Abstract
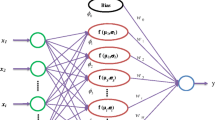
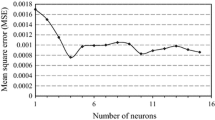
Application research of neural networks to geotechnical engineering has become a hotspot nowadays. General model may not reach the predicting precision in practical application due to different characteristics in different fields. In allusion to this, an elasto-plastic constitutive model based on clustering radial basis function neural network(BC-RBFNN) was proposed for moderate sandy clay according to its properties. Firstly, knowledge base was established on triaxial compression testing data; then the model was trained, learned and emulated using knowledge base; finally, predicting results of the BC-RBFNN model were compared and analyzed with those of other intelligent model. The results show that the BC-RBFNN model can alter the training and learning velocity and improve the predicting precision, which provides possibility for engineering practice on demanding high precision.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
CHEN S, COWAN C F N, GRANT P M. Orthogonal least squares learning algorithm for radial basis function networks[J]. IEEE Trans Neural Networks, 1991, 2(2): 302–309.
ZEKERLYA U, ERTUGRUL C G M, HELKKI N. Analysis of input-output clustering for determining centers of RBFN[J]. IEEE Trans on Neural Networks, 2000, 11(4): 851–858.
GAO Lang, XIE Kang-he. Application of artificial neural networks to geotechnical engineering[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal, 2002, 35(4): 77–80. (in Chinese)
PENG Xiang-hua, LUO Ying-she, ZHOU Jing-ye, YU Min, LUO Tao. Research on creep constitutive model of TC11 titanium alloy based on RBFNN[J]. Materials Science Forum, 2008, 575/578: s1050–1055.
ZHAO Sheng-li, LIU Yan. Performance prediction of commercial concrete based on RBF neural network[J]. Computer Engineering, 2005, 31(18): 36–39. ( in Chinese)
LI Qiang. Numerical modeling method of sand and finite element analysis[D]. Wuhan: Geotechnical Engineering of Huazhong University of Science and Technology, 2004. (in Chinese)
ZHOU Jing-ye, PENG Xiang-hua, WANG Zhi-chao, YU Min. A mode of RBF neuron network based on clustering[J]. Natural Science Journal of Xiangtan University, 2007, 29(4): 99–103. ( in Chinese)
ZHU Q M, HILLINGS S A. Fast orthogonal identification of nonlinear stochastic models and radial basis function neural networks[J]. Int J Contr, 1996, 64(5): 871–886.
ZHENG Ying-ren, CHEN Yu-yao, DUAN Jian-li. Loading-unloading criterions and constitutive models in generalized plastic mechanics[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2000, 21(4): 226–300. ( in Chinese)
CHEN S, BILLINGS S A, GRANT P M. Recursive hybrid algorithm for nonlinear system identification using radial basis function networks[J]. Int J Contr, 1992, 55(5): 1051–1057.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: Project(07031B) supported by the Scientific Research Fund of Central South University of Forestry and Technology; Project(06C843) supported by the Scientific Research Fund of Hunan Provincial Education Department
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peng, Xh., Wang, Zc., Luo, T. et al. An elasto-plastic constitutive model of moderate sandy clay based on BC-RBFNN. J. Cent. South Univ. Technol. 15 (Suppl 1), 47–50 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-008-0312-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-008-0312-4