Abstract
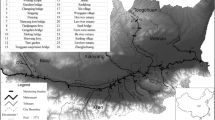
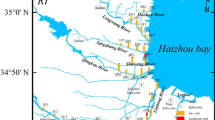
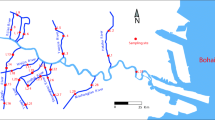
Heavy metal pollutants are a worldwide concern due to slow decomposition, biocondensation, and negative effects on human health. We investigated seasonal and spatial variations of the five heavy metals and evaluated their health risk in the Liaohe River, Northeast China. A total of 324 surface water samples collected from 2009 to 2010 were analyzed. Levels (high to low) of heavy metals in the Liaohe River were: zinc (Zn) > chromium (Cr) > copper (Cu) > cadmium (Cd) > mercury (Hg). Spatial and seasonal changes impacting concentrations of Cu and Zn were significant, but not significant for Cr, Cd and Hg. The highest concentrations of heavy metals were: Hg at Liuheqiao, Cu at Fudedian, Zn at Tongjiangkou, Cr at Mahushan, and Cd at Shenglitang. The highest concentrations of Hg and Cr were found in the wet period, Cu and Cd in the level period, and Zn in the dry period. The surface water of a tributary was an important accumulation site for heavy metals. Health risks from carcinogens and non-carcinogens increased from upstream to downstream in the mainstream of the Liaohe River. The total health risk for one person in the Liaohe River exceeded acceptable levels. The total health risk was the greatest during the wet period and least in the dry period. Among the five heavy metals in the Liaohe River, Cr posed the greatest single health risk.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ayenimo J G, Adeeyinwo C E, Amoo L A, 2005. Heavy metal pollutants in Warri River, Nigeria. Kragujevac Journal of Science, 27: 43–50.
Bryan G, Langston W J, 1992. Bioavailability, accumulation and effects of heavy metals in Sediments with special reference to United Kingdom Estuaries: a review. Environmental Pollution, 76: 89–131. doi: 10.1016/0269-7491(92)90099-V
Bu Jihong, Chen Huihui, Xu Yiping et al., 2014. Ecological risk of interstitial water heavy metals and toxicity characterization of surface sediments in branches of Liaohe River. Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology, 9(1): 24–34. (in Chinese)
Chen C Q, Tang S L, Pan Z L et al., 2007. Remotely sensed a assessment of water quality levels in the Pearl River Estuary, China. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 54: 1267–1272. doi: 10. 1016/j.marpolbul.2007.03.010
Demirak A, Yilmaz F, Tuna A L et al., 2006. Heavy metals in water, sediment and tissues of Leuciscus cephalus from a stream in southwestern Turkey. Chemosphere, 63: 1451–1458. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2005.09.033
Deng Baole, Zhu Lingyan, Liu Man et al., 2011. Sediment quality criteria and ecological risk assessment for heavy metals in Taihu Lake and Liao River. Research of Environmental Sciences, 24: 33–42. (in Chinese)
Diagomanolin V, Farhang M, Ghazi-Khansari M et al., 2004. Heavy metals (Ni, Cr, Cu) in the Karoon waterway river, Iran. Toxicology Letters, 151: 63–68. doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2004. 02.018
Guo Fen, 2009. The Study on Temporal and Spatial Variation Characters of Water Ecological and Water Environmental Factors in Liao River Basin. Bejing: Chinese Research Academy of Environmental Sciences, 31–32. (in Chinese)
Jonnalagadda S B, Mhere G, 2001. Water quality of the Odzi River in the eastern highlands of Zimbabwe. Water Research, 35(10): 2371–2376. doi: 10.1016/S0043-1354(00)00533-9
Kai Xiaoli, Gao Liangmin, Wu Chengguo, 2010. Water environmental health risk assessment for Wuhu reach of Qingyi River. Guangdong Agricultural Sciences, 2: 158–161. (in Chinese)
Kalay M, Canli M, 2000. Elimination of essential (Cu, Zn) and non-essential (Cd, Pb) metals from tissues of a freshwater fish Tilapia zilli. Turkish Journal of Zoology, 24(4): 429–436.
Kar D, Sur P, Mandanl S K et al., 2008. Assessment of heavy metal pollution in surface water. International Journal of Environmental Science & Technology, 5(1): 119–124. doi: 10. 1007/BF03326004
Khan K, Lu Y L, Khan H et al., 2013. Health risks associated with heavy metals in the drinking water of Swat, northern Pakistan. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 25(10): 2003–2013. doi: 10.1016/S1001-0742(12)60275-7
Krishna A K, Satyanarayanan M, Govil P K, 2009. Assessment of heavy metal pollution in water using multivariate statistical techniques in an industrial area: a case study from Patancheru, Medak District, Andhra Pradesh, India. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 167(1–3): 366–373. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.12.131
Li Junwen, 2008. Monitoring and analysis on water quality in Liaohe Area. Underground Water, 30(1): 61–64. (in Chinese)
Li Siyue, Xu Zhifang, Cheng Xiaoli et al., 2008. Dissolved trace elements and heavy metals in the Danjiangkou Reservoir, China. Environmental Geology, 55(5): 977–983. (in Chinese)
Li S, Zhang Q, 2010. Spatial characterization of dissolved trace elements and heavy metals in the upper Han River (China) using multivariate statistical techniques. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 176(1–3): 579–588. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.11.069
Li Yongli, Liu Jingling, 2009. Health risk assessment on heavy metal pollution in the water environment of Luan River. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 28(6): 94–98. (in Chinese)
Liu H, Li W, 2011. Dissolved trace elements and heavy metals from the shallow lakes in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River region, China. Environmental Earth Sciences, 62(7): 1503–1511. doi: 10.1007/s12665-010-0634-z
Macklin M G, Brewer P A, Hudson-Edwards K A et al., 2006. A geomorphological approach to the management of rivers contaminated by metal mining. Geomorphology, 79(3–4): 423–447. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2006.06.024
Memet V, 2013. Dissolved heavy metal concentrations of the Kralkizi, Dicle and Batman dam reservoirs in the Tigris River basin, Turkey. Chemosphere, 93(6): 954–962. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.05.061
Nriagu J O, 1989. A global assessment of natural sources of atmospheric trace metals. Nature, 338: 47–49.
Obasohan E E, Oronsaye J A O, Eguavoen O I, 2008. A comparative assessment of the heavy metal loads in the tissue of a common catfish (Clarias Gariepinus) from Ikpoba and Ogba River in Benin City, Nigeria. African Scientist, 9(1): 13–23.
Obasohan E E, Oronsaye J A O, Obano E E, 2006. Heavy metal concentrations in Malapterurus Electricus and Chrysichthys Nigrodigitatus from Ogba River in Benin City, Nigeria. African Journal of Biotechnology, 5(10): 974–982.
Pertsemli E, Voutsa D, 2007. Distribution of heavy metals in Lakes Doirani and Kerkini, Northern Greece. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 148(3): 529–537.
Rauf A, Javed M, Ubaidullah M, 2009. Heavy metal levels in three major carps (Catla Catla, Labeo Rohita and Cirrhina Mrigala) from the River Ravi. Pakistan Veterinary Journal, 29(1): 24–26.
Sin S N, Chua H, Lo W et al., 2001. Assessment of heavy metal cations in sediments of Shing Mun River, Hong Kong. Environment International: A Journal of Environmental Science, Risk and Health, 26(5): 297–301.
Su Wei, Liu Jingshuang, Li Fang, 2006. Assessment on health risk of heavy metals in the Second Songhua River. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 25(6): 1611–1615. (in Chinese)
Song S, Li F D, Li J et al., 2013. Distribution and contamination risk assessment of dissolved trace metals in surface waters in the Yellow River Delta. Human and Ecological Risk Assessment, 19: 1514–1529. doi: 10.1080/10807039.2012.708254
Suresh G, Sutharsan P, Ramasamy V et al., 2012. Assessment of spatial distribution and potential ecological risk of the heavy metals in relation to granulometric contents of Veeranam lake sediments, India. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 84: 117–124. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2012.06.027
Tang W Z, Zhao Y, Wang C et al., 2013. Heavy metal contamination of overlying waters and bed sediments of Haihe Basin in China. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 98: 317–323. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2013.09.038
Taweel A, Shuhaimi-Othman M, Ahmad A K, 2013. Assessment of heavy metals in tilapia fish (Oreochromis niloticus) from the Langat River and Engineering Lake in Bangi, Malaysia, and evaluation of the health risk from tilapia consumption. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 93: 45–51. doi: 10. 1016/j.ecoenv.2013.03.031
Tian Lirong, 2005. Analysis on present water quality of Tieling Section in the Liao River Basin. Groundwater, 27(6): 425–426. (in Chinese)
Varol M, 2011. Assessment of heavy metal contamination in sediments of the Tigris River (Turkey) using pollution indices and multivariate statistical techniques. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 195: 355–364. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.08.051
Wajahat N, Sajida P, Syed A S, 2006. Evaluation of irrigation water for heavy metals of Akbarpura Area. Journal of Agricultural and Biological Science, 1(1): 51–54.
Xiao R, Bai J H, Gao H F et al., 2012. Distribution and contamination assessment of heavy metals in water and soils from the college town in the Pearl River Delta, China. Clean-Soil Air Water, 40: 1167–1173. doi: 10.1002/clen.201200016
Zeng Fanping, Xiao Huayun, Zhou Wenbin, 2007. Spatial and temporal variations and their source analysis of copper, lead and zinc in river waters and sediments of the Le′an River. Research of Environmental Sciences, 20(6): 14–20. (in Chinese)
Zhang J, Wang S Q, Xie Y et al., 2008a. Distribution and pollution character of heavy metals in the surface sediments of Liao River. Environmental Science, 29(9): 2413–2418.
Zhang June, Pan Jun, Zhou Lidong et al., 2008b. Environmental health risk assessment for water supply sources of LiuHe in XinMin. Environmental Science and Management, 33(3): 179–183. (in Chinese)
Zou Bin, Zeng Yongnian, Benjamin F. Zhan et al., 2009. Spatial and temporal health risk assessment of water environment in urban area. Geography and Geo-Information Science, 25(2): 94–98. (in Chinese)
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the staff of Shenyang University Laboratory of Eco-Remediation and Resource Reuse for their support during field sampling, logistics and laboratory analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: Under the auspices of Major Science and Technology Program for Water Pollution Control and Treatment (No. 2012ZX07202-004-05), National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41401352), Science and Enterprise Competitive Selection Project of Shenyang City, Shenyang Science and Technology Plan Project (No. F14-133-9-00)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, H., Sun, L., Liu, Z. et al. Spatial distribution and seasonal variations of heavy metal contamination in surface waters of Liaohe River, Northeast China. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 27, 52–62 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11769-017-0846-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11769-017-0846-1