Abstract
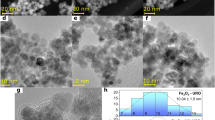
Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles with diameters varying from 10 to 426 nm were synthesized and characterized. Heating effects of Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles under radiofrequency capacitive field (RCF) with frequency of 27.12 MHz and power of 60–150 W were investigated. When the power of RCF is lower than 90 W, temperatures of Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles (75–150 mg/mL) can be raised and maximal temperatures are all lower than 50 °C. When the power of RCF is 90–150 W, temperatures of Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles can be quickly raised and are all obviously higher than those of normal saline and distilled water under the same conditions. Temperature of Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles can even reach 70.2 °C under 150 W RCF. Heating effects of Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles are related to RCF power, particle size and particle concentration.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
LAURENCE D E, HERVEE M, KATEL H, EMILIE M, MARTIN S, CLAUDE L, PIERRE D, IGOR C. Nanovectors for anticancer agents based on superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles [J]. Int J Nanomedicine, 2007, 2(4): 541–550.
JOHANNSEN M, JORDAN A, SCHOLZ R, KOCH M, LEIN M, DEGER S, ROIGAS J, JUNG K, LOENING S. Evaluation of magnetic fluid hyperthermia in a standard rat model of prostate cancer [J]. J Endourol, 2004, 18(5): 495–500.
LATORRE M, RINALDI C. Applications of magnetic nanoparticles in medicine: Magnetic fluid hyperthermia [J]. P R Health Sci J, 2009, 28(3): 227–238.
SHIDO Y, NISHIDA Y, SUZUKI Y, KOBAYASHI T, ISHIGURO N. Targeted hyperthermia using magnetite cationic liposomes and an alternating magnetic field in a mouse osteosarcoma model [J]. J Bone Joint Surg Br, 2010, 92(4): 580–585.
GUO Zhong-hua, TANG Lu-Xin, TANG Jin-tian, XIE Bin, DENG Xiao-hui. Development of measurement and control technologies for hyperthermia treatments of tumors with AC magnetic field [J]. Chinese Journal of Medical Instrumentation, 2006, 30(1): 39–42. (in Chinese)
LIU Xuan, XU Bo, XIA Qi-sheng, ZHAO Tian-de, TANG Jin-tian. A method of showing thermal effect of iron oxide nanoparticles in alternating magnetic field [J]. Chinese Journal of Cancer, 2005, 24(9): 1148–1150. (in Chinese)
HERGT R, DUTZ S. Magnetic particle hyperthermia: Biophysical limitations of a visionary tumour therapy [J]. J Magn Magn Mater, 2005, 293: 80–86.
MA Ming, WU Ya, ZHOU Jie, SUN Yong-kang, ZHANG Yu, GU Ning. Size dependence of specific power absorption of Fe3O4 particles in AC magnetic field [J]. J Magn Magn Mater, 2004, 268: 33–39.
HABASH R W, BANSAL R, KREWSKI D, ALHAFID H T. Thermal therapy. Part I: An introduction to thermal therapy [J]. Crit Rev Biomed Eng, 2006, 34: 459–489.
PALUSSIERE J, DESCAT E, FONCK M, BONICHON F, CHOMY F, BECOUARN Y, AVRIL A, KIND M, RAVAUD A. Radiofrequency ablation in the treatment of liver and lung tumors [J]. Bull Cancer, 2009, 96(11): 1099–1109.
HABASH R W, BANSAL R, KREWSKI D, ALHAFID H T. Thermal therapy. Part II: Hyperthermia techniques [J]. Crit Rev Biomed Eng, 2006, 34(6): 491–542.
STAUFFER P R. Evolving technology for thermal therapy of cancer [J]. Int J Hyperthermia, 2005, 21(8): 731–744.
MOLDAY R S. Magnetic iron-dextran microspheres: US, 4452773 [P]. 1984-06-05.
SUGIMOTO T, MATIJEVIC E. Formation of uniform spherical magnetite particles by crystallization from ferrous hydroxide gels [J]. J Colloid Interface Sci, 1980, 74: 227–243.
DU Yi-qun, ZHANG Dong-sheng, NI Hai-yan, GU Ning, YAN Shi-yan, TANG Qiu-sha, JIN Li-qiang, WAN Mei-ling. Preparation and characterization of Fe3O4 nano-magnetic particles for tumor hyperthermia [J]. Journal of Chinese Electron Microscopy Society, 2005, 24(6): 608–612. (in Chinese)
OHGURI T, IMADA H, YAHATA K, MORIOKA T, NAKANO K, TERASHIMA H, KOROGI Y. Radiotherapy with 8-MHz radiofrequency-capacitive regional hyperthermia for stage III non-small-cell lung cancer: The radiofrequency-output power correlates with the intraesophageal temperature and clinical outcomes [J]. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys, 2009, 73(1): 128–135.
SHIELDS N, O’HARE N, GORMLEY J. An evaluation of safety guidelines to restrict exposure to stray radiofrequency radiation from short-wave diathermy units [J]. Phys Med Biol, 2004, 49(13): 2999–3015.
WAN Bai-kun, ZHU Xin, CHENG Xiao-man, ZHANG Li-xin, LIN Shi-yin, WANG Wei. Parameter optimization of temperature field in RF-capacitive hyperthermia [J]. Progress in Natural Science, 2001, 11(9): 667–674.
HABASH R W, BANSAL R, KREWSKI D, ALHAFID H T. Thermal therapy. Part IV: Electromagnetic and thermal dosimetry [J]. Crit Rev Biomed Eng, 2007, 35: 123–182.
JORDAN A, SCHOLZ R, MAIER-HAU K, JOHANNSEN M, WUST P, NADOBNY J, SCHIRRA H, SCHMIDT H, DEGER S, LOENING S, LANKSCH W, FELIX R. Presentation of a new magnetic field therapy system for the treatment of human solid tumors with magnetic fluid hyperthermia [J]. J Magn Magn Mater, 2001, 225: 118–126.
HE Han-wei, LIU Hong-jiang, ZHOU Ke-chao, WANG Wei, RONG Peng-fei. Characteristics of magnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles encapsulated with human serum albumin [J]. J Cent South Univ Technol, 2006, 13(3): 6–11.
MATSUI Y, NAKAGAWA A, KAMIYAMA Y, YAMAMOTO K, KUBO N, NAKASE Y. Selective thermocoagulation of unresectable pancreatic cancers by using radiofrequency capacitive heating [J]. Pancreas, 2000, 20(1): 14–20.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: Projects(30571779, 10775085) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China; Project(Z07000200540704) supported by Beijing Municipal Science and Technology Commission, China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Xh., Feng, Zm., Ouyang, Ww. et al. Synthesis and characterization of Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles and their heating effects under radiofrequency capacitive field. J. Cent. South Univ. Technol. 17, 1185–1189 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-010-0616-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-010-0616-z