Abstract
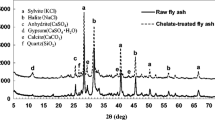
To analyze the feasibility of utilization of thermal technology in fly ash treatment, thermal properties and microstructures of municipal solid waste incineration (MSWI) fly ash were studied by measuring the chemical element composition, specific surface area, pore sizes, functional groups, TEM image, mineralogy and DSC-TG curves of raw and sintered fly ash specimens. The results show that MSWI fly ash particles mostly have irregular shapes and non-typical pore structure, and the supersonic treatment improves the pore structure; MSWI fly ash consists of such crystals as SiO2, CaSO4 and silica-aluminates, and some soluble salts like KCl and NaCl. During the sintering process, mineralogy changes largely and novel solid solutions are produced gradually with the rise of temperature. Therefore, the utilization of a proper thermal technology not only destructs those persistent organic toxicants but also stabilizes hazardous heavy metals in MSWI fly ash.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
WAN Xiao, WANG Wei, YE Tun-min. A study on the chemical and mineralogical characterization of MSWI fly ash using a sequential extraction procedure [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2006, 134(1/2/3): 197–201.
LIU Yang-sheng, ZHENG Li-ting, LI Xiao-dong. SEM/EDS and XRD characterization of raw and washed MSWI fly ash sintered at different temperatures [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2009, 162(1): 161–173.
ZHAO Guang-jie, LI Hai-bin, ZHAO Zeng-li, YAN Chang-feng, CHEN Yong. Basic properties of fly ash from incineration of municipal solid waste [J]. Journal of Fuel Chemistry and Technology, 2005, 33(2): 184–188. (in Chinese)
KIRBY C S, RLMSTLDT J D. Mineralogy and surface properties of municipal solid waste ash [J]. Environ Sci Technol, 1993, 27(4): 652–660.
ONTEVAROS J L, CLAPP T L, KOSSON D S. Physical properties and chemical species distributions within municipal waste combustor ashes [J]. Environ Progress, 1989, 8(3): 200–206.
EIGHMY T T, EUSDEN J D, KRZANOWSKI J E, DOMINGO D S, STAMPFLI D, MARTIN J R, ERICKSON P M. Comprehensive approach toward understanding element speciation and leaching behavior in municipal solid waste incineration electrostatic precipitator ash [J]. Environ Sci Technol, 1995, 29(3): 629–646.
ZHANG Da-jie, LIU Wen-shi, HOU Hao-bo. Strength, leachability and microstructure characterisation of Na2SiO3-activated ground granulated blast-furnace slag solidified MSWI fly ash [J]. Waste Management & Research, 2008, 25(5): 402–407.
ZHAO You-cai, SONG Li-jie, LI Guo-jian. Chemical stabilization of MSW incinerator fly ashes [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials B, 2002, 95: 47–63.
KASTUURA H, INOUE T, HIRAOKA M, SAKAI S. Full-scale plant study on fly ash treatment by the acid extraction process [J]. Waste Management, 1996, 16: 491–499.
KARAMANOV A, PELINO M, HREGLICH A. Sintered glass-ceramics from municipal solid waste-incinerator fly ashes-part I: The influence of the heating rate on the sinter-crystallisation [J]. J Eur Ceram Soc, 2003, 23(6): 827–832.
YAN Jian-hua, MA Zeng-yi, PENG Wen, LI Xiao-dong, LI Jian-xin, CEN Ke-fa. Experimental study on solidification of MSW incinerator fly ash by mixing with asphalt [J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2004, 24(4): 71–74. (in Chinese)
JIN Chong-yang, CUI Di-chen. Discussion on solid wastes incineration residues treatment technology [J]. Science of Environment Protection, 2003, 4: 32–35. (in Chinese)
ZHANG Hai-ying, ZHAO You-cai, QI Jing-yu. Study on use of MSWI fly ash in ceramic tile [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2007, 141(1): 106–114.
TAKAOKA M, TAKEDA N, MIARA S. The behaviour of heavy metals and phosphorus in an ash melting process [J]. Water Science and Technology, 1997, 36: 275–282.
ZHANG Hai-ying. Utilization of MSWI fly ash in the production of ceramic tile [D]. Shanghai: Tongji University, 2005: 34–37. (in Chinese)
HE Pin-jing, ZHANG Hua, CAO Qun-ke, ZHANG Pei-jun. Characterization of APC residues from Shanghai Pudong waste-to-energy facility [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2004, 23(1): 38–42. (in Chinese)
YUAN Ling, SHI Hui-sheng, YUE Peng. Research on potential cementitious reactivity of fly ash from incinerator of municipal solid wastes [J]. Journal of Tongji University: Natural Science, 2003, 12(31): 1444–1448. (in Chinese)
YUE Peng, SHI Hui-sheng, SHU Xin-ling. Preliminary research on cementitious activities of municipal solid wastes incineration ash [J]. Cement, 2003(5): 12–15. (in Chinese)
KARAMANOV A, PELINO M, HREGLICH A. Sintered glass-ceramics from municipal solid waste-incinerator fly ashes—Part I: The influence of the heating rate on the sinter-crystallisation [J]. J Eur Ceram Soc, 2003, 23(6): 827–832.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: Project(50808184) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Yy., Wang, Jj., Lin, X. et al. Microstructures and thermal properties of municipal solid waste incineration fly ash. J. Cent. South Univ. Technol. 19, 855–862 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-012-1083-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-012-1083-5