Abstract
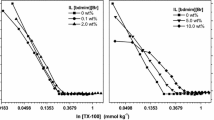
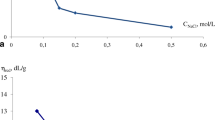
The hydrophobic aggregation of ultrafine kaolinite in cationic surfactant suspension was investigated by sedimentation test, zeta potential measurement and SEM observation. SEM images reveal that kaolinite particles show the self-aggregation of edge-face in acidic media, the aggregation of edge-face and edge-edge in neutral media, and the dispersion in alkaline media due to electrostatic repulsion. In the presence of the dodecylammonium acetate cationic surfactant and in neutral and alkaline suspension, the hydrophobic aggregation of face-face is demonstrated. The zeta potential of kaolinite increases with increasing the concentration of cationic surfactant. The small and loose aggregation at a low concentration but big and tight aggregation at a high concentration is presented. At pH=7 alkyl quarterly amine salt CTAB has the best hydrophobic aggregation among three cationic surfactants, namely, dodecylammonium acetate, alkyl quarterly amine salts 1227 and CTAB.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
WANG En-fu, MA Chao-jian, LU Qin-fang, LI Yao-wu. Discussion of disposal high silica bauxite ore by ore-dressing Bayer process in alumina production of China [J]. Light Metals, 1996(7): 3–6. (in Chinese)
JIANG Hao, HU Yue-hua, WANG Dian-zuo, QIN Wen-qing, GU Guo-hua. Structure of the adsorbed layer of cationic surfactant at diaspore-water interface [J]. Journal of China University of Mining and Technology, 2005, 34(4): 500–501. (in Chinese)
LI Long-feng. Desilication and iron removal research for diasporic-hauxite by mineral processing [J]. Journal of Central South Institute of Mining and Metallurgy, 1980(4): 82–84. (in Chinese)
LIANG An-zhen, LI Ting-hui. Discussion on reasonable technology flowsheet of bauxite processing [J]. Light Metal, 1982(11): 1–6. (in Chinese)
FENG Qi-ming, ZHANG Guo-fan, LU Yi-ping. The 90’s research and outlook of bauxite on impurity removing by mineral processing [J]. Light Metal, 1998(4): 9–13. (in Chinese)
ZHANG Guo-fan. Theory and technology of flotation on bauxite desilication [D]. Changsha: Central South University, 2001. (in Chinese)
LU Yi-ping, ZHANG Guo-fan, FENG Qi-ming, OU Le-ming. A novel collector RL for flotation of bauxite [J]. J Cent South Univ Technol, 2002, 9(1): 21–24.
JIANG Hao, HU Yue-hua, QIN Wen-qing, WANG Yu-hua, WANG Dian-zuo. Mechanism of flotation for diaspore and aluminium-silicate minerals with alkyl-amine collectors [J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2001, 11(4): 688–692. (in Chinese).
LI Hai-pu, HU Yue-hua, WANG Dian-zuo, XU Jing. Mechanism of interaction between cationic surfactant and kaolinite [J]. Journal of Central South University: Natural Science, 2004, 35(12): 228–233. (in Chinese)
WANG Yu-hua, HU Yue-hua, LIU Xiao-wen. Flotation desilicating from diasporic-bauxite with cetyl trimethylammonium bromide [J]. J Cent South Univ Technol, 2003, 10(4): 324–328.
WANG Yu-hua, HU Yue-hua, CHEN Xiang-qing. Alum inum-silicates flotation with quaternary ammonium salts [J]. Trans Nonferrous Met Soc China, 2003, 13(3): 715–719.
HU Yue-hua, SUN Wei, JIANG Hao, MILLER J D, FA Ke-qing. The anomalous behavior of kaolinite flotation with dodecyl amine collector as explained from crystal structure considerations [J]. Mineral Processing, 2005, 76: 163–172.
TARL G, BOBOS J. Modification of surface charge properties during kaolinite to halloysite-7A transformation [J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 1999, 210(2): 360–366.
CUI Ji-rang, FANG Qi-xue, HUANG Guo-zhi. Crystal structures and surface properties of diaspore and kaolinite [J]. Nonferrous Metals, 1999, 51(4): 25–30. (in Chinese)
SADOWSKI Z., Study on hydrophobic aggregation of calcite aqueous suspensions [J]. Powder Technol, 1994, 80(2): 93–98.
HU Yue-hua, SUN Wei, LIU Xiao-wen, WANG Dian-zuo. Cleavage nature, electrokinetics, aggregation and dispersion of kaolinite [J]. Trans Nonferrous Met Soc China, 2003, 13(6): 1430–1434.
LUO Zhao-jun, HU Yue-hua, WANG Yu-hua, QIU Guan-zhou. Mechanism of dispersion and aggregation in reverse flotation for bauxite [J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2001, 11(4): 680–683. (in Chinese)
MAREK Z, HORN R G. Hydrophobic attraction may contribute to aqueous flocculation of clays [J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochem Eng Aspects, 2003, 222: 323–328.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: Project(2005CB623701) supported by the Major State Basic Research Development Program of China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Xp., Hu, Yh. & Liu, Rq. Hydrophobic aggregation of ultrafine kaolinite. J. Cent. South Univ. Technol. 15, 368–372 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-008-0069-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-008-0069-9