Abstract
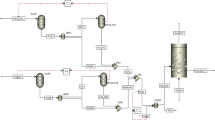
The unburned carbon concentration in fly ash and the influence of main factors on the reduction of nitrogen oxides during gaseous fuel reburning process were experimentally studied in a 36 kW down-fired furnace when five typical coals with different qualities were served as the primary fuel. It is found that the higher nitrogen oxide reduction efficiency can be obtained by reburning process when the coal used as the primary fuel contains more volatile matter. But under the optimizational operating conditions, both above 50% nitrogen oxide reduction and low carbon loss can be achieved by reburning process even though the primary fuel is the low-volatile coal. The experimental results show that the reasonable residence time in reburn zone is 0.6–0.9 s, the appropriate gaseous reburn fuel percentage is 10%—15% and the optimal average excess air coefficient in reburn zone is 0.8–0.9. These results extend the ranges of the key parameter values for reburning process with respect to that the low-volatile coals are used as the primary fuel.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
GLARBORG P, JENSEN A D, JOHNSSON J E. Fuel nitrogen conversion in solid fuel fired systems [J]. Progress in Energy and Combustion Science, 2003, 29(2): 89–113.
HE De-wen, PENG Chang-hong, WANG Yun-yan. Main influence factors on desulfurization of coal by sulfolobas [J]. Journal of Central South University of Technology, 2003, 10(2): 113–116.
HILL S C, SMOOT L D. Modeling of nitrogen oxides formation and destruction in combustion systems [J]. Progress in Energy and Combustion Science, 2000, 26(4/6): 417–458.
YANG Wei-hong, JIANG Shao-jiang, HSIAO Tse-chiang, YANG Li-xing. Numerical simulation of high temperature air combustion flames properties [J]. Journal of Central South University of Technology, 2000, 7(3): 156–158.
SMOOT L D, HILL S C, XU H. NOx control through reburning [J]. Progress in Energy and Combustion Science, 1998, 24(5): 385–408.
ZHANG Zhong-xiao, YAO Xiang-dong, WU Xiao-jiang, WEI Hua-yan, TAO Xiao-hua, ZHU Ji-mu. Experimental study on low NOx emission using gas reburning [J]. Proceeding of the CSEE, 2005, 25(9): 99–102. (in Chinese)
BILBAO R, MILLERA A, ALZUETA M U, PRADA L. Evaluation of the use of different hydrocarbon fuels for gas reburning [J]. Fuel, 1997, 76(14/15): 1401–1407.
FANG Bing, LUO Yong-hao, LU Fang, FENG Yan-lei. The characteristics and selection of reburned fuels involved in the reburning technology of a coal-fired boiler [J]. Journal of Engineering for Thermal Energy and Power, 2004, 19(5): 443–446. (in Chinese)
BILBAO R, ALZUETA M U, MILLERA A. Experimental study of the influence of the operating variables on natural gas reburning efficiency [J]. Ind Eng Chem Res, 1995, 34(12): 4531–4539.
LI Sen, XU Tong-mo, ZHOU Qu-lan, TAN Hou-zhang, HUI Shi-en, HU Hong-li. Optimization of coal reburning in a an MW tangentially fired furnace [J]. Fuel, 2007, 86(7/8): 1169–1175.
SHEN Bo-xiong, YAO Qiang, XU Xu-chang. Kinetic model for natural gas reburning [J]. Fuel Processing Technology, 2004, 85(11): 1301–1315.
DIMITRIOU D J, KANDAMBY N, LOCKWOOD F C. A mathematical modeling technique for gaseous and solid fuel reburning in pulverized coal combustors [J]. Fuel, 2003, 82(15/17): 2107–2114.
HAMPARTSOUMIAN E, FOLAYAN O O, NIMMO W, GIBBS B M. Optimisation of NOx reduction in advanced coal reburning systems and the effect of coal type [J]. Fuel, 2003, 82(4): 373–384.
QIU Zhong-zhu, PAN Wei-guo, REN Jian-xing, LI Peng, SUN Jian-rong, WANG Wen-huan. Experimental study on reburning with natural gas for reducing NOx emission [J]. Journal of Power Engineering, 2007, 27(1): 126–129. (in Chinese)
HE Xue-zhi, WANG Chun-chang. Study on adaptability of low NOx burners to various coal quality [J]. Thermal Power Generation, 2003, 8: 12–15. (in Chinese)
MCCAHEY S, MCMULLAN J T, WILLIAMS B C. Techno-economic analysis of NOx reduction technologies in p.f. boilers [J]. Fuel, 1999, 78(14): 1771–1778.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: Projects(50806025; 50721005) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Su, S., Xiang, J., Sun, Ls. et al. Main influencing factors and coal fly ash characteristics of gasoues fuel reburning process. J. Cent. South Univ. Technol. 16, 160–165 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-009-0027-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-009-0027-1