Abstract
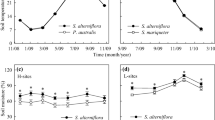
In recent years, herbaceous species such as Deyeuxia angustifolia (Kom.) Y. L. Chang has invaded alpine tundra regions of the western slope of the Changbai Mountains. Because atmospheric nitrogen deposition is predicted to increase under a warming climate and D. angustifolia is sensitive to nitrogen addition, field experiments were conducted from 2010 to 2013 to determine the effect of increased nitrogen deposition on the mechanisms of D. angustifolia invasion. The goal of this study is to evaluate the impact of increased nitrogen deposition on the changes in alpine tundra vegetation (consisting mostly of Rhododendron chrysanthum Pall. and Vaccinium uliginosum Linn.). The results showed that: 1) simulated nitrogen deposition affected overall characteristics and structure of R. chrysanthum and V. uliginosum communities and had a positive impact on the growth of tundra vegetation invaded by D. angustifolia; 2) R. chrysanthum was more resistant to invasion by D. angustifolia than V. uliginosum; 3) simulated nitrogen deposition could improve the growth and enhance the competitiveness of D. angustifolia, which was gradually replacing R. chrysanthum and V. uliginosum and might become the dominant species in the system in future, transforming alpine tundra into alpine meadow in the Changbai Mountains.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berendse F, 1994. Competition between plant populations at low and high nutrient supplies. Oikos, 71(2): 253–260. doi: 10.2307/3546273
Bobbink R, Hicks K, Galloway J et al., 2010. Global assessment of nitrogen deposition effects on terrestrial plant diversity: a synthesis. Ecological Applications, 20(1): 30–59. doi: 10.1890/08-1140.1
Bobbink R, Hornung M, Roelofs J G M, 1998. The effects of air-borne nitrogen pollutants on species diversity in natural and semi-natural European vegetation. Journal of Ecology, 86(5): 717–738. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2745.1998.8650717.x
Bowman W D, Garner J R, Holland K et al., 2006. Nitrogen critical loads for alpine vegetation and terrestrial ecosystem response: are we there yet? Ecological Applications, 16(3): 1183–1193. doi: 10.1890/1051-0761(2006)016[1183:NCLFAV] 2.0.CO;2
Bowman W D, Steltzer H, 1998. Positive feedbacks to anthropogenic nitrogen deposition in Rocky Mountain alpine tundra. Ambio, 27(7): 514–517.
Bowman W D, Theodose T A, Schardt J C et al., 1993. Constraintsof nutrient availability on primary production in two alpinetundra communities. Ecology, 74(7): 2085–2097. doi: 10.2307/1940854
Bret-Harte M S, Garcia E A, Sacre V M et al., 2004. Plant and soil responses to neighbour removal and fertilization in Alaskan tussock tundra. Journal of Ecology, 92(4): 635–647. doi: 10.1111/j.0022-0477.2004.00902.x
Burns D A, 2003. Atmospheric nitrogen deposition in the Rocky Mountains of Colorado and southern Wyoming—a review and new analysis of past study results. Atmospheric Environment, 37(7): 921–932. doi: 10.1016/S1352-2310(02)00993-7
Cai H, Xie S, 2007. Estimation of vehicular emission inventories in China from 1980 to 2005. Atmospheric Environment, 41 (39): 8963–8979. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2007.08.019
Chen X Y, Mulder J, Wang, Y H et al., 2004. Atmospheric deposition, mineralization and leaching of nitrogen in subtropical forested catchments, South China. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 26(2-3): 179–186. doi: 10.1023/B:EGAH. 0000039580.79321.1a
Clark C M, Morefield P E, Gilliam F S et al., 2013. Estimated losses of plant biodiversity in the United States from historical N deposition (1985–2010). Ecology, 94(7): 1441–1448. doi: 10.1890/12-2016.1
Dise N B, Rothwell J J, Gauci V et al., 2009. Predicting dissolved inorganic nitrogen leaching in European forests using two independent databases. Science of the Total Environment, 407(5): 1798–1808. doi: 10.1016j.scitotenv.2008.11.003
Dorrepaal E, Cornelissen J H C, Aerts R et al., 2005. Are growth forms consistent predictors of leaf litter quality and decomposability across peatlands along a latitudinal gradient? Journal of Ecology, 93(4): 817–828. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2745.2005.01024.x
Driscoll C T, Lawrence G B, Bulger A J et al., 2001. Acidic deposition in the northeastern United States: sources and inputs, ecosystem effects, and management strategies. Bioscience, 51(3): 180–198. doi: 10.1641/0006-3568(2001) 051[0180:ADITNU]2.0.C0;2
Du E Z, Jiang Y, Fang J Y et al., 2014. Inorganic nitrogen deposition in China’s forests: Status and characteristics. Atmospheric Environment, 98: 474–482. doi: org/10.1016/j.atmosenv. 2014.09.005
Gallowy J N, Dentener F J, Capone D G et al., 2004. Nitrogen cycles: past, present and future. Biogeochemistry, 70(2): 153–226. doi: jstor.org/stable/4151466
Galloway J N, Townsend A R, Erisman J W et al., 2008. Transformation of the nitrogen cycle: recent trends, questions, and potential solutions. Science, 320(5878): 889–892. doi: 10.1126/science.1136674
Geiser L H, Neitlich P N, 2007. Air pollution and climate gradients in western Oregon and Washington indicated by epiphytic macrolichens. Environment Pollution, 145(1): 203–218. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2006.03.024
Gerdol R, Brancaleoni L, Marchesini R et al., 2002. Nutrient and carbon relations in subalpine dwarf shrubs after neighbor removal or fertilization in northern Italy. Oecologia, 130(3): 476–783. doi: 10.1007/s00442-001-0823-2
Gough L, Osenberg C W, Gross K L et al., 2000. Fertilization effects on species density and primary productivity in herbaceous plant communities. Oikos, 89(3): 428–439. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0706.2000.890302.x
Graglia E, Jonasson S, Michelsen A et al., 2001. Effects of environmental perturbations on abundance of subarctic plants after three, seven and ten years of treatment. Ecography, 24(1): 5–12. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0587.2001.240102.x
Hurkuck M, Brümmer C, Mohr K et al., 2014. Determination of atmospheric nitrogen deposition to a semi-natural peat bog site in an intensively managed agricultural landscape. Atmospheric Environment, 97: 296–309. doi: org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2014.08.034
Jiang C M, Yu W T, Ma Q et al., 2013. Atmospheric organic nitrogen deposition: analysis of nation wide data and a case study in Northeast China. Environment Pollution, 182: 430–436. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2013.08.003
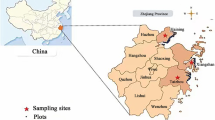
Jin Yinghua, Xu Jiawei, Liang Yu et al., 2013. Effects of volcanic interference on the vegetation distributionof Changbai Mountain. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 33(2): 203–208. (in Chinese)
Jin Yinghua, Xu Jiawei, Zong Shengwei et al., 2014. Experimental study on the effects of nitrogen deposition on the tundra vegetation of the Changbai Mountains. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 34(12): 1526–1532. (in Chinese)
Johnson D R, Ebert-May D, Webber P J et al., 2011. Forecasting alpine vegetation change using repeat sampling and a novel modeling approach. Ambio, 40(6): 693–704. doi: 10.1007/s13280-011-0175-z
Kool A, Heijmans M M P D, 2009. Dwarf shrubs are stronger competitors than graminoid species at high nutrient supply in peat bogs. Plant Ecology, 204(1): 125–134. doi: 10.1007/s11258-009-9574-7
Liu X J, Duan L, Mo J M et al., 2011. Nitrogen deposition and its ecological impact in China: an overview. Environmental Pollution, 159(10): 2251–2264. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2010.08.002
Liu X J, Zhang Y, Han W X et al., 2013. Enhanced nitrogen deposition over China. Nature, 494(7438): 459–462. doi: 10.1038/nature11917
Lu Xiankai, Mo Jiangming, Dong Shaofeng, 2008. Effects of nitrogen deposition on forest biodiversity. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 28(11): 5532–5548. (in Chinese)
Mac Donald J A, Dise N B, Matzner E et al., 2002. Nitrogen input together with ecosystem nitrogen enrichment predict nitrate leaching from European forests. Global Change Biology, 8: 1028–1033. doi: 10.1046/j.1365–2486.2002.00532.x
Magill A H, Aber J D, Currie W S et al., 2004. Ecosystem response to 15 years of chronic nitrogen additions at the Harvard Forest LTER, Massachusetts, USA. Forest Ecology and Management, 196(1): 7–28. doi: 10.1016/j.foreco.2004.03.033
Matson P, Lohse K A, Hall S J, 2002. The globalization of nitrogen deposition: consequences for terrestrial ecosystems. Ambio, 31(2): 113–119. doi: 10.1639/0044-7447(2002)031 [0113:TGONDC]2.0.CO;2
McDonough A M, Watmough S A, 2015. Impacts of nitrogen deposition on herbaceous ground flora and epiphytic foliose lichen species in southern Ontario hardwood forests. Environmental Pollution, 196: 78–88. doi: org/10.1016/j.envpol.2014.09.013
Nordin A, Strengbom J, Witzell J et al., 2005. Nitrogen deposition and the biodiversity of boreal forests: implications for the critical load. Ambio, 34(1): 20–24.
Ren H Y, Xu Z W, Zhang W H et al., 2013. Linking ethylene to nitrogen-dependent leaf longevity of grassspecies in a temperate steppe. Annals of Botany, 112(9): 1879–1885. doi: 10.1093/aob/mct223
Stevens C J, Thompson K, Grime P J et al., 2010. Contribution of acidification and eutrophication to declines in species richness of calcifuges grasslands along a gradient of atmospheric nitrogen deposition. Functional Ecology, 24(2): 478–484. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2435.2009.01663.x
van Dobben H F, de Vries W, 2010. Relation between forest vegetation, atmospheric deposition and site conditions and regional and European scales. Environmental Pollution, 158(3): 921–933. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2009.09.015
Verhoeven T, Beltman B, Dorland E et al., 2011. Differential effects of ammonium and nitrate deposition on fen phanerogams and bryophytes. Applied Vegetation Science, 14(2): 149–157. doi: 10.1111/j.1654-109 X.2010.01113.x
Wardle D A, Gundale M J, Jaderlund A et al., 2013. Decoupled long-term effects of nutrient enrichment on aboveground and belowground properties in subalpine tundra. Ecology, 94(4): 904–919. doi: org/10.1890/12-0948.1
Wright R F, Rasmussen L, 1998. Introduction to the NITREX and EXMAN projects. Forest Ecology and Management, 101: 1–7. doi: 10.1016/S0378-1127(97)00120-5
Yoshida L C, Allen E B, 2001. Response to ammonium and nitrate by a mycorrhizal annual invasive grassand native shrub in southern California. American Journal of Botany, 88(8): 1430–1436. doi: 10.2307/3558450
Zbieranowski A L, Aherne J, 2012. Spatial and temporal concentration of ambient atmospheric ammonia in southern Ontario, Canada. Atmospheric Environment, 62: 441–450. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2012.08.041
Zhan Xiaoyun, Yu Guirui, He Nianpeng et al., 2014. Nitrogen deposition and its spatial pattern in main forest ecosystems along north-south transect of eastern China. Chinese Geographical Science, 24(2): 137–146. doi: 10.1007/s11769-013- 0650-5
Zong Shengwei, Xu Jiawei, Wu Zhengfang, 2013. Investigation and mechanism analysis on the invasion of Deyeuxia angustifolia to tundra zone in western slope of Changbai Mountain. Journal of Mountain Science, 31(4): 448–455. (in Chinese)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: Under the aupices of Special Fund of National Seismological Bureau, China (No. 201208005), National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41171072, 41101523)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jin, Y., Xu, J., Wang, Y. et al. Effects of nitrogen deposition on tundra vegetation undergoing invasion by Deyeuxia angustifolia in Changbai Mountains. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 26, 99–108 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11769-015-0746-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11769-015-0746-1