Abstract
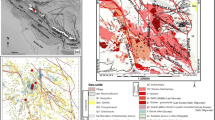
In Xikuangshan antimony ore-field, the western fracture zone is a composite of major fault, F75, and its secondary faults, such as F71, F72 and F3 etc.. On plane, the fracture zone scatters from southwest to northeast, and concentrates from upper to deeper level on profile. All ore-bodies exist in the carbonate of footwall of the major fault or that of the footwall of its secondary faults. From 480 m and 320 m to 120 m level, the fractal dimensional number of the fault system decreases from 1.482 2 and 1.448 6 to 1.339 2, which indicates the form of fracture zone becoming more simple at deeper level. And in five sub-ranges, the III and IV sub-ranges are the known area, and the I, II and V sub-ranges are unknown. The fractal studies of the western fracture zone in these sub-ranges show that the fractal dimensional numbers of the I and II, being 1.201 5 and 1.278 0, respectively, are smaller than that of the III and IV, being 1.475 9 and 1.576 9, respectively; and that of the V, being 1.571 2, keeps with that of the III, IV sub-ranges. So mineralization is not well in I and II sub-ranges, and V sub-range is the best to benefit mineralization.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kewate D L. Fractal and chaos-application in geology and geophysics (in Chinese)[M]. Beijing: Seismic Press, 1993.
YI Shun-min, TANG Hui-ming. Fractal structure features of active fault[J]. Earth Science-Journal of China University of Geosciences (in Chinese), 1995, 20(1): 58–62.
HAN Yu-ying. Fractal analysis of tectonic fracture[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information (in Chinese), 1992, 1(3): 79–83.
ZHOU Li-qun. Primary discussion on mineralization in Qiziqiao group of Xikuangshan antimony mine[J]. Journal of Central South University of Technology (in Chinese), 1997, 28(suppl. 1): 112–114.
DAI Ta-gen, CHEN Guo-da. Three floors model of are controlling structures and its significance in Xikuangshan Sb deposit[J]. Journal of Central South University of Technology (in Chinese), 1999, 30(4): 342–344.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Foundation item: The National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 49772152)
Biography of the first author: TANG Shi-jia, doctoral student, born in 1971, majoring in metallogenetic structure geology and tectonic simulation.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tang, Sj., Gao, Gm., Peng, Es. et al. Fractal feature of western fracture zone in Xikuangshan antimony mine and its geological significance. J Cent. South Univ. Technol. 7, 212–215 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-000-0056-2
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-000-0056-2