Abstract
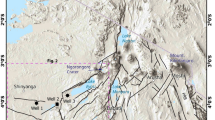
In the present work, 15 400 yr old geochemical records of a core from the subalpine Daping swamp are presented with the aim to examine the relationship between the chemical weathering and the climatic changes in the region of the western Nanling Mountains, China. The climate of the study region was deeply controlled by the East Asian summer monsoon. The results indicate that, in the past 15 400 yrs, the values of chemical index of alteration (CIA) ranged from 73.9% to 88.2% (mean: 85.3%), suggested a medium and high intensity of chemical weathering. The local exogenous clastic materials, which were derived from the weathered residues, played a key role in contributing towards the sediments. Since the climate-induced chemical weathering exerted strong influences on the geochemical features of weathered residues, the geochemical characteristics of the sediments were deeply impacted by climatic conditions. Wetter and warmer conditions would favor increased chemical weathering, resulting in more leaching of soluble and mobile elements (e.g., Ba and Sr) and leaving the resistant and immobile elements (e.g., Al and Ti) enriched in the weathered residues. These materials were then eroded and transported into the lake, and led to the sediments characterized by the characteristic of having depleted soluble elements. In contrast, dry and cold conditions would result in an opposite trend. In this sense, the geochemical records can serve as proxies to indicate changes of chemical weathering intensity, which were closely related to the evolution of summer monsoon.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aggarwal P K, Fröhlich K, Kulkarni K M et al., 2004. Stable isotope evidence for moisture sources in the Asian summer monsoon under present and past climate regimes. Geophysical Research Letters, 31(8): L08203. doi: https://doi.org/10.1029/2004GL019911
Babeesh C, Lone A, Achyuthan H, 2017. Geochemistry of Manasbal lake sediments, Kashmir: weathering, provenance and tectonic setting. Journal of the Geological Society of India, 89(5): 563–572. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-017-0645-4
Berger A, Loutre M F, 1991. Insolation values for the climate of the last 10 million years. Quaternary Science Reviews, 10(4): 297–317. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/0277-3791(91)90033-Q
Boës X, Rydberg J, Martinez-Cortizas A et al., 2011. Evaluation of conservative lithogenic elements (Ti, Zr, Al, and Rb) to study anthropogenic element enrichments in lake sediments. Journal of Paleolimnology, 46(1): 75–87. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10933-011-9515-z
Chen F H, Xu Q H, Chen J H et al., 2015. East Asian summer monsoon precipitation variability since the last deglaciation. Scientific Reports, 5(1): 11186. doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/srep11186
Chen J A, Wan G J, Tang D G, 2000. Recent climate changes recorded by sediment grain sizes and isotopes in Erhai Lake. Progress in Natural Science, 10(1): 54–61.
Chen J A, Wan G J, Zhang D D et al., 2005. The ‘little ice age’ recorded by sediment chemistry in Lake Erhai, southwest China. The Holocene, 15(6): 925–931. doi: https://doi.org/10.1191/0959683605hl863rr
Davison W, 1993. Iron and manganese in lakes. Earth-Science Reviews, 34(2): 119–163. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/0012-8252(93)90029-7
Degeai J P, Villa V, Chaussé C et al., 2018. Chemical weathering of palaeosols from the Lower Palaeolithic site of Valle Giumentina, central Italy. Quaternary Science Reviews, 183: 88–109. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.quascirev.2018.01.014
Dykoski C A, Edwards R L, Cheng H et al., 2005. A high-resolution, absolute-dated Holocene and deglacial Asian monsoon record from Dongge Cave, China. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 233(1–2): 71–86. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2005.01.036
Fan J W, Xiao J L, Wen R L et al., 2017. Carbon and nitrogen signatures of sedimentary organic matter from dali lake in inner mongolia: implications for holocene hydrological and ecological variations in the east asian summer monsoon margin. Quaternary International, 452: 65–78. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.quaint.2016.09.050
Fedo C M, Wayne Nesbitt H, Young G M, 1995. Unraveling the effects of potassium metasomatism in sedimentary rocks and paleosols, with implications for paleoweathering conditions and provenance. Geology, 23(10): 921–924. doi: https://doi.org/10.1130/0091-7613(1995)023<0921:UTEOPM>2.3.CO;2
Fleitmann D, Burns S J, Mudelsee M et al., 2003. Holocene forcing of the Indian monsoon recorded in a stalagmite from southern Oman. Science, 300(5626): 1737–1739. doi: https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1083130
Gao Y X, Xu S Y, Guo Q Y et al., 1962. Monsoon region and regional climate in China. In: Gao Y et al. (ed). Some Problems of East Asian Monsoon. Beijing: Science Press, 49–63. (in Chinese)
Gislason S R, Oelkers E H, Eiriksdottir E S et al., 2009. Direct evidence of the feedback between climate and weathering. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 277(1–2): 213–222. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2008.10.018
Haberyan K A, Hecky R E, 1987. The late Pleistocene and Holocene stratigraphy and paleolimnology of Lakes Kivu and Tanganyika. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 61: 169–197. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/0031-0182(87)90048-4
Hartmann J, Moosdorf N, 2011. Chemical weathering rates of silicate-dominated lithological classes and associated liberation rates of phosphorus on the Japanese Archipelago—Implications for global scale analysis. Chemical Geology, 287(3–4): 125–157. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2010.12.004
Heinrich H, 1988. Origin and consequences of cyclic ice rafting in the northeast Atlantic Ocean during the past 130 000 years. Quaternary Research, 29(2): 142–152. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/0033-5894(88)90057-9
Jin Z D, Wang S M, Shen J et al., 2001a. Weak chemical weathering during the Little Ice Age recorded by lake sediments. Science in China Series D: Earth Sciences, 44(7): 652–658. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02875338
Jin Z D, Wang S M, Shen J et al., 2001b. Chemical weathering since the Little Ice Age recorded in lake sediments: a high-resolution proxy of past climate. Earth Surface Processes and Landforms, 26(7): 775–782. doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/esp.224
Jin Z D, Li F C, Cao J J et al., 2006. Geochemistry of Daihai Lake sediments, Inner Mongolia, North China: implications for provenance, sedimentary sorting, and catchment weathering. Geomorphology, 80(3–4): 147–163. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2006.02.006
Li C, Yang S Y, 2010. Is chemical index of alteration (CIA) a reliable proxy for chemical weathering in global drainage basins? American Journal of Science, 310(2): 111–127. doi: https://doi.org/10.2475/02.2010.03
Li J R, Liu S F, Shi X F et al., 2021. Applicability and variability of chemical weathering indicators and their monsoon-controlled mechanisms in the Bay of Bengal. Frontiers in Earth Science, 9: 633713. doi: https://doi.org/10.3389/feart.2021.633713
Li X Z, Liu X D, Qiu L J et al., 2013. Transient simulation of orbital-scale precipitation variation in monsoonal East Asia and arid central Asia during the last 150 ka. Journal of Geophysical Research:Atmospheres, 118(14): 7481–7488. doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/jgrd.50611
Liu J, Zhong J, Chen S et al., 2021. Hydrological and biogeochemical controls on temporal variations of dissolved carbon and solutes in a karst river, South China. Environmental Sciences Europe, 33(1): 53. doi: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12302-021-00495-x
Liu S F, Li J R, Zhang H et al., 2020. Complex response of weathering intensity registered in the Andaman Sea sediments to the Indian Summer Monsoon over the last 40 kyr. Marine Geology, 426: 106206. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.margeo.2020.106206
Machlus M L, Ramezani J, Bowring S A et al., 2015. A strategy for cross-calibrating U-Pb chronology and astrochronology of sedimentary sequences: an example from the Green River Formation, Wyoming, USA. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 413: 70–78. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2014.12.009
Mackereth F J H, 1966. Some chemical observations on post-glacial lake sediments. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. Series B, Biological Sciences, 250(765): 165–213. doi: https://doi.org/10.2307/2416701
Miriyala P, Sukumaran N P, Nath B N et al., 2017. Increased chemical weathering during the deglacial to mid-Holocene summer monsoon intensification. Scientific Reports, 7(1): 44310. doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/srep44310
Nesbitt H W, Young G M, 1982. Early proterozoic climates and plate motions inferred from major element chemistry of lutites. Nature, 299(5885): 715–717. doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/299715a0
Nesbitt H W, Young G M, 1989. Formation and diagenesis of weathering profiles. The Journal of Geology, 97(2): 129–147. doi: https://doi.org/10.1086/629290
Pan J Y, Zhong W, Wei Z Q et al., 2020. A 15, 400-year record of natural and anthropogenic input of mercury (Hg) in a subalpine lacustrine sediment succession from the western Nanling Mountains, South China. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 27(16): 20478–20489. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-08421-z
Peng Y J, Xiao J L, Nakamura T et al., 2005. Holocene East Asian monsoonal precipitation pattern revealed by grain-size distribution of core sediments of Daihai Lake in Inner Mongolia of north-central China. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 233(3–4): 467–479. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2005.02.022
Qian W H, Lin X, Zhu Y F et al., 2007. Climatic regime shift and decadal anomalous events in China. Climatic Change, 84(2): 167–189. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10584-006-9234-z
Rao Z G, Chen F H, Zhang X et al., 2012. Spatial and temporal variations of C3/C4 relative abundance in global terrestrial ecosystem since the Last Glacial and its possible driving mechanisms. Chinese Science Bulletin, 57(31): 4024–4035. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-012-5233-9
Rao Z G, Guo W K, Cao J T et al., 2017. Relationship between the stable carbon isotopic composition of modern plants and surface soils and climate: a global review. Earth-Science Reviews, 165: 110–119. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earscirev.2016.12.007
Reimer P J, Austin W E N, Bard E et al., 2020. The IntCal20 Northern Hemisphere radiocarbon age calibration curve (0–55 cal kBP). Radiocarbon, 62(4): 725–757. doi: https://doi.org/10.1017/RDC.2020.41
Shen J, Yang L Y, Yang X D et al., 2005. Lake sediment records on climate change and human activities since the Holocene in Erhai catchment, Yunnan Province, China. Science in China Series D:Earth Sciences, 48(3): 353–363. doi: https://doi.org/10.1360/03yd0118
Stanford J D, Rohling E J, Bacon S et al., 2011. A new concept for the paleoceanographic evolution of Heinrich event 1 in the North Atlantic. Quaternary Science Reviews, 30(9–10): 1047–1066. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.quascirev.2011.02.003
Sun Q L, Wang S M, Zhou J et al., 2010. Sediment geochemistry of Lake Daihai, north-central China: implications for catchment weathering and climate change during the Holocene. Journal of Paleolimnology, 43(1): 75–87. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10933-009-9315-x
Wang Chunlong, Liu Sha, Wu Jing et al., 2013. Ore-forming element distribution around the southwestern domain of the Miaoershan-Yuechengling complex in the northeastern Guangxi and its geological implication. Geochimica, 42(5): 405–413. (in Chinese)
Wang P, Du Y S, Yu W C et al., 2020. The chemical index of alteration (CIA) as a proxy for climate change during glacial-interglacial transitions in Earth history. Earth-Science Reviews, 201: 103032. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earscirev.2019.103032
Wang Shaowu, 2011. The Holocene Climate Change. Beijing: China Meteorological Press, 114–116. (in Chinese)
Wang X J, Zhong W, Li T H et al., 2021. A 16.2-kyr lacustrine sediment record of mercury deposition in Dahu Swamp, eastern Nanling Mountains, southern China: analysis of implications for climatic changes. Quaternary International, 592: 12–21. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.quaint.2021.04.013
Wang X S, Chu G Q, Sheng M et al., 2016. Millennial-scale Asian summer monsoon variations in South China since the last deglaciation. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 451: 22–30. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2016.07.006
Wang Y J, Cheng H, Edwards R L et al., 2001. A high-resolution absolute-dated late Pleistocene monsoon record from Hulu Cave, China. Science, 294(5550): 2345–2348. doi: https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1064618
Wang Y J, Cheng H, Edwards R L et al., 2005. The Holocene Asian monsoon: links to solar changes and North Atlantic climate. Science, 308(5723): 854–857. doi: https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1106296
Wei Z Q, Zhong W, Xue J B et al., 2020. Late Quaternary East Asian summer monsoon variability deduced from lacustrine mineral magnetic records of Dahu Swamp, southern China. Paleoceanography and Paleoclimatology, 35(2): e2019PA003796. doi: https://doi.org/10.1029/2019PA003796
White A F, Blum A E, 1995. Effects of climate on chemical weathering in watersheds. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 59(9): 1729–1747. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/0016-7037(95)00078-E
White A F, Brantley S L, 2003. The effect of time on the weathering of silicate minerals: why do weathering rates differ in the laboratory and field?. Chemical Geology, 202(3–4): 479–506. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2003.03.001
Wu Xudong, Shen Ji, Wang Yong, 2011. The Holocene climate linkage between low latitude area and North Atlantic: case study on element and element ratios of Huguangyan Maar lake. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 29(5): 926–934. (in Chinese)
Wu Zhengyi, 1980. Vegetation of China. Beijing: Science Press, 825 (in Chinese)
Xiao J Y, Lü H B, Zhou W J et al., 2007. Evolution of vegetation and climate since the last glacial maximum recorded at Dahu peat site, South China. Science in China Series D:Earth Sciences, 50(8): 1209–1217. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11430-007-0068-y
Xu H, Liu B, Wu F, 2010. Spatial and temporal variations of Rb/Sr ratios of the bulk surface sediments in Lake Qinghai. Geochemical Transactions, 11(1): 3. doi: https://doi.org/10.1186/1467-4866-11-3
Xue Jibin, Zhong Wei, Zheng Yanming et al., 2009. A new high-resolution Late Glacial-Holocene climatic record from eastern Nanling Mountains in South China. Chinese Geographical Science, 19(3): 274–282. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11769-009-0274-y
Xue J B, Zhong W, Cao J Y, 2014. Changes in C3 and C4 plant abundances reflect climate changes from 41, 000 to 10, 000 yr ago in northern Leizhou Peninsula, South China. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 396: 173–182. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.palaeo.2014.01.003
Yancheva G, Nowaczyk N R, Mingram J et al., 2007. Influence of the intertropical convergence zone on the East Asian monsoon. Nature, 445(7123): 74–77. doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature05431
Yang S Y, Li C X, Cai J G, 2006. Geochemical compositions of core sediments in eastern China: implication for Late Cenozoic palaeoenvironmental changes. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 229(4): 287–302. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.palaeo.2005.06.026
Yeloff D, Bennett K D, Blaauw M et al., 2006. High precision 14C dating of Holocene peat deposits: a comparison of Bayesian calibration and wiggle-matching approaches. Quaternary Geochronology, 1(3): 222–235. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.quageo.2006.08.003
Zhao K, Wang Y J, Edwards R L et al., 2016. Contribution of ENSO variability to the East Asian summer monsoon in the late Holocene. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 449: 510–519. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.palaeo.2016.02.044
Zhong W, Cao J Y, Xue J B et al., 2015a. A 15, 400-year record of climate variation from a subalpine lacustrine sedimentary sequence in the western Nanling Mountains in South China. Quaternary Research, 84(2): 246–254. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yqres.2015.06.002
Zhong W, Cao J Y, Xue J B et al., 2015b. Last deglacial and Holocene vegetation evolution and climate variability in the subalpine western Nanling Mountains in South China. The Holocene, 25(8): 1330–1340. doi: https://doi.org/10.1177/0959683615584206
Zhong W, Wei Z Q, Chen Y et al., 2017. A 15.4-ka paleoclimate record inferred from δ13C and δ15N of organic matter in sediments from the sub-alpine Daping Swamp, western Nanling Mountains, South China. Journal of Paleolimnology, 57(2): 127–139. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10933-016-9935-x
Zhou W J, Yu X F, Jull A J T et al., 2004. High-resolution evidence from southern China of an early holocene optimum and a mid-Holocene dry event during the past 18, 000 years. Quaternary Research, 62(1): 39–48. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yqres.2004.05.004
Zhu J C, Wang R C, Zhang P H et al., 2009. Zircon U-Pb geochronological framework of Qitianling granite batholith, middle part of Nanling Range, South China. Science in China Series D: Earth Sciences, 52(9): 1279–1294. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11430-009-0154-4
Acknowledgement
Measurement of conventional 14C dates was carried out at the Key Lab of Western China’s Environmental Systems (Ministry of Education of China), Lanzhou University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: Under the auspices of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41971101, 41571187, 41071137)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, B., Zhong, W., Zhu, C. et al. Geochemistry of Sediments from a Subalpine Lake Sedimentary Succession in the Western Nanling Mountains, Southern China: Implications for Catchment Weathering During the Last 15 400 Years. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 32, 537–548 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11769-022-1282-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11769-022-1282-4