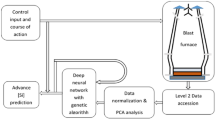
Abstract
A soft-measuring approach is presented to measure the flux of liquid zinc with high temperature and causticity. By constructing mathematical model based on neural networks, weighing the mass of liquid zinc, the flux of liquid zinc is acquired indirectly, the measuring on line and flux control are realized. Simulation results and industrial practice demonstrate that the relative error between the estimated flux value and practical measured flux value is lower than 1.5%, meeting the need of industrial process.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lehtokangas M. Modelling with constructive backpropagation [J]. IEEE Trans neural networkss, 1999, 10(12): 707–716.
Reyes J S, Duro R J. Influence of noise on discrete time backpropagation trained networks [J]. Neural Computer, 2001, 41(1):67–89.
WANG Zheng’ou, LIN Chen. A fast learning algorithm of feedforward neural networkss and its application to system identification[J]. Acta Automatic Sinica(in Chinese), 1997, 23(6):728–735.
TAN Hao, LI Li-yuan, CHEN Wei-nan. Burner flame recognition based on backpropagation neural networks identification of burning state of boiler hearth flame on BP network[J]. Acta Automatic Sinica (in Chinese), 1998, 24(5):667–670.
GUO Chuang-xin, JING Lei, LIANG Nian-sheng, et al. A robust BP algorithm and its application on identification of non-linear mechanics system [J]. Information and Control (in Chinese), 1996, 25(6): 354–360.
LAI Xiao-ping, ZHOU Hong-xing. Self-learning neurons and self-learning BP networks [J]. Information and Control(in Chinese), 1999, 28(6): 407–415.
LI Guo-jun, ZHAN Bo-qiong. Engineering Liquid Mechanics [M]. Wuhan: Huzhong University of Science and Technology Press, 1991.
LIU Ding, WAN Bai-wu. Model identification and steady-state optimizing control of wind system for air preheater [J]. Acta Automatic Sinica (in Chinese), 1999, 25(6):321–324.
WANG Chao-jun, LIU Yan-ming. An optimization controller in milling compacting genetic algorithm with neural networkss [J]. Control Theory and Applications(in Chinese), 1999, 16(4):607–610.
WANG Yin, RONG Gang. A self-organizing neural-network-based fuzzy system [J]. Control Theory and Application, 1999, 16(6):455–457.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: Project (201AA411040) supported by National Plan and Development Committee.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, Yy., Gui, Wh. & Li, Yg. Flux-measuring approach of high temperature metal liquid based on BP neural networks. J Cent. South Univ. Technol. 10, 244–247 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-003-0017-7
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-003-0017-7