIL K, SALVATORE S. Verifying genre-based clustering approach to content extraction [C]// The 15th International World Wide Web Conference. Budapest: ACM Press, 2006: 875–876.
DEBNATH S, Automatic identification of informative sections of web pages [J]. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 2005, 17(9): 1233–1246.
GOTTRON T. Combining content extraction heuristics: the combined system [C]// The 10th International Conference on Information Integration and Web-based Application & Services. New York: ACM Press, 2008: 591–594.
GOTTRON T. An evolutionary approach to automatically optimize web content extraction [C]// The Joint Venture of the 17th International Conference Intelligent Information System (IIS) and the 24th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AI). Krakow: The IEEE Computational Intelligence Society, 2009: 331–341.
JAVIER A M, KOEN D, MARIE F M. Language independent content extraction from web pages [C]// The 9th Dutch-Belgian Information Retrieval Workshop. Netherland: University of Twente, 2009: 50–55.
TIM W, WILLIAM H H. Web content extraction through histogram clustering [C]// The 18th International Conference on Artificial Neural Networks in Engineering (ANNIE 2008). St. Louis: Lecture Notes in Computer Science, 2008: 124–132.
THOMAS G. Content code blurring: A new approach to content extraction [C]// The 2008 19th International Conference on Database and Expert Systems Application. Washington: IEEE Computer Society, 2008: 29–33.
BING L D, WANG Y X, ZHANG Y. Primary content extraction with mountain model [C]// The 8th IEEE International Conference on Computer and Information Technology. Sydney: IEEE Press, 2008: 479–484.
W3C. Document object model [EB/OL]. [2011-3-5]. http://www.w3.org/DOM/.
MACQUEEN J. Some methods for classification and analysis of multivariate observations [C]// The 5th Berkeley Symposium on Mathematical Statistics and Probability. Berkeley: Berkeley Press, 1967: 281–297.
Computer Networks and Distributed System Laboratory, Peking University. CWIRF [EB/OL]. [2011-3-8]. http://www.cwirf.org/.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: Project(2012BAH18B05) supported by the Supporting Program of Ministry of Science and Technology of China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, Q., Chen, Xs., Zhu, K. et al. Relevance-based content extraction of HTML documents. J. Cent. South Univ. 19, 1921–1926 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-012-1226-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-012-1226-8