Abstract
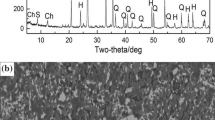
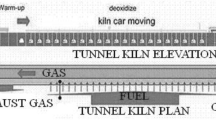
Successfully developed an innovative process of direct reduction of cold-bound pellets from iron ore concentrate with a coal-based rotary kiln, in comparison with the traditional direct reduction of fired oxide pellets in coal-based rotary kilns, possesses such advantages as: shorter flowsheet, lower capital investment, greater economic profit, good quality of direct reduced iron. The key technologies, such as the composite binder and corresponding feasible techniques were employed in practice. A mill utilizing this process and with an annual capacity of 50 thousand ton DRI has been put into operation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Terence E Dancy. The development of direct reduction process[J]. Scand J Metallurgy, 1993, 22: 100–108
LU W-K. Usage of sponge iron in ironmaking[J]. Scand J Metallurgy, 1993, 22: 122–127
Balli D F. Agglomeration of iron ores[M]. London: Heinemann Educational Book Limited, 1973
XU Jin-chang, FU Be-yi, LIU Zhong-huei, et al. Direct reduction of cold bound pellets in a scale-up coal-based rotary kiln. In: the First National Meeting for Direct Reduction of Iron in a Coal-based Rotary Kiln (in Chinese)[C]. Northeast University Press, 1991
ZHU De-qing, FU Shou-chen, CAI Yu-zuo, et al. Study of interaction of binder with iron ore concentrate[J]. Sintering & pelleting (in Chinese), 1995(3): 19–21
HU Pen-sheng. Moulding sand (in Chinese) [M]. Shanghai: Shanghai Science and Technology Press, 1980
ZHU De-qing. Study of mechanisms of cold bonded agglomeration of fine ground concentrates and its application in direct reduction: [dissertation][D]. Changsha: Central South University of Technology, 1994
HUANG B H, LU W K. Kinetics and mechanisms of reactions in iron ore/coal composite[J]. ISIJ International, 1993, 33(10): 1055–1061
ZHU De-qing, Chen Jin, FU Shou-chen, et al. Reduction behavior of cold bound pellets from iron ore concentrate in a commercial rotary kiln[J]. J Cent South Univ Technology (in Chinese), 1995, 26(4): 470–475
ZHU De-qing, Jiang Tao, QIU Guan-zhou, et al. Mechanism and application of enforced classification for disc pelletizer[J]. J Cent South Univ Technology (in Chinese), 1999, 30(2): 140–143
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Foundation item: The Key Project of the 9th Five-year Plan of Ministry of Science and Technology(No. 96040202A) and the Foundation for University Key Teacher by the Ministry of Education
Biography of the first author: ZHU De-qing, associate professor, received Ph. D. in Mineral Engineering in 1994, majoring in mineral processing and ferrous metallurgy.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, Dq., Qiu, Gz., Jiang, T. et al. An innovative process for direct reduction of cold-bound pellets from Iron concentrate with a coal-based rotary kiln. J Cent. South Univ. Technol. 7, 68–71 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-000-0034-8
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-000-0034-8