Abstract
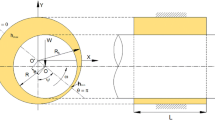
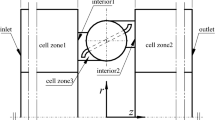
In order to predict accurately the characteristics of supersonic flow in new type externally pressurized spherical air bearings under large bearing clearance and high air supply pressure, which could decrease their load carrying capacity and stability, a CFD-based analysis was introduced to solve the three-dimensional turbulent complete compressible air flow governing equations. The realizable κ-ɛ model was used as a turbulent closure. The supersonic flow field near air inlets was analyzed. The flow structures illustrate that the interaction exists between shock waves and boundary layer, and the flow separation is formed at the lower corner and the lower wall around the point of a maximum velocity. The numerical results show that the conversion from supersonic flow to subsonic flow in spherical air bearing occurs through a shock region (pseudo-shock), and the viscous boundary layer results in the flow separation and reverse flow near the shock. The calculation results basically agree with the corresponding experimental data.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
KAZUYASU M, YOSHIAKI M, HEUY-DONG K. Shock train and pseudo-shock phenomena in internal gas flows [J]. Progress in Aerospace Sciences, 1999, 35: 33–100.
WANG Yun-fei. Air lubrication theory and design of air bearings [M]. Beijing: China Machine Press, 1999. (in Chinese)
LIU Z S, ZHANG G H, XU H J. Performance analysis of rotating externally pressurized air bearings [J]. Proc IMechE Part J: J Engineering Tribology, 1999, 223(4): 653–663.
YUNTANG L, HAN D. Influence of the geometrical parameters of aerostatic thrust bearings with pocketed orifice-type restrictor on its performance [J]. Tribology Int, 2007, 40(3): 1120–1126.
HIKICHI K, GOTO S, TOGO S, ISOMURA K. hydroinertia gas bearings for micro spinners [J]. Journal of Micromechanics and Microengineering, 2005, 15(9): 228–232.
YOSHIMOTO S, YAMAMOTO M, TODA K. Numerical calculations of pressure distribution in the bearing clearance of circular aerostatic thrust bearings with a single air supply inlet [J]. Journal of Tribology, 2007, 129(4): 384–390.
MORI H. A theoretical investigation of pressure depression in externally pressurized gas lubricated circular thrust bearings [J]. Trans ASME-J Basic Engineering, 1961, 83(1): 201–208.
MORI H, EZUKA H. A pseudo shock theory of pressure depression in externally pressurized circular thrust gas bearings [C]//Proceeding JSLE-ASLE International Lubrication Conference, 1975: 286–294.
STAHLER A F. Further comments on the pressure depression effect in externally pressurized gas-lubricated bearings [J]. ASLE Trans, 1964, 7: 366–376.
DOWSON D. Laboratory experiments and demonstrations in tribology-externally pressurized air lubricated thrust bearings [J]. Tribology, 1969, 11: 217–220.
FLUENT Inc. Fluent user’s guide [M]. New Hampshire: Fluent Inc, 2003: (11-2)–(11-9).
VERSTEEG H K, MALALASEKERA W. An introduction to computational fluid dynamics: The finite volume method [M]. New York: Wiley, 1995: 67–75.
WHITE F M. Viscous fluid flow [M]. New York: NcGraw-Hill, 1974: 26–29.
SHIH T H, LIOU W W, SHABBIR A, ZHU J. A new κ-ɛ eddy-viscosity model for high Reynolds number turbulent flows model development and validation [J]. Comput Fluids, 1995, 24(3): 227–238.
WANG Fu-jun. Computational fluid dynamics analysis—Principle and application of CFD software [M]. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2004: 120–126. (in Chinese)
MAYRIPLIS D J. Mesh generation and adaptivity for complex geometries and flows [M]// Handbook of Computational Fluid Mechanics. Salt Lake City: Academic Press, 1996.
MOLLER P S. Radial flow without swirl between parallel disks having both supersonic and subsonic regions [J]. Trans ASME-J Basic Eng, 1966, 88(1): 147–154.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: Project(2002AA742049) supported by the National High Technology Research and Development Program of China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Fs., Bao, G. Characteristics of supersonic flow in new type externally pressurized spherical air bearings. J. Cent. South Univ. Technol. 19, 128–134 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-012-0981-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-012-0981-x