Abstract
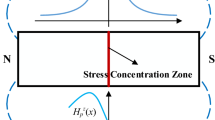
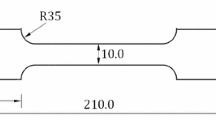
To test the magnetic signals leaked from the surface of specimens during loading, the experiments of the static tensile of medium carbon 45# steel were carried out. The results show that the magnetic field strength values rapidly vary when the load began, and the curves of the magnetic field strength change from irregularity to regularity with the increase of the load. Furthermore, by comparing with the state of on-line testing, it is found that the magnetic signals of out-of-line testing has more practicability. In the course of loading, though the dots of passing zero of the magnetic field strength continually changed their positions and quantities, the last rupture places were always approached by the dots of passing zero since the elastic loading phase. Some certain relations should exist between external stress and changing of magnetic signals inside the material, and correlative explanation is made based on dislocation theory and the mechanism of magnetic domain action, which provides the basis for further research of magnetic memory.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Doubov A A. Screening of quality using the metal magnetic memory [J]. Welding in the World, 1998 (41): 196–199.
Jile D C, Atherton D L. Theory of ferromagnetic hysteresis [J]. J Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 1986, 61: 48–60.
Jiles D C. Theory of the magnetomechanical effect[J]. J Phys D: Appl Phys, 1995, 28: 1537–1547.
Maker J M, Tanner B K. The effect of stresses approaching and exceeding the yield point on the magnetic properties of high strength perlitic steels [J]. NDT&E International, 1998, 31(2): 117–127.
Chechko I I. Using the method of magnetic memory of metal to evaluate the service life of the items of power equipment at the konakovo district power station[J]. Thermal Engineering, 2002, 49(12): 1028–1031.
LI Lu-ming, HUANG Song-ling, WANG Xiao-feng, et al. Magnetic field abnormality caused by welding residual stress[J]. Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 2003, 261: 385–391.
Doubov A A. A technique for monitoring the bends of boiler and steam-line tubes using the magnetic memory of etal[J]. Thermal Engineering, 2001, 48(4): 289–295.
ZHANG Ying, SONG Kai, REN Ji-lin, et al. Application of software ansys in metal magnetic memory testing[J]. Nondestructive Testing, 2004, 26(5): 218–220. (in Chinese)
ZHANG Yi-liang, XU Xue-dong, GE Sen. Measurement and analysis on residual stresses of techniques in high pressure gas cylinders[J]. Journal of Experimental Mechanics, 2004, 19(2): 194–199. (in Chinese)
LI Lian-xiu. Study on magnetostriction and magnetic memory[J]. Nondestructive Testing, 2004, 26(3): 109–112. (in Chinese)
Ren Ji-lin, Lin Jun-ming. The Testing Technology of Metal Magnetic Memory[M]. Beijing: Electronic Power in China Press, 2000. (in Chinese)
YIN Da-wei, DONG Shi-yun, XU Bin-shi, et al. Progress of research on metal magnetic memory testing method[J]. Nondestructive Inspection, 2005, 29(2): 1–5. (in Chinese)
WANG De-fu, LUO Shi-hua. Magnetism Physics[M]. Beijing: Electronic Industry Press, 1987. (in Chinese)
ZHOU Ke-yin, ZHANG Jing, YAO En-tao, et al. Detecting hidden damage in component based on metal magnetic memory effect[J]. Journal of Nanjing University of Aeronautics & Astronautics, 2004, 36(6): 713–717. (in Chinese)
ZHANG Wei-min, LIU Hong-guang, SUN Hai-tao. Magnetic memory effect of low and medium carbon steel under static tension conditions[J]. Transactions of Beijing Institute of Technology, 2004, 24(7): 571–574. (in Chinese)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: Project(50235030) supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yin, Dw., Xu, Bs., Dong, Sy. et al. Characteristics of magnetic memory signals for medium carbon steel under static tensile conditions. J Cent. South Univ. Technol. 12, 107–111 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-005-0020-2
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-005-0020-2