Abstract
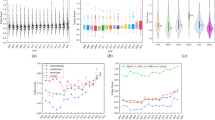
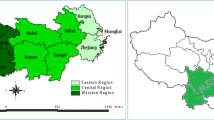
In this study, we developed an evaluation index system for green total-factor water-use efficiency (GTFWUE) which reflected both economic and green efficiencies of water resource utilization. Then we measured the GTFWUE of 30 provinces/municipalities/autonomous regions (hereafter provinces) in China (not including Tibet, Hong Kong, Macao, Taiwan as no data) from 2000 to 2018 using a minimum distance to the strong frontier model that contained an undesirable output. We further analyzed the regional differences and spatial correlations of GTFWUE using these values based on Global and Local Moran’s I statistics, and empirically determined the factors affecting GTFWUE using a spatial econometric model. The evaluation results revealed that the GTFWUE differed substantially between the regions. The provinces with high and low GTFWUE values were located in the coastal and inland areas of China, respectively. The eastern region had a significantly higher GTFWUE than the central and western regions. The GTFWUEs for all three regions (eastern, central, and western regions) decreased slowly from 2000 to 2011 (except 2005), remained stable from 2012 to 2016, and rapidly increased in 2017 before decreasing again in 2018. We found significant spatial correlations between the provincial GTFWUEs. The GTFWUE for most provinces belonged to the high-high or low-low cluster region, revealing a significant spatial clustering effect of provincial GTFWUEs. We also found that China’s GTFWUE was highly promoted by economic growth, population size, opening-up level, and urbanization level, and was evidently hindered by water endowment, technological progress, and government influence. However, the water-use structure had little impact on GTFWUE. This study fully demonstrated that the water use mode would be improved, and water resources needed to be used more efficiently and green in China. Moreover, based on the findings of this study, several policy recommendations were proposed from the aspects of cross-regional cooperation, economy, society, and institution.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acemoglu D, Aghion P, Bursztyn L et al., 2012. The environment and directed technical change. American Economic Review, 102(1): 131–166. doi: https://doi.org/10.1093/oxrep/gru031
Anselin L, 1988. Spatial Econometrics: Methods and Models. Dordrecht: Springer Science.
Anselin L, Getis A, 1992. Spatial statistical analysis and geographic information systems. The Annals of Regional Science, 26(1): 19–33. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01581478
Anselin L, Syabri I, Kho Y, 2010. GeoDa: An Introduction to Spatial Data Analysis: Handbook of Applied Spatial Analysis. Berlin: Springer, 73–89.
Azad A S, Ancev T, Hernández-Sancho F, 2015. Efficient water use for sustainable irrigation industry. Water Resources Management, 29(5): 1683–1696. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-014-0904-8
Bryan B A, Gao L, Ye Y et al., 2018. China’s response to a national land-system sustainability emergency. Nature, 559(7713): 193–204. doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-018-0280-2
Cao X C, Ren J, Wu M Y et al., 2018. Effective use rate of generalized water resources assessment and to improve agricultural water use efficiency evaluation index system. Ecological Indicators, 86: 58–66. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2017.12.016
Chen Q, Ai H S, Zhang Y B et al., 2019. Marketization and water resource utilization efficiency in China. Sustainable Computing: Informatics and Systems, 22: 32–13. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.suscom.2019.01.018
Chen S J, Cao Y Y, Li J, 2021. The effect of water rights trading policy on water resource utilization efficiency: evidence from a quasi-natural experiment in China. Sustainability, 13(9): 5281. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/su13095281
Chemak F, Boussemart J P, Jacquet F, 2010. Farming system performance and water use efficiency in the Tunisian semi — arid region: data envelopment analysis approach. International Transactions in Operational Research, 17(3): 381–396. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1475-3995.2009.00736.x
Deason J P, Schad T M, Sherk G W, 2001. Water policy in the United States: a perspective. Water Policy, 3(3): 175–192. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/S1366-7017(01)00011-3
Deng G Y, Li L, Song Y N, 2016. Provincial water use efficiency measurement and factor analysis in China: based on SBM-DEA model. Ecological Indicators, 69: 12–18. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2016.03.052
Ding X L, Fu Z, Jia H W, 2019. Study on urbanization level, urban primacy and industrial water utilization efficiency in the Yangtze River Economic Belt. Sustainability, 11(23): 6571. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/su11236571 au_Ding Xuhui, He Juhua, Wang Liuyuan, 2018. Inter-provincial water resources utilization efficiency and its driving factors considering undesirable outputs: based on SE-SBM and Tobit model. China Population, Resources and Environment, 28(1): 157–164. (in Chinese)
Dong H J, Geng Y, Fujita T et al., 2014. Uncovering regional disparity of China’s water footprint and inter-provincial virtual water flows. Science of the total environment, 500–501: 120–130. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.08.094
Elhorst J P, 2010. Spatial panel data models. In: Fischer M M and Getis A (eds.). Handbook of Applied Spatial Analysis: Software Tools, Methods and Applications. Berlin: Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 377–407.
Fischer M M, Getis A, 2009. Handbook of Applied Spatial Analysis: Software Tools, Methods and Applications. Berlin: Springer.
Fujii H, Managi S, Kaneko S, 2013. Decomposition analysis of air pollution abatement in China: empirical study for ten industrial sectors from 1998 to 2009. Journal of Cleaner Production, 59: 22–31. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2013.06.059
Gao L, Bryan B A, 2017. Finding pathways to national-scale land-sector sustainability. Nature, 544(7649): 217–222. doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature21694
Geng Q L, Ren Q, Nolan R H et al., 2019. China’s agricultural water use efficiency in a green-blue water perspective: a study based on data envelopment analysis. Ecological Indicators, 86: 58–66. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2018.09.011
Guo Zheng, Sophia Shuang Chen, Yao Shimou et al., 2021. Does foreign direct investment affect SO2 emissions in the Yangtze River Delta? A spatial econometric analysis. Chinese Geographical Science, 31(3): 400–412. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11769-021-1197-5
Haining R, 1993. Spatial Data Analysis in the Social and Environmental Sciences. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Hu J L, Wang S C, Yeh F Y, 2006. Total-factor water efficiency of regions in China. Resources Policy, 31(4): 217–230. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resourpol.2007.02.001
Jahanshahloo G R, Vakili J, Zarepisheh M, 2012. A linear bilevel programming problem for obtaining the closest targets and minimum distance of a unit from the strong efficient frontier. Asia-Pacific Journal of Operational Research, 29(2): 1250011. doi: https://doi.org/10.1142/S021759591250011X
Jefferson G H, Bai H M, Guan X J, 2006. R&D performance in Chinese industry. Economics of Innovation New Technology, 15(4–5): 345–366. doi: https://doi.org/10.1080/10438590500512851
Kaneko S, Tanaka K, Toyota T et al., 2004. Water efficiency of agricultural production in China: regional comparison from 1999 to 2002. International Journal of Agricultural Resources, Governance and Ecology (IJARGE), 3(3–4): 231–251. doi: https://doi.org/10.1504/IJARGE.2004.006038
Kurle D, Thiede S, Herrmann C, 2015. A tool-supported approach towards water efficiency in manufacturing. Procedia Cirp, 28: 34–39. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procir.2015.04.007
Li K, Lin B Q, 2015. Measuring green productivity growth of Chinese industrial sectors during 1998–2011. China Economic Review, 36: 279–295. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chieco.2015.09.008
Liang Jingxi, Zhang Ankang, Li Caifeng, 2018. An empirical study on agriculture irrigation water use efficiency based on weight constraints DEA and Tobit model—a case study of Heilongjiang Province. Water Saving Irrigation, (4): 62–68. (in Chinese)
Liu K D, Yang G L, Yang D G, 2020. Industrial water-use efficiency in China: regional heterogeneity and incentives identification. Journal of Cleaner Production, 258: 120828. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.120828
Ma H L, Shi C L, Chou N T, 2016. China’s water utilization efficiency: an analysis with environmental considerations. Sustainability, 8(6): 516. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/su8060516
Mei K, Liao L L, Zhu Y L et al., 2014. Evaluation of spatial-temporal variations and trends in surface water quality across a rural-suburban-urban interface. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 21(13): 8036–8051. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-2716-z
Mielnik O, Goldemberg J, 2002. Foreign direct investment and decoupling between energy and gross domestic product in developing countries. Energy Policy, 30(2): 87–89. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0301-4215(01)00080-5
Molinos-Senante M, Maziotis A, Sala-Garrido R, 2014. The Luenberger productivity indicator in the water industry: an empirical analysis for England and Wales. Utilities Policy, 30: 18–28. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jup.2014.07.001
Moran P A P, 1948. The interpretation of statistical maps. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society: Series B (Methodological), 10(2): 243–251. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.2517-6161.1948.tb00012.x
Moran P A P, 1950. Notes on continuous stochastic phenomena. Biometrika, 37(1–2): 17–23. doi: https://doi.org/10.2307/2332142
National Bureau of Statistics of China (NBSC), 2019. China Statistical Yearbook. Beijing: China Statistics Press. (in Chinese)
National Bureau of Statistics of China (NBSC), 2001a–2019a. China Statistical Yearbook. Beijing: China Statistics Press. (in Chinese)
National Bureau of Statistics of China (NBSC), 2001b–2019b. China Statistical Yearbook on Science and Technology. Beijing: China Statistics Press. (in Chinese)
National Bureau of Statistics of China (NBSC), 2001c–2019c. China Population and Employment Statistics Yearbook. Beijing: China Statistics Press. (in Chinese)
National Bureau of Statistics of China (NBSC), Ministry of Ecology and Environment (MEE), 2001–2019. China Statistics Yearbook on Environment. Beijing: China Statistics Press. (in Chinese)
Njiraini G W, Guthiga P M, 2013. Are small-scale irrigators water use efficient? Evidence from Lake Naivasha Basin, Kenya. Environmental Management, 52(5): 1192–1201. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00267-013-0146-1
Qi Q, Song S B, 2020. Measurement and influencing factors of industrial water resource utilization efficiency in Yangtze River Economic Belt. International Journal of Design & Nature and Ecodynamics, 15(5): 653–658. doi: https://doi.org/10.18280/ijdne.150506
Qian Wenjing, He Canfei, 2011. China’s regional difference of water resource use efficiency and influencing factors. China Population, Resources and Environment, 21(2): 54–60. (in Chinese)
Sahin O, Stewart R A, Helfer F, 2015. Bridging the water supply-demand gap in Australia: coupling water demand efficiency with rain-independent desalination supply. Water Resources Management, 29(2): 253–272. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-014-0794-9 au_Shan Haojie, 2008. Re-estimating the capital stock of China: 1952–2006. The Journal of Quantitative & Technical Economics, 25(10): 17–31. (in Chinese)
Shi Tiange, Zhang Xiaole, Du Hongru et al., 2015. Urban water resource utilization efficiency in China. Chinese Geographical Science, 25(6): 684–697. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11769-015-0773-y
Song M L, Wang R, Zeng X Q, 2018. Water resources utilization efficiency and influence factors under environmental restrictions. Journal of Cleaner Production, 184: 611–621. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.02.259
Sun Caizhi, Ma Qifei, Zhao Liangshi, 2020. Analysis of driving mechanism based on a GWR model of green efficiency of water resources in China. Acta Geographica Sinica, 75(5): 1022–1035. (in Chinese)
Sun C Z, Zhao L S, Zou W et al., 2014a. Water resource utilization efficiency and spatial spillover effects in China. Journal of Geographical Sciences, 24(5): 771–788. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11442-014-1119-x
Sun Caizhi, Zhao Liangshi, Zou Wei, 2014b. The interprovincial water resources global environmental technology efficiency measurement in China and its spatial effect. Journal of Natural Resources, 29(4): 553–563. (in Chinese)
Tone K, 2001. A slacks-based measure of efficiency in data envelopment analysis. European journal of operational research, 130(3): 498–509. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0377-2217(99)00407-5
Wang F T, Yu C, Xiong L C et al., 2019. How can agricultural water use efficiency be promoted in China? A spatial-temporal analysis. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 145: 411–418. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2019.03.017
Wang G F, Chen J C, Wu F et al., 2015. An integrated analysis of agricultural water-use efficiency: a case study in the Heihe River Basin in Northwest China. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth, Parts A/B/C, 89–90: 3–9. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pce.2015.10.009
Wang L, Chen Z C, Ma D L et al., 2013. Measuring carbon emissions performance in 123 Countries: application of minimum distance to the strong efficiency frontier analysis. Sustainability, 5(12): 5319–5332. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/su5125319
Wang M Q, Huang Y, Li D, 2021. Assessing the performance of industrial water resource utilization systems in China based on a two-stage DEA approach with game cross efficiency. Journal of Cleaner Production, 312: 127722. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.127722
Wang W P, Gao L, Liu P et al., 2014. Relationships between regional economic sectors and water use in a water-scarce area in China: a quantitative analysis. Journal of Hydrology, 515: 180–190. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2014.04.057
Wang Y S, Bian Y W, Xu H, 2015. Water use efficiency and related pollutants’ abatement costs of regional industrial systems in China: a slacks-based measure approach. Journal of Cleaner Production, 101: 301–310. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2015.03.092
Wei J, Zhang H Q, Liu S S et al., 2019. Technological innovation, environmental regulation, and green total factor efficiency of industrial water resources. Journal of Cleaner Production, 211: 61–69. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.11.172
Wibowo A, Alfen H W, 2015. Benchmarking the efficiencies of Indonesia’s municipal water utilities using Stackelberg data envelopment analysis. Benchmarking: An International Journal, 22(4): 588–609. doi: https://doi.org/10.1108/BIJ-01-2014-0009
Wolfe J R, Goldstein R A, Maulbetsch J S et al., 2009. An electric power industry perspective on water use efficiency. Journal of Contemporary Water Research & Education, 143(1): 30–34. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1936-704X.2009.00062.x
Xie H L, Chen Q R, Lu F C et al., 2019. Spatial-temporal disparities and influencing factors of total-factor green use efficiency of industrial land in China. Journal of Cleaner Production, 207: 1047–1058. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.10.087
Xu S C, Liang H, 2020. Study of the utilization efficiency and its influencing factors of water resources in Yangtze River Economic Belt. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 1549: 022017. doi: https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1549/2/022017
Yao X L, Feng W, Zhang X L et al., 2018. Measurement and decomposition of industrial green total factor water efficiency in China. Journal of Cleaner Production, 198: 1144–1156. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.07.138
Yang F, Wang D W, Zhao L L et al., 2021. Efficiency evaluation for regional industrial water use and wastewater treatment systems in China: a dynamic interactive network slacks-based measure model. Journal of Environmental Management, 279: 111721. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.111721
Yang G M, Zhang F T, Zhang F et al., 2021. Spatiotemporal changes in efficiency and influencing factors of China’s industrial carbon emissions. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 28: 36288–36302. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-13003-8
Yang J, Liu X J, Ying L M et al., 2019. Correlation analysis of environmental treatment, sewage treatment and water supply efficiency in China. Science of The Total Environment, 708(1): 135128. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.135128
Yang Jiangmin, Tan Yiming, Xue Desheng et al., 2021. The environmental impacts of informal economies in China: inverted U-shaped relationship and regional variances. Chinese Geographical Science, 31(4): 585–599. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11769-021-1210-z
Yang Yang, Jiang Shubin, 2016. Irrigation water efficiency evaluation of agricultural irrigation water efficiency based on DEA and Malmquist index. Ecological Economy, 32(5): 147–151. (in Chinese)
Zeng P H, Wei X C, 2021. Measurement and convergence of transportation industry total factor energy efficiency in China. Alexandria Engineering Journal, 60(5): 4267–4274. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aej.2021.03.032
Zhang Lingling, Ding Xueli, Shen Ying et al., 2019. Spatial heterogeneity and influencing factors of agricultural water use efficiency in China. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, 28(4): 817–827. (in Chinese)
Zhang X L, Kong Y S, Ding X H, 2020. How high-quality urbanization affects utilization efficiency of agricultural water resources in the Yellow River Basin under double control action? Sustainability, 12(7): 2869. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/su12072869
Zhang Xiyue, Sun Fangcheng, Wang Huaizu, 2020. A study of the green efficiency of industrial water resource in Yangtze River Economic Zone based on the Two-stage evaluation of production and treatment. Journal of Jiangxi University of Finance and Economics, (2): 26–36. (in Chinese)
Zhao H P, Wang Z F, Chan T C et al., 2016. Design of regeneration recycling water networks by means of concentration potentials and a linear programming method. Journal of Cleaner Production, 112: 4667–4673. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2015.07.130
Zhao Jing, Ni Hongzhen, Chen Genfa, 2015. Evaluation on water use efficiency of water-intensive industries in China. Water Resources and Hydropower Engineering, 46(4): 11–15. (in Chinese)
Zhao L S, Sun C Z, Liu F C, 2017a. Interprovincial two-stage water resource utilization efficiency under environmental constraint and spatial spillover effects in China. Journal of Cleaner Production, 164: 715–725. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.06.252
Zhao Liangshi, Sun Caizhi, Liu Fengchao, 2017b. Two-tage utilization efficiency of the interprovincial water resources under environmental constraint and its influence factors in China. China Population, Resource and Environment, 27(5): 27–36. (in Chinese)
Zhao Xueyan, Wang Rong, Wang Xiaoqi et al., 2019. Spatiotemporal distribution and influencing factors of environmental pollution incidents based on multi-scales in China. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 39(9): 1361–1370. (in Chinese)
Zhou Liang, Zhou Chenhu, Yang Fan et al., 2017. Spatio-temporal evolution and the influencing factors of PM2.5 in China between 2000 and 2011. Acta Geographica Sinica, 72(11): 2079–2092. (in Chinese)
Zhou Z X, Wu H Q, Song P F, 2019. Measuring the resource and environmental effciency of industrial water consumption in China: a non-radial directional distance function. Journal of Cleaner Production, 240: 118169. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.118169
Zoebl D, 2006. Is water productivity a useful concept in agricultural water management? Agricultural Water Management, 84(3): 265–273. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2006.03.002
Zou D L, Cong H B, 2020. Evaluation and influencing factors of China’s industrial water resource utilization efficiency from the perspective of spatial effect. Alexandria Engineering Journal, 60(1): 173–182. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aej.2020.06.053
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Foundation item
Under the auspices of Chinese Ministry of Education Humanities and Social Sciences Project (No. 19YJCZH241), Project of Chongqing Social Science Planning Project of China (No. 2020QNGL38), Science and Technology Research Program of Chongqing Education Commission of China (No. KJQN201901143), Humanities and Social Sciences Research Program of Chongqing Education Commission of China (No. 20SKGH169)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, D., Zhang, F., Gao, L. et al. Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Green Total-factor Water-use Efficiency and Its Influencing Factors in China. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 31, 795–814 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11769-021-1227-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11769-021-1227-3