Abstract
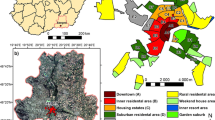
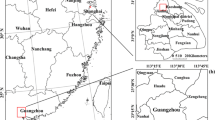
Multi-scale data have had a wide-ranging level of performance in the area of urban change monitoring. Herein we investigate the correlation between the impervious surface fraction (ISF) and the Defense Meteorological Satellite Program/Operational Linescan System (DMSP/OLS) nighttime stable light (NTL) data with respect to the urban expansion in the main districts of Guangzhou. Landsat 5 Thematic Mapper and Landsat 8 Operational Land Image (OLI) data from 1988 to 2015 were used to extract the ISF using the linear spectral mixture analysis model and normal difference build-up index at the sub-pixel scale. DMSP/OLS NTL data from 1992 to 2013 were calibrated to illustrate the urban nighttime light conditions at the regional scale. Urban expansion directions were identified by statistics and kernel density analysis for the ISF study area at the sub-pixel scale. In addition, the correlation between the ISF and DMSP/OLS NTL data were illustrated by linear regression analysis. Furthermore, Profile Graph in ArcGIS was employed to illustrate the urban expansion from the differences in correlation in different directions. The conclusions are as follows: 1) The impervious surface (IS) in the study area has expanded to the northeast and the east, starting with the old urban zones, and the high-density IS area has increased by 321.14 km2. 2) The linear regression analysis reveals a positive correlation between the ISF and the DMSP/OLS NTL data. The multi-scale data changes are consistent with the actual urban planning of Guangzhou. 3) The DMSP/OLS NTL data overestimate the urban extent because of its saturation and blooming effects, causing its correlation with ISF to decrease. The pattern of urban expansion influences the saturation and blooming effects of the DMSP/OLS NTL data.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brodley C E, 1995. Recursive automatic bias selection for classifier construction. Machine Learning, 20(1–2): 4–94. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/bf00993475
Chen Yunhao, Feng Tong, Shi Peijun et al., 2006. Classification of remot sensing image based on object oriented and class rules. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 31(4): 316–320. (in Chinese)
Deng C B, Wu C S, 2012. BCI: a biophysical composition index for remote sensing of urban environments. Remote Sensing of Environment, 127: 247–259. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2012.09.009
Elvidge C D, Tuttle B T, Sutton P S et al., 2007. Global distribution and density of constructed impervious surfaces. Sensors, 7(9): 1962–1979. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/s7091962
Fan F L, Fan W, Weng Q H, 2015. Improving urban impervious surface mapping by linear spectral mixture analysis and using spectral indices. Canadian Journal of Remote Sensing: Journal Canadien de Télédétection, 41(6): 577–586. doi: https://doi.org/10.1080/07038992.2015.1112730
Fang C L, Ma H T, Wang J, 2015. A regional categorization for ‘new-type urbanization’ in China. PLoS One, 10(8): e0134253. doi: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0134253
Fragkias M, Güneralp B, Seto K C et al., 2013. A synthesis of global urbanization projections. In: Assessment G A, (ed.) Urbanization, Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services: Challenges and Opportunities, Dordrecht: Springer, 409–435. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-007-7088-1_21
Fu H Y, Shao Z F, Fu P et al., 2017. The dynamic analysis between urban nighttime economy and urbanization using the DMSP/OLS nighttime light data in China from 1992 to 2012. Remote Sensing, 9(5): 416. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9050416
Gao Zhihong, Zhang Lu, Li Xinyan et al., 2010. Detection and analysis of urban land use changes through multi-temporal impervious surface mapping. Journal of Remote Sensing, 14(3): 593–606. (in Chinese)
Haase D, Nuissl H, 2010. The urban-to-rural gradient of land use change and impervious cover: a long-term trajectory for the city of Leipzig. Journal of Land Use Science, 5(2): 123–141. doi: https://doi.org/10.1080/1747423X.2010.481079
Letu H, Hara M, Yagi H et al., 2010. Estimating energy consumption from night-time DMPS/OLS imagery after correcting for saturation effects. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 31(16): 4443–4458. doi: https://doi.org/10.1080/01431160903277464
Li Deren, 2015. An overview on data mining of nighttime light remote sensing. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 44(6): 591–601. (in Chinese)
Li Xinyu, 2015. On the Urban Growth of Jiangsu Province from 1985–2014 Based on Impervious Surface Information from Remote Sensing Imagery. Nanjing: Nanjing University. (in Chinese)
Liu Z F, He C Y, Zhang Q F et al., 2012a. Extracting the dynamics of urban expansion in China using DMSP-OLS nighttime light data from 1992 to 2008. Landscape and Urban Planning, 106(1): 62–72. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landurbplan.2012.02.013
Liu Zhenhuan, Wang Yanglin, Peng Jian, et al., 2012b. Quatifying spatiotemporal patterns dynamics of impervious surface in Shenzhen. Geographical Research, 31(8): 1535–1545. (in Chinese)
Lu D S, Weng Q H, 2006. Use of impervious surface in urban land-use classification. Remote Sensing of Environment, 102(1–2): 4–160. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2006.02.010
Lu D S, Weng Q H, 2009. Extraction of urban impervious surfaces from an IKONOS image. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 30(5): 1297–1311. doi: https://doi.org/10.1080/01431160802508985
Pan Jinghu, Li Xiaoxue, Feng Zhaodong et al., 2010. Analysis of Spatial and Temporal Patterns of Impervious Surfaces and Vegetation Covers in Lanzhou Based on the V-I-AP Model. Resources Science, 32(3): 520–527. (in Chinese)
Ridd M K, 1995. Exploring a V-I-S (vegetation-impervious surface-soil) model for urban ecosystem analysis through remote sensing: comparative anatomy for cities. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 16(12): 2165–2185. doi: https://doi.org/10.1080/01431169508954549
Su Yongxian, 2015. Study on the Carbon Emissions from Energy Consumption in China Using DMSP/OLS Night Light Imageries. Guangzhou: Guangzhou Institute of Geochemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences. (in Chinese)
Wang Qinjun, Lin Qizhong, Li Mingxiao et al., 2009. Comparison of two spectral mixture analysis models. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 29(10): 2602–2605. (in Chinese)
Wang W, Yao X F, Ji M, 2016. Integrating seasonal optical and thermal infrared spectra to characterize urban impervious surfaces with extreme spectral complexity: a Shanghai case study. Journal of Applied Remote Sensing, 10(1): 016018. doi: https://doi.org/10.1117/1.jrs.10.016018
Wei Haiyang, Jing Changfeng, Du Mingyi, 2015. Kernel density analysis of different scales for distributiontrend of urban. Urban Geotechnical Investigation & Surveying, (1): 18–20. (in Chinese)
Weng Q H, Lu D S, 2008. A sub-pixel analysis of urbanization effect on land surface temperature and its interplay with impervious surface and vegetation coverage in Indianapolis, United States. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation, 10(1): 68–83. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jag.2007.05.002
Wu C S, Murray A T, 2003. Estimating impervious surface distribution by spectral mixture analysis. Remote Sensing of Environment, 84(4): 493–505. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0034-4257(02)00136-0
Wu C S, 2004. Normalized spectral mixture analysis for monitoring urban composition using ETM + imagery. Remote Sensing of Environment, 93(4): 480–492. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2004.08.003
Xie Y H, Weng Q H, 2016. Updating urban extents with nighttime light imagery by using an object-based thresholding method. Remote Sensing of Environment, 187: 1–13. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2016.10.002
Xie Y H, Weng Q H, 2017. Spatiotemporally enhancing time- series DMSP/OLS nighttime light imagery for assessing large-scale urban dynamics. Isprs Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 128: 1–15. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2017.03.003
Xin X, Liu B, Di K et al, 2017. Monitoring urban expansion using time series of night-time light data: a case study in Wuhan, China. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 38(21): 6110–6128. doi: https://doi.org/10.1080/01431161.2017.1312623
Xu Hanqiu, 2005. A study on information extraction of water body with the modified normalized difference water index (MNDWI). Journal of Remote Sensing, 9(5): 589–595. (in Chinese)
Xu Hanqiu, 2008. A new remote sensing index for fastly extracting impervious surface information. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 33(11): 1150–1153. (in Chinese)
Xu Hanqiu, 2009. Quantitative analysis on the relationship of urban impervious surface with other components of the urban ecosystem. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 29(5): 2456–2462. (in Chinese)
Xu H Q, 2010. Analysis of impervious surface and its impact on urban heat environment using the normalized difference impervious surface index (NDISI). Photogrammetric Engineering & Remote Sensing, 76(5): 557–565. doi: https://doi.org/10.14358/pers.76.5.557
Xu Hanqiu, Wang Meiya, 2016. Remote sensing-based retrieval of ground impervious surfaces. Journal of Remote Sensing, 20(5): 1270–1289. (in Chinese)
Xu J H, Zhao Y, Zhong K W et al., 2016. Coupling modified linear spectral mixture analysis and soil conservation service curve number (SCS-CN) models to simulate surface runoff: application to the main urban area of Guangzhou, China. Water, 8(12): 550. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/w8120550
Xu R, Zhang H S, Lin H, 2017. Urban impervious surfaces estimation from optical and sar imagery: a comprehensive comparison. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 10(9): 4010–4021. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/JSTARS.2017.2706747
Yuan Linshan, Du Peijun, Zhang Huapeng et al., 2008. CBERS imagery classification based on decision tree and derformance analysis. Remote Sensing for Land & Resources, (2): 92–98. (in Chinese)
Zhang Xichuan, Zhao Yingshi, 1999. Application of line spectral mixture to rapid assessment of land degradation in semiarid area. Journal of Graduate School, Academia Sinica, 16(2): 169–176. (in Chinese)
Zhang H S, Lin H, Zhang Y et al., 2015. Remote Sensing of Impervious Surfaces in Tropical and Subtropical Areas. Boca Raton: CRC Press, 14–20.
Zhou Cunlin, Xu Hanqiu, 2007. A spectral mixture analysis and mapping of impervious surfaces in built-up land of Fuzhou city. Journal of Image and Graphics, 12(5): 875–881. (in Chinese)
Zhu Aili, Lv Chengwen, 2010. Advances in the methods of extracting urban impervious surface based on remote sensing. Journal of Anhui Normal University (Natural Science), 33(5): 485–489 (in Chinese)
Zhu H L, Ying L, Fu B L, 2013. Estimating impervious surfaces by linear spectral mixture analysis under semi-constrained condition. In: RSETE 2013. Atlantis Press, 357–360. doi: https://doi.org/10.2991/rsete.2013.87
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: Under the auspices of the Special Project of Science and Technology Development (No. 2017GDASCX-0101), the Science and Technology Planning Project of Guangdong Province (No. 2017A020217005, 2018B020207002), Guangdong Innovative and Entrepreneurial Research Team Program (No. 2016ZT06D336)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, Y., Zhong, K., Xu, J. et al. Directional Analysis of Urban Expansion Based on Sub-pixel and Regional Scale: A Case Study of Main Districts in Guangzhou, China. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 29, 652–666 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11769-019-1048-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11769-019-1048-9