Abstract
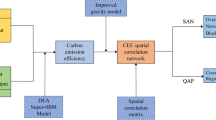
City cluster is an effective platform for encouraging regionally coordinated development. Coordinated reduction of carbon emissions within city cluster via the spatial association network between cities can help coordinate the regional carbon emission management, realize sustainable development, and assist China in achieving the carbon peaking and carbon neutrality goals. This paper applies the improved gravity model and social network analysis (SNA) to the study of spatial correlation of carbon emissions in city clusters and analyzes the structural characteristics of the spatial correlation network of carbon emissions in the the Yangtze River Delta (YRD) city cluster in China and its influencing factors. The results demonstrate that: 1) the spatial association of carbon emissions in the YRD city cluster exhibits a typical and complex multi-threaded network structure. The network association number and density show an upward trend, indicating closer spatial association between cities, but their values remain generally low. Meanwhile, the network hierarchy and network efficiency show a downward trend but remain high. 2) The spatial association network of carbon emissions in the YRD city cluster shows an obvious ‘core-edge’ distribution pattern. The network is centered around Shanghai, Suzhou and Wuxi, all of which play the role of ‘bridges’, while cities such as Zhoushan, Ma’anshan, Tongling and other cities characterized by the remote location, single transportation mode or lower economic level are positioned at the edge of the network. 3) Geographic proximity, varying levels of economic development, different industrial structures, degrees of urbanization, levels of technological innovation, energy intensities and environmental regulation are important influencing factors on the spatial association of within the YRD city cluster. Finally, policy implications are provided from four aspects: government macro-control and market mechanism guidance, structural characteristics of the ‘core-edge’ network, reconfiguration and optimization of the spatial layout of the YRD city cluster, and the application of advanced technologies.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anser M K, 2019. Impact of energy consumption and human activities on carbon emissions in Pakistan: application of STIRPAT model. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 26(13): 13453–13463. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-04859-y
Badi S, Wang L S, Pryke S, 2017. Relationship marketing in Guanxi networks: a social network analysis study of Chinese construction small and medium-sized enterprises. Industrial Marketing Management, 60: 204–218. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indmarman.2016.03.014
Bai C Q, Zhou L, Xia M L et al., 2020. Analysis of the spatial association network structure of China’s transportation carbon emissions and its driving factors. Journal of Environmental Management, 253: 109765. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.109765
Barnett G A, 2011. Encyclopedia of Social Networks. Los Angeles: SAGE Publications.
Ben Amara D, Qiao J J, Zada M, 2023. How to reconcile the climate change issue with economic growth? Spatial dual mediating effects of carbon emissions and foreign investment. Journal of Cleaner Production, 411: 137285. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2023.137285
Bruner M W, McLaren C D, Mertens N et al., 2022. Identity leadership and social identification within sport teams over a season: A social network analysis. Psychology of Sport and Exercise, 59: 102106. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psychsport.2021.102106
Bu Y, Wang E D, Bai J H et al., 2020. Spatial pattern and driving factors for interprovincial natural gas consumption in China: based on SNA and LMDI. Journal of Cleaner Production, 263: 121392. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.121392
Chen X L, Di Q B, Jia W H et al., 2023. Spatial correlation network of pollution and carbon emission reductions coupled with high-quality economic development in three Chinese urban agglomerations. Sustainable Cities and Society, 94: 104552. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scs.2023.104552
Chu H, Liu M K, Wang M J et al., 2023. Measurement and analysis of the comprehensive emission intensity and coupling coordination relationship of carbon dioxide emissions and pollutant emissions in the Yangtze River Delta Urban Agglomeration. Atmospheric Pollution Research, 14(11): 101897. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apr.2023.101897
De Oliveira-De Jesus P M, 2019. Effect of generation capacity factors on carbon emission intensity of electricity of Latin America & the Caribbean, a temporal IDA-LMDI analysis. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 101: 516–526. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2018.11.030
Dong J, Li C B, 2022. Structure characteristics and influencing factors of China’s carbon emission spatial correlation network: a study based on the dimension of urban agglomerations. Science of the Total Environment, 853: 158613. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.158613
Fan J S, Zhou L, 2019. Impact of urbanization and real estate investment on carbon emissions: evidence from China’s provincial regions. Journal of Cleaner Production, 209: 309–323. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.10.201
Fang G C, Huang M, Zhang W B et al., 2024. Exploring global embodied carbon emissions transfer network—an analysis based on national responsibility. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 202: 123284. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2024.123284
Güneralp B, Zhou Y Y, Ürge-Vorsatz D et al., 2017. Global scenarios of urban density and its impacts on building energy use through 2050. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 114(34): 8945–8950. doi: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1606035114
Han F, Xie R, Lu Y et al., 2018. The effects of urban agglomeration economies on carbon emissions: Evidence from Chinese cities. Journal of Cleaner Production, 172: 1096–1110. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.09.273
Hu Y, Yu Y, Mardani A, 2021. Selection of carbon emissions control industries in China: An approach based on complex networks control perspective. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 172: 121030. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2021.121030
Huang M X, Wang Z Z, Chen T, 2019. Analysis on the theory and practice of industrial symbiosis based on bibliometrics and social network analysis. Journal of Cleaner Production, 213: 956–967. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.12.131
Huang Yin, Huang Shumin, Nie Xiaoqian, 2021. Comparison of freight and economic connection network from the perspective of Yangtze River Delta integration. Journal of Rail Way Science and Engineering, 18(4): 1050–1055. (in Chinese)
Huo T F, Cao R F, Xia N Net al., 2022. Spatial correlation network structure of China’s building carbon emissions and its driving factors: a social network analysis method. Journal of Environmental Management, 320: 115808. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.115808
Jansuwan S, Chen A, Xu X D, 2021. Analysis of freight transportation network redundancy: an application to Utah’s bimodal network for transporting coal. Transportation Research Part a-Policy and Practice, 151: 154–171. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tra.2021.06.019
Jiang P, Gong X J, Yang Y R et al., 2023. Research on spatial and temporal differences of carbon emissions and influencing factors in eight economic regions of China based on LMDI model. Scientific Reports, 13(1): 7965. doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-023-35181-w
Jiang Q C, Ma X J, 2021. Spillovers of environmental regulation on carbon emissions network. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 169: 120825. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2021.120825
Kong H J, Shi L F, Da D et al., 2022. Simulation of China’s carbon emission based on influencing factors. Energies, 15(9): 3272. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/en15093272
Lan F, Sun L, Pu W Y, 2021. Research on the influence of manufacturing agglomeration modes on regional carbon emission and spatial effect in China. Economic Modelling, 96: 346–352. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.econmod.2020.03.016
Li F Y, Li X M, 2022. An empirical analysis on regional natural gas market of China from a spatial pattern and social network perspective. Energy, 244: 122598. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2021.
Li H M, Xu R Z, 2023. How does digital finance affect the efficiency of urban green economies? Evidence from China. Finance Research Letters, 58: 104595. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.frl.2023.104595.
Li Z L, Sun L, Geng Y et al., 2017. Examining industrial structure changes and corresponding carbon emission reduction effect by combining input-output analysis and social network analysis: a comparison study of China and Japan. Journal of Cleaner Production, 162: 61–70. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.05.200
Liang H W, Dong L, Luo X et al., 2016. Balancing regional industrial development: analysis on regional disparity of China’s industrial emissions and policy implications. Journal of Cleaner Production, 126: 223–235. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.02.145
Liu C X, Tang R E, Guo Y Q et al., 2022. Research on the structure of carbon emission efficiency and influencing factors in the Yangtze River Delta Urban Agglomeration. Sustainability, 14(10): 6114. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/su14106114
Liu J B, Peng X B, Zhao J, 2023. Analyzing the spatial association of household consumption carbon emission structure based on social network. Journal of Combinatorial Optimization, 45(2): 79. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10878-023-01004-x
Liu S N, Xiao Q T, 2021. An empirical analysis on spatial correlation investigation of industrial carbon emissions using SNAICE model. Energy, 224: 120183. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2021.120183
Liu W D, Sun Y H, Cai W G et al., 2022. A Study on the spatial association network of co2 emissions from the perspective of city size: evidence from the Yangtze River Delta Urban Agglomeration. Buildings, 12(5): 617. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings12050617
Liu X J, Jin X B, Luo X L et al., 2023. Quantifying the spatiotemporal dynamics and impact factors of China’s county-level carbon emissions using ESTDA and spatial econometric models. Journal of Cleaner Production, 410: 137203. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2023.137203
Lorant V, Soto Rojas V, Bécares L et al., 2016. A social network analysis of substance use among immigrant adolescents in six European cities. Social Science & Medicine, 169: 58–65. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.socscimed.2016.09.031
Lv K, Feng X, Scott K et al., 2019. A study on embodied carbon transfer at the provincial level of China from a social network perspective. Journal of Cleaner Production, 225: 1089–1104. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.03.233
Ma F, Wang Y X, Yuen K F et al., 2019. The Evolution of the Spatial Association Effect of Carbon Emissions in Transportation: A Social Network Perspective. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 16(12): 2154. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16122154
Magazzino C, Pakrooh P, Abedin M Z, 2023. A decomposition and decoupling analysis for carbon dioxide emissions: evidence from OECD countries. Environment Development and Sustainability,. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-023-03824-7
Marbuah G, Amuakwa-Mensah F, 2017. Spatial analysis of emissions in Sweden. Energy Economics, 68: 383–394. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2017.10.003
Meng B, Wang J G, Andrew R et al., 2017. Spatial spillover effects in determining China’s regional CO2 emissions growth: 2007–2010. Energy Economics, 63: 161–173. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2017.02.001
Pattak D C, Tahrim F, Salehi M et al., 2023. The driving factors of Italy’s CO2 emissions based on the STIRPAT model: ARDL, FMOLS, DOLS, and CCR approaches. Energies, 16(15): 5845. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/en16155845
Priyashani N, Kankanamge N, Yigitcanlar T, 2023. Multisource open geospatial big data fusion: application of the method to demarcate urban agglomeration footprints. Land, 12(2): 407. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/land12020407
Shao Shuai, Xu Lili, Yang Lili, 2023. Structural characteristics and formation mechanism of carbon emission spatial association networks within China. Systems Engineering-Theory & Practice, 43(4): 958–983. (in Chinese)
Shao Xiaoyu, Weng Zongyuan, Miao Qingsong et al., 2022. Evolution and element analysis of regional green technology innovation output network: evidence from the urban agglomeration of the Yangtze River Economic Belt. Geography and Geo-information Science, 38(4): 40–49. (in Chinese)
Shi X Y, Huang X X, Zhang W X et al., 2024. Examining the characteristics and influencing factors of China’s carbon emission spatial correlation network structure. Ecological Indicators, 159: 111726. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2024.111726
Song H H, Gu L Y, Li Y F et al., 2022. Research on carbon emission efficiency space relations and network structure of the Yellow River Basin city cluster. International journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(19): 12235. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191912235
Song J Z, Feng Q, Wang X P et al., 2019. Spatial association and effect evaluation of co2 emission in the Chengdu-Chongqing urban agglomeration: quantitative evidence from social network analysis. Sustainability, 11(1): 1. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/su11010001
Sporkmann J, Liu Y, Spinler S, 2023. Carbon emissions from European land transportation: a comprehensive analysis. Transportation Research Part D-Transport and Environment, 121: 103851. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trd.2023.103851
Su H, Yang J T, 2023. Research on the influence of spatial structure on carbon emission synergy of urban agglomeration-based on the development process of Yangtze River Delta Urban Agglomeration in China. Sustainability, 15(12): 20. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/su15129178
Sun X S, Li M R, Hou S Y et al., 2023. Research on the spatial network characteristics, synergistic emission reduction effects and mechanisms of carbon emission in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Urban Agglomeration. Sustainability, 15(10): 8176. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/su15108176
Thorpe A K, Dennison P E, Guanter L et al., 2022. Special issue on remote sensing of greenhouse gas emissions. Remote Sensing of Environment, 277: 113069. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2022.113069.
Uddin M S, Smirnov O, 2022. Spatial distribution of the annual atmospheric carbon dioxide in the contiguous USA and their controlling factors. Environmental Modeling & Assessment, 27(1): 57–76. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10666-021-09780-8
Wang B, Sun Y F, Wang Z H, 2018. Agglomeration effect of C02 emissions and emissions reduction effect of technology: a spatial econometric perspective based on China’s province-level data. Journal of Cleaner Production, 204: 96–106. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.08.243
Wang L K, Zhang M, Song Y, 2024. Research on the spatiotemporal evolution characteristics and driving factors of the spatial connection network of carbon emissions in China: new evidence from 260 cities. Energy, 291: 130448. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2024.130448
Wang Y Y, He X B, 2019. Spatial economic dependency in the environmental kuznets curve of carbon dioxide: the case of China. Journal of Cleaner Production, 218: 498–510. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.01.318
Wang Z S, Xie W C, Zhang C Y, 2023. Towards COP26 targets: characteristics and influencing factors of spatial correlation network structure on U. S. carbon emission. Resources Policy, 81: 103285. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resourpol.2022.103285
Wen L J, Chatalova L, Gao X et al., 2021. Reduction of carbon emissions through resource-saving and environment-friendly regional economic integration: evidence from Wuhan metropolitan area, China. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 166: 120590. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2021.120590
Xia Q, Tian G L, Wu Z, 2022. Examining embodied carbon emission flow relationships among different industrial sectors in China. Sustainable Production and Consumption, 29: 100–114. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spc.2021.09.021
Xiao M, Peng X Z, 2023. Decomposition of carbon emission influencing factors and research on emission reduction performance of energy consumption in China. Frontiers in Environmental Science, 10: 11096650. doi: https://doi.org/10.3389/fenvs.2022.1096650
Xu W Z, 2021. The impact and influencing path of the pilot carbon emission trading market—evidence from China. Frontiers in Environmental Science, 9: 787655. doi: https://doi.org/10.3389/fenvs.2021.787655
Xu H C, Li Y L Zheng Y J et al., 2022. Analysis of spatial associations in the energy-carbon emission efficiency of the transportation industry and its influencing factors: evidence from China. Environmental Impact Assessment Review, 97: 106905. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eiar.2022.106905
You W H, Lv Z K, 2018. Spillover effects of economic globalization on CO2 emissions: a spatial panel approach. Energy Economics, 73: 248–257. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2018.05.016
Zhang D G, Yao X J, 2023. Analysis of spatial correlation networks of carbon emissions in emerging economies. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 30(37): 87465–87482. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-28384-1
Zhang J K, Zhang Y, 2023. Tourism and regional carbon emissions: city-level evidence from China. Tourism Review, 78(3): 888–906. doi: https://doi.org/10.1108/tr-08-2022-0389
Zhang R J, Tai H, Cheng K Tet al., 2022. Carbon emission efficiency network formation mechanism and spatial correlation complexity analysis: taking the Yangtze River Economic Belt as an example. Science of The Total Environment, 841: 156719. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.156719
Zhou C S, Wang S J, 2018. Examining the determinants and the spatial nexus of city-level CO2 emissions in China: a dynamic spatial panel analysis of China’s cities. Journal of Cleaner Production, 171: 917–926. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.10.096
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Conceptualization was proposed by BI Xi and SUN Renjin. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by BI Xi, SHI Hongling and HU Dongou. The first draft of the manuscript was written by BI Xi and supervised by SUN Renjin. The manuscript was proofread by ZHANG Han. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors have no competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Additional information
Foundation item: Under the auspices of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 72273151)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bi, X., Sun, R., Hu, D. et al. Structural Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Carbon Emission Spatial Association Network: A Case Study of Yangtze River Delta City Cluster, China. Chin. Geogr. Sci. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11769-024-1435-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11769-024-1435-8