Abstract
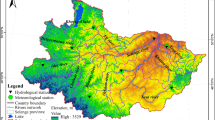
In the case of increasing fragmentation of wetlands, the study of the relationship between wetland landscape characteristics and total nitrogen (TN) in water is of great significance to reveal the mechanism of wetland water purification. Taking the Naoli River (NR) wetlands in Northeast China as the research object, 10 uniformly distributed sampling sites in the study area were sampled in August 2015 to test the TN concentration and interpret the images of NR wetlands in the same period. Taking the sampling site as the control point, the whole wetlands were divided into 10 regions, and the landscape index of each region was extracted. In order to reveal whether the landscape characteristics are related to the TN concentration in the wetlands water body, the landscape index and the TN concentration in the control point water body were analyzed by correlation analysis, step-by-step elimination analysis and path analysis to reveal whether the landscape characteristics are related to the TN concentration under wetlands receiving agricultural drainages. The results showed that the correlation coefficients between four area indexes or eight shape indexes and TN concentration did not reach a significant correlation level (P > 0.05), indicating that TN removal was not only determined by a single landscape index. The path coefficient of edge density (ED) index is −0.41, indicating that wetland patch connectivity is the primary factor of TN removal, and there is no relationship between the larger patch area and the higher TN removal. The removal of TN in wetlands is restricted by the synergistic effect of landscape area and shape characteristics.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Deane D C, Fordham D A, He F L et al., 2017. Future extinction risk of wetland plants is higher from individual patch loss than total area reduction. Biological Conservation, 209: 27–33. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocon.2017.02.005
Du L, Trinh X, Chen Q R et al., 2018. Effect of clinoptilolite on ammonia emissions in integrated vertical-flow constructed wetlands (IVCWs) treating swine wastewater. Ecological Engineering, 122: 153–158. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2018.07.037
Gao C Y, Zhang S Q, Liu H X et al., 2018. The impacts of land reclamation on the accumulation of key elements in wetland ecosystems in the Sanjiang Plain, Northeast China. Environmental Pollution, 237: 487–498. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2018.02.075
Guo Y D, Lu Y Z, Song Y Y et al., 2014. Concentration and characteristics of dissolved carbon in the Sanjiang Plain influenced by long-term land reclamation from marsh. Science of the Total Environment, 466–467: 777–787. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.07.076
Fan Y W, Li J, Men X Y et al., 2012. Preliminary description of diatom community and its relationship with water physico-chemical variables in Qixinghe Wetland. Chinese Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 30(3): 379–387. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00343-012-1108-9
Han Zhiwei, Zhang Shui, Wu Pan et al., 2017. Distribution characteristics of nitrogen and phosphorus in waters and release flux estimation in the sediment of Caohai basin, Guizhou. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 36(9): 2501–2506. (in Chinese)
Hille S, Andersen D K, Kronvang B et al., 2018. Structural and functional characteristics of buffer strip vegetation in an agricultural landscape — high potential for nutrient removal but low potential for plant biodiversity. Science of the Total Environment, 628–629: 805–814. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.02.117
Hu Zhifeng, Chen Aimin, Qiu Zhi et al., 2016. The effects of plant species and plant diversity on nitrogen removal in simulated vertical sub-surface flow constructed wetlands. Environmental Pollution and control, 38(3): 45–49. (in Chinese)
Jiang Ming, Lu Xianguo, Wang Hongqing et al., 2011. Transfer and transformation of soil iron and implications for hydrogeomorpholocial changes in Naoli river catchment, Sanjiang plain, northeast China. Chinese Geographical Science, 21(2): 149–158. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11769-011-0454-4
Jiao Sheng, Yang Na, Peng Kai et al., 2014. The effects of land-use and landscape pattern on water quality in Weihe river watershed. Geographical Research, 33(12): 2263–2274. (in Chinese)
Li Zhaofu, Liu Hongyu, Li Hengpeng, 2012. Impact on nitrogen and phosphorous export of wetlands in Tianmu lake watershed. Environmental Science, 33(11): 3753–3759. (in Chinese)
Liu Jiping, Dong Chunyue, Sheng Lianxi et al., 2016. Landscape pattern change of marsh and its response to human disturbance in the small Sanjiang Plain, 1955–2010. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 36(6): 879–887. (in Chinese)
Liu S, Ryu D, Webb J A et al., 2018. Characterisation of spatial variability in water quality in the Great Barrier Reef catchments using multivariate statistical analysis. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 137: 137–151. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2018.10.019
Liu X H, Dong G H, Wang X G et al., 2013. Characterizing the spatial pattern of marshlands in the Sanjiang Plain, Northeast China. Ecological Engineering, 53: 335–342. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2012.12.071
Miller K M, Mitchell B R, Mcgill B J, 2016. Constructing multimetric indices and testing ability of landscape metrics to assess condition of freshwater wetlands in the Northeastern US. Ecological Indicators, 66: 143–152. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2016.01.017
Niu Z G, Gong P, Cheng X et al., 2009. Geographical characteristics of China’s wetlands derived from remotely sensed data. Science in China Series D: Earth Sciences, 52(6): 723–738. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11430-009-0075-2
Ouyang W, Yang W X, Tysklind M et al., 2018. Using river sediments to analyze the driving force difference for non-point source pollution dynamics between two scales of watersheds. Water Research, 139: 311–320. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2018.04.020
Racchetti E, Bartoli M, Soana E et al., 2011. Influence of hydrological connectivity of riverine wetlands on nitrogen removal via denitrification. Biogeochemistry, 103(1–3): 335–354. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10533-010-9477-7
Shiels D R, 2010. Implementing landscape indices to predict stream water quality in an agricultural setting: an assessment of the Lake and River Enhancement (LARE) protocol in the Mississinewa River watershed, East-Central Indiana. Ecological Indicators, 10(6): 1102–1110: doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2010.03.007
Tuboi C, Irengbam M, Hussain S A, 2018. Seasonal variations in the water quality of a tropical wetland dominated by floating meadows and its implication for conservation of Ramsar wetlands. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth, Parts A/B/C, 103: 107–114. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pce.2017.09.001
Wang Jianhua, Lu Xianguo, Tian Jinghan et al., 2008. Fuzzy synthetic evaluation of water quality of Naoli river using parameter correlation analysis. Chinese Geographical Science, 18(4): 361–368. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11769-008-0361-5
Wang R, Bai N, Xu S J et al., 2018a. The adaptability of a wetland plant species Myriophyllum aquaticum to different nitrogen forms and nitrogen removal efficiency in constructed wetlands. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 25(8): 7785–7795. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-1058-z
Wang Xiaodong, Chu Lijuan, Jiang Ming et al., 2018b. Comparative analysis of water quality between restore wetland and nature wetland in Naoli River Basin. Wetland Science, 16(2): 179–184. (in Chinese)
Wu M Y, Xue L, Jin W B et al., 2012. Modelling the linkage between landscape metrics and water quality indices of hydrological units in Sihu Basin, Hubei province, China: an allometric model. Procedia Environmental Sciences, 13: 2131–2145. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proenv.2012.01.202
Xu E Q, Zhang H Q, 2016. Aggregating land use quantity and intensity to link water quality in upper catchment of Miyun Reservoir. Ecological Indicators, 66: 329–339. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2016.02.002
Yin Shiping, Li Binjiang, Pan Huasheng et al., 2017. Analysis of driving influence of climate change on the hydrological situation in Naoli river basin. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 24(4): 38–45. (in Chinese)
Yu Y H, Suo A N, Jiang N, 2011. Response of ecosystem service to landscape change in Panjin coastal wetland. Procedia Earth and Planetary Science, 2: 340–345. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeps.2011.09.053
Zhang Yan, 2013. Removal Effect and Management Measures of Nitrogen and Phosphorus in Agricultural Drainage Ditches. Changchun: Northeast Institute of Geography and Agroecology, Chinese Academy of Sciences. (in Chinese)
Zhong Jingjing, Liu Maosong, Wang Yu et al., 2014. Spatial correlation of major water quality indices between the lake and rivers in Taihu Lake Basin. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 33(8): 2176–2182. (in Chinese)
Zou Y C, Duan X, Xue Z S et al., 2018. Water use conflict between wetland and agriculture. Journal of Environmental Management, 224: 140–146. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.07.052
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: Under the auspices of National Natural Science Foundations of China (No. 41620104005, 31500307, 41601263, 41771120), Technology Development Program of Jilin Province (No. 20180101082JC, 20180520085JC, 20190201256JC, 20190201018JC), Natural Science Foundation of Changchun Normal University (No. 2016-009) and Northeast Institute of Geography and Agroecology, Chinese Academy of Sciences (No. IGA-135-05)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, H., Wang, X., Chu, L. et al. Is There Any Correlation Between Landscape Characteristics and Total Nitrogen in Wetlands Receiving Agricultural Drainages?. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 29, 712–724 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11769-019-1037-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11769-019-1037-8