Abstract
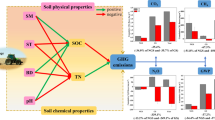
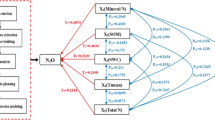
Globally, agricultural soils are considered as one of the most important sources of greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions. No-tillage (NT), one of the most admired ways of climate-smart agriculture, has been deemed to have co-benefit to mitigation of GHG emissions and sustainability for crop yield, however, the effect of NT on GHG emissions is controversial. This study analyzed the overall effects of NT on GHG emissions, as well as the moderators that significantly influenced the overall effects, of the wheat-based rotation cropping systems in China through meta-analysis. The results showed that the overall effect size of NT on methane (CH4) uptake, nitrous oxide (N2O) emission, and global warming potential (GWP) was 0.70 (95% Confidence Interval (CI): 0.21–1.19), −0.27 (95%CI: −0.72–0.18), and −0.39 (95%CI: −1.01–0.23), respectively. In temperate climate zones with alkaline soils, the nitrogen application rate of 120–240 kg/ha, NT could significantly reduce GHG emissions and GWP. However, the mitigation effect will be weakened along with NT duration, except for proper straw addition. Overall, NT has the potential to reduce GHG emissions from wheat-based rotation systems in China, but it is necessary to implement NT depending on local conditions, soil characteristics, and field management.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bahram M, Espenberg M, Pärn J et al., 2022. Structure and function of the soil microbiome underlying N20 emissions from global wetlands. Nature Communications, 13(1): 1430. doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-29161-3
Bai Bing, Yang Yuhao, Wang Xiaohui et al., 2019. Spatio-temporal changes of China’s wheat production based on division of farming system during 1985–2015. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 45(10): 1554–1564. (in Chinese)
Cheng C F, Li M, Xue Z S et al., 2020. Impacts of climate and nutrients on carbon sequestration rate by wetlands: a meta-analysis. Chinese Geographical Science, 30(3): 483–492. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11769-020-1122-3
Cheng Y, Elrys A S, Wang J et al., 2022. Application of enhanced-efficiency nitrogen fertilizers reduces mineral nitrogen usage and emissions of both N2O and NH3 while sustaining yields in a wheat-rice rotation system. Agriculture. Ecosystems & Environment, 324: 107720. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2021.107720
Gao J, Shahid R, Ji X et al., 2022. Climate Change resilience and sustainable tropical agriculture: farmers’ perceptions, reactive adaptations and determinants of reactive adaptations in Hainan, China. Atmosphere, 13(6): 955. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13060955
Hoffman E, Cavigelli M A, Camargo G et al., 2018. Energy use and greenhouse gas emissions in organic and conventional grain crop production: accounting for nutrient inflows. Agricultural Systems, 162: 89–96. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agsy.2018.01.021
Huang Y W, Ren W, Wang L X et al., 2018. Greenhouse gas emissions and crop yield in no-tillage systems: a meta-analysis. Ecosystems & Environment, 268: 144–153. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2018.09.002
IPCC, 2006. 2006 IPCC guidelines for national greenhouse gas inventories. In: Eggleston H S (Ed.), Prepared by the National Greenhouse Gas Inventories Programme. Japan: IGES.
Jiang Z D, Yin S, Zhang X X et al., 2017. Research and development of a DNDC online model for farmland carbon sequestration and GHG emissions mitigation in China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 14(12): 1493. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph14121493
Li B, Chen X Y, Shi X X et al., 2021. Effects of ridge tillage and straw mulching on cultivation the fresh faba beans. Agronomy, 11(6): 1054. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11061054
Li Haifang, Xia Hanping, Xiong Yanmei et al., 2007. Mechanism of greenhouse gases fluxes from soil and its controlling factors: a review. Ecology and Environment, 16(6): 1781–1788. (in Chinese)
Li Hu, Qiu Jianjun, Wang Ligang et al., 2012. The characterization of greenhouse gases fluxes from croplands of China and mitigation technologies. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 21(1): 159–165. (in Chinese)
Li Jing, Feng Shuyi, Chen Ligen et al., 2016. Effects on greenhouse gas emissions under straw returning in paddy fields in middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River: a meta-analysis. China Population, Resources and Environment, 26(5): 91–100. (in Chinese)
Lin Bin, Xu Meng, Wang Xiaoxi, 2022. Mitigation of greenhouse gas emissions in China’s agricultural sector: Current status and future perspectives. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 30(4): 500–515. (in Chinese)
Liu Quanquan, 2015. Effect of simulated precipitation change on greenhouse gases emission in a drylang winter wheat field on the Loess Plateau. Xi’an: Northwest University, (in Chinese)
National Bureau of Statistics of China (NBSC), 2021. China Statistical Yearbook. Beijing: China Statistics Press, (in Chinese)
Necpalova M, Lee J, Skinner C et al., 2018. Potentials to mitigate greenhouse gas emissions from Swiss agriculture. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 265: 84–102. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2018.05.013
Prajapati P, Jacinthe P A, 2014. Methane oxidation kinetics and diffusivity in soils under conventional tillage and long-term notill. Geoderma, 230–231: 161–170. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2014.04.013
Shakoor A, Shahbaz M, Farooq T H et al., 2021. A global metaanalysis of greenhouse gases emission and crop yield under notillage as compared to conventional tillage. Science of the Total Environment, 750: 142299. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.142299
Shi Hongai, 2013. Impacts of management regimes on soil N2O emission from mollisols in agroecosystem. Haerbing: Northeast Agricultural University, (in Chinese)
Shu X X, Qi L, 2019. Effect of Different Tillage Methods on Soil Emissions of N20 and Crop Yield in North China Grain Field. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 310(4): 042020. doi: https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/310/4/042020
Sui Yanting, 2006. Comparative study of emission of N2O and CH4 and CO2 in glebe systems by no-tillage and normal tillage. Changchun: Northeast Normal University, (in Chinese)
Sun Guang, Li Guo, Luo Zunlan et al., 2018. Characteristics and influencing factors of N2O emission in dryland soil. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 49(5): 1220–1224. (in Chinese)
Tu C, Li F D, 2017. Responses of greenhouse gas fluxes to experimental warming in wheat season under conventional tillage and no-tillage fields. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 54: 314–327. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2016.09.016
Wang J L, Liu K L, Zhao X Q et al., 2021. Balanced fertilization over four decades has sustained soil microbial communities and improved soil fertility and rice productivity in red paddy soil. Science of The Total Environment, 793: 148664. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.148664
Yang Binjuan, Deng Liping, Yuan Jiaxin et al., 2022. Annual greenhouse gas emission and comprehensive benefit evaluation under multiple cropping and rotation in rice fields. Jiangsu Agricultural Science, 50(2): 225–231. (in Chinese)
Yao Fanyun, Liu Zhiming, Cao Yujun et al., 2021. Diurnal variation of N2O and CO2 emissions in spring maize fields in Northeast China under different nitrogen fertilizers. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 54(17): 3680–3690. (in Chinese)
Yin Minhua, Li Yuannong, Chen Pengpeng et al., 2018. Effect of no-tillage on maize yield in northern region of China—a metaanalysis. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 51(5): 843–854. (in Chinese)
Zhai Yangyang, Cheng Yunxiang, Chang Shenghua et al., 2015. Mechanism of greenhouse gas emission from agro-ecosystem soil in arid regions. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 31(9): 231–236. (in Chinese)
Zhang Guo, Wang Xiaoke, 2020. Impacts of conservation tillage on greenhouse gas emissions from cropland in China: A review. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 39(4): 872–881. (in Chinese)
Zhang Ran, Zhao Xin, Pu Chao et al., 2015. Meta-analysis on effects of residue retention on soil N2O emissions and influence factors in China. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 31(22): 1–6. (in Chinese)
Zhang Z S, Chen J, Liu T Q et al., 2016. Effects of nitrogen fertilizer sources and tillage practices on greenhouse gas emissions in paddy fields of central China. Atmospheric Environment, 144: 274–281. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2016.09.003
Zhou Yanhui, Zhu Xinkai, Guo Wenshan et al., 2019. Meta-analysis of the Response of Wheat Yield and Yield Components to Straw Returning in China. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences, 33(1): 129–137. (in Chinese)
Zhu G B, Wang X M, Wang S Y et al., 2022. Towards a more labor-saving way in microbial ammonium oxidation: a review on complete ammonia oxidization (comammox). Science of the Total Environment, 829: 154590. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.154590
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Foundation item: Under the auspices of the National Key Research and Development Program of China (No. 2018YFD0300708-4), College Students’ Innovative Entrepreneurial Training (No. 202210476024)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yan, G., Wang, J., Luo, T. et al. A Meta-analysis of No-tillage Effects on Greenhouse Gas Emissions from Wheat-based Rotation Cropping Agroecosystem in China. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 33, 503–511 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11769-023-1356-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11769-023-1356-y