Abstract
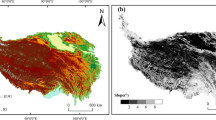
Human activities significantly alter ecosystems and their services; however, quantifying the impact of human activities on ecosystems has been a great challenge in ecosystem management. We used the Universal Soil Loss Equation and county-level socioeconomic data to assess the changes in the ecosystem service of soil conservation between 2000 and 2010, and to analyze its spatial characteristics and driving factors in the southwestern China. The results showed that cropland in the southwestern China decreased by 3.74%, while urban land, forest, and grassland areas increased by 46.78%, 0.86%, and 1.12%, respectively. The soil conservation increased by 1.88 × 1011 kg, with deterioration only in some local areas. The improved and the degraded areas accounted for 6.41% and 2.44% of the total land area, respectively. Implementation of the Sloping Land Conversion Program and urbanization explained 57.80% and 23.90% of the variation in the soil conservation change, respectively, and were found to be the main factors enhancing soil conservation. The 2008 Wenchuan earthquake was one of the factors that led to the degradation of soil conservation. Furthermore, industrial adjustment, by increasing shares of Industry and Service and reducing those of Agriculture, has also promoted soil conservation. Our results quantitatively showed and emphasized the contributions to soil conservation improvement made by implementing ecological restoration programs and promoting urbanization. Consequently, these results provide basic information to improve our understanding of the effects of ecological restoration programs, and help guide future sustainable urban development and regional industrial restructuring.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Carter H J, Eslinger D L, 2004. Nonpoint Source Pollution and Erosion Comparison Tool (N-SPECT) Technical Guide. NOAA-CSC.
Chazdon R L, 2008). Beyond deforestation: restoring forests and ecosystem services on degraded lands. Science, 320(5882): 1458–1460. doi: 10.1126/science.1155365
Faulkner S, 2004. Urbanization impacts on the structure and function of forested wetlands. Urban Ecosystems, 7(2): 89–106. doi: 10.1023/B:UECO.0000036269.56249.66
Feng X, Wang Y, Chen L et al., 2010. Modeling soil erosion and its response to land-use change in hilly catchments of the Chinese Loess Plateau. Geomorphology, 118(3–4): 239–248. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2010.01.004
Fu B, Liu Y, Lyu Y et al., 2011. Assessing the soil erosion control service of ecosystems change in the Loess Plateau of China. Ecological Complexity, 8(4): 284–293. doi: 10.1016/j.ecocom. 2011.07.003
Grau H R, Aide T M, 2007. Are rural-urban migration and sustainable development compatible in mountain systems? Mountain Research and Development, 27(2): 119–123. doi: 10.1659/mrd.0906
Grimm N B, Foster D, Groffman P et al., 2008. The changing landscape: ecosystem responses to urbanization and pollution across climatic and societal gradients. Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment, 6(5): 264–272. doi: 10.1890/070147
Han Huali, 2010. Study on Land Use Changes and Its Ecological Effects in Mountainous Areas at China’s Southwest Border Driven by the Project of Converting Farmland to Forest: a Case Study in Luxi City, Yunnan Province. Chongqing: Southwest University. (in Chinese)
Jiang G, Liu M, Han N et al., 2003. Potential for restoration of degraded steppe in the Xilingol Biosphere Reserve through urbanization. Environmental Conservation, 30(3): 304–310. doi: 10.1017/S0376892903000304
Jiang Z, Lian Y, Qin X, 2014. Rocky desertification in southwest China: impacts, causes, and restoration. Earth-Science Reviews, 132: 1–12. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2014.01.005
Li H, Aide T M, Ma Y et al., 2007. Demand for rubber is causing the loss of high diversity rain forest in SW China. Biodiversity and Conservation, 16(6): 1731–1745. doi: 10.1007/s10531-006-9052-7
Li Jingbao, Zhong Saixiang, Yang Yan et al., 2005. Effects on the functions of ecosystem services of Dongting Lake from silt deposit and land reclamation. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 13(2): 179–182. (in Chinese)
Liu Bingzheng, Liu Shihai, Zheng Suiding, 1999. Soil conservation and coefficient of soil conservation of crops. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 6(2): 32–36, 113. (in Chinese)
Liu J, Li S, Ouyang Z et al., 2008. Ecological and socioeconomic effects of China’s policies for ecosystem services. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 105(28): 9477–9482. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0706436105
Lyu Y, Fu B, Feng X et al., 2012. A policy-driven large scale ecological restoration: quantifying ecosystem services changes in the Loess Plateau of China. Plos One, 7(2): e31782. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0031782
McDonald R I, 2008. Global urbanization: can ecologists identify a sustainable way forward? Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment, 6(2): 99–104. doi: 10.1890/070038
Nagendra H, Sudhira H S, Katti M et al., 2014. Urbanization and its impacts on land use, biodiversity and ecosystems in India. Interdisciplina, 2(2): 305–313.
Ouyang Zhiyun, Zheng Hua, 2009. Ecological mechanisms of ecosystem services. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 29(11): 6183–6188. (in Chinese)
Pimentel D, Harvey C, Resosudarmo P et al., 1995. Environmental and economic costs of soil erosion and conservation benefits. Science, 267(5201): 1117–1123. doi: 10.1126/science. 267.5201.1117
Rao E, Ouyang Z, Yu X et al., 2014. Spatial patterns and impacts of soil conservation service in China. Geomorphology, 207: 64–70. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2013.10.027
Rey Benayas J M, Newton A C, Diaz A et al., 2009. Enhancement of biodiversity and ecosystem services by ecological restoration: a meta-analysis. Science, 325(5944): 1121–1124. doi: 10.1126/science.1172460
Ricardo G H, Aide M, 2008. Globalization and land-use transitions in Latin America. Ecology and Society, 13(2): 16.
SCO (State Council Office), 2010. Training Manual of the First Nationwide Water Resources Survey: Census of Soil and Water Conservation. Beijing: China Water Power Press. (in Chinese)
Shen W, Wu J, Grimm N B et al., 2008. Effects of urbanizationinduced environmental changes on ecosystem functioning in the Phoenix metropolitan region, USA. Ecosystems, 11(1): 138–155. doi: 10.1007/s10021-007-9085-0
Su C, Fu B, 2013. Evolution of ecosystem services in the Chinese Loess Plateau under climatic and land use changes. Global and Planetary Change, 101: 119–128. doi: 10.1016/j.gloplacha. 2012.12.014
van Beynen P E, 2011. Karst Management. Netherlands: Springer. doi: 10.1007/978-94-007-1207-2
Wang S J, Liu Q M, Zhang D F, 2004. Karst rocky desertification in southwestern China: geomorphology, landuse, impact and rehabilitation. Land Degradation & Development, 15(2): 115–121. doi: 10.1002/ldr.592
Wang Y K, Fu B, Xu P, 2012. Evaluation the impact of earthquake on ecosystem services. Procedia Environmental Sciences, 13: 954–966. doi: 10.1016/j.proenv.2012.01.089
Wei Hongbo, Li Rui, Yang Qinke, 2002. Research advances of vegetation effect on soil and water conservation in China. Acta Phytoecologica Sinica, 26(4): 489–496. (in Chinese)
Wei Xingping, 2011. The Study on the Characteristics and Mechanism of Soil Erosion in Karst Valley Area, Chongqing. Chongqing: Southwest University. (in Chinese)
Wischmeier W H, Smith D D, 1978. Predicting Rainfall Erosion Losses: A Guide to Conservation Planning. Washington, DC: U.S. Department of Agriculture.
Xu J, Yin R, Li Z et al., 2006. China’s ecological rehabilitation: unprecedented efforts, dramatic impacts, and requisite policies. Ecological Economics, 57(4): 595–607. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolecon.2005.05.008
Yang D, Kanae S, Oki T et al., 2003. Global potential soil erosion with reference to land use and climate changes. Hydrological Processes, 17(14): 2913–2928. doi: 10.1002/hyp.1441
Yang Guishan, Ma Ronghua, Zhang Lu et al., 2010. Lake status, major problems and protection strategy in China. Journal of Lake Science, 22(6): 799–810. (in Chinese)
Yang Miao, Xie Qiang, Tan Xiaorong et al., 2013. Assessment of restoration of soil and water conservation function in watershed in earthquake disaster area based on GIS/RS. Sichuan Environment, 32(1): 39–45. (in Chinese)
Ye Y, Chen G, Fan H, 2003. Impacts of the Grain for Green? project on rural communities in the Upper Min River Basin, Sichuan, China. Mountain Research and Development, 23(4): 345–352. doi: 10.1659/0276-4741(2003)023[0345:IOTGFG]2.0.CO;2
Yin R, Zhao M, 2012. Ecological restoration programs and payments for ecosystem services as integrated biophysical and socioeconomic processes—China’s experience as an example. Ecological Economics, 73: 56–65. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolecon. 2011.11.003
Zhang Chunmin, Wang Genxu, 2008. Impacts of Wenchuan Earthquake disasters on ecosystem and its spatial pattern: case study of Qingchuan, Pingwu and Maoxian counties. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 28(12): 5833–5841. (in Chinese)
Zhang K L, Shu A P, Xu X L et al., 2008. Soil erodibility and its estimation for agricultural soils in China. Journal of Arid Environments, 72(6): 1002–1011. doi: 10.1016/j.jaridenv.2007.11.018
Zhang Min, Zou Xiaoming, 2009. Comparison of soil C and N in rubber plantation and seasonal rain forest. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 20(5): 1013–1019. (in Chinese)
Zheng Hua, Ouyang Zhiyun, Zhao Tongqian et al., 2003. The impact of human activities on ecosystem services. Journal of Natural Resources, 18(1): 118–126. (in Chinese)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: Under the auspices of National Key Technology Research and Development Program of China (No. 2011BAC09B08), Special Issue of National Remote Sensing Survey and Assessment of Eco-Environment Change between 2000 and 2010 (No. STSN-04-01)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rao, E., Xiao, Y., Ouyang, Z. et al. Changes in ecosystem service of soil conservation between 2000 and 2010 and its driving factors in southwestern China. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 26, 165–173 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11769-015-0759-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11769-015-0759-9