Abstract
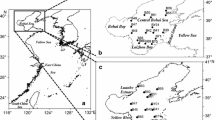
The southern sea area of the Huludao City, Liaoning Province might be polluted by heavy metals because it is close to the Jinzhou Bay, one of the heaviest sea area polluted by heavy metals in China. The undisturbed modern sediment core can be used to analyze the accumulation and source of the pollutants using 137Cs and 210Pbex. Thirty-five samples of surface sediment and two core sediments were collected from the southern sea area of Huludao City. The concentrations of copper (Cu), lead (Pb), chrome (Cr), zinc (Zn), arsenic (As) and mercury (Hg) in the surface sediments as well as Cu, Pb, Zn, Cr, 137Cs and 210Pbex in the core sediments were determined to research the spatial distribution and accumulation characteristics, and to analyze the sources and the potential risks of heavy metals. The results show that the pollution levels of Zn and Hg are serious, and 26 stations are at moderate or heavy ecological risks. The concentrations of the heavy metals increase from east to west, as well as from open sea to offshore marine area. The concentrations of heavy metals are not high in the sediments adjacent to the Jinzhou Bay, and the influence caused by the seawater exchange with the Jinzhou Bay is little. The concentrations of the heavy metals in the core sediments show low-high-low characteristic, and it coincides with the pollution history of Huludao City. The atmospheric deposition of heavy metals from the Huludao Zinc Plant is likely to be the main source of pollution without direct discharge of wastewater. The high concentrations of heavy metals appear on the upper sediment of 20 cm. The shallow sediment with high heavy metal contents might be exposed to surface when it was disturbed by the ocean engineering and big storm surge, then cause risk to the safety of aquaculture and human healthy.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Appleby P G, 1998. Dating recent sediments by 210Pb: Problems and solutions. In: Proceedings of 2 nd NKS/EKO-1 Seminar. STUK-A, Helsinki, 7–24.
Baskaran M, Naidu A S, 1995. 210Pb-derived chronology and the fluxes of 210Pb and 137Cs isotopes into continental shelf sediments, East Chukchi Sea, Alaskan Arctic. Journal of Geochemistry and Cosmochemistry, 59(21): 2487–2505. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(95)00248-X
Boughriet A, Ouddane B, Fischer J C et al., 1992. Variability of dissolved Mn and Zn in the Seine estuary and chemical speciation of these metals in suspended matter. Water Reseach, 26(10): 1359–1378. doi: 10.1016/0269-7491(92)90099-V
Bryan G W, Langston W J, 1992. Bioavailability, accumulation and effects of heavy metals in sediments with special reference to United Kingdom estuaries: A review. Environmental Pollution, 76(2): 89–131.
Chen Jingsheng, 1992. Study on Heavy Metals in Water Environment of China. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press. (in Chinese)
Dltoro D M, Mahony J D, Kirchgraber P R et al., 1986. Effects of nonreversibility, particle concentration, and ionic strength on heavy metal sorption. Environment Science & Technology, 20(1): 55–63. doi: 10.1021/es00143a006
Du J, Wu Y, Huang D et al., 2010. Use of 7Be, 210Pb and 137Cs tracers to the transport of surface sediments of the Changjiang Estuary, China. Journal of Marine Systems, 82(4): 286–294. doi: 10.1016/j.jmarsys.2010.06.003
Fan Wenhong, Zhang Bo, Chen Jingsheng, 2006. Pollution and potential biological toxicity assessment using heavy metals from surface sediments of Jinzhou Bay. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 26(6): 1000–1005. (in Chinese)
Fu Wenxia, Liu Guoxian, 1994. Hydraulic features and silt status of Jinzhou Bay. Marine Science Bulletin, 13(3): 42–53. (in Chinese)
Hakanson L A, 1980. Ecological risk index for quality pollution control, a sedimentological approach. Water Research, 14(8): 975–1001.
Jin Xiangcan, Wang Guiling, 1984. Study on the effect of adsorption heavy metal by sediment. Environmental Science and Technology, 2(1): 6–11. (in Chinese)
Kang Qinshu, Wu Ying, Zhang Jing et al., 2003. The distribution and pollution of heavy metals in Chongming wetland. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 25(Supp. 2): 1–7. (in Chinese)
Li Zhigang, Li Xiaoyu, Gao Bin et al., 2011. Temporal changes of shoal reclamation in Jinzhou Bay sea area based on remote sensing analysis. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 22(4): 943–949. (in Chinese)
Liu Guangshan, 2006. The Measuring Method of Marine Radionuclide. Beijing: China Ocean Press. (in Chinese)
Liu Hengkui, 1995. A preliminary study of the characteristics of the waves and currents near Jinzhou Bay. Transactions of Oceanology and Limnology, 17(1): 1–6. (in Chinese)
Lopez P, Lluch X, 2000. Sediment geochemistry of ameromictic coastal lagoon. Escibollar (Majorca, Spain). Limnetica, 18: 15–27.
Lu C A, Zhang J F, Jiang H M et al., 2010. Assessment of soil contamination with Cd, Pb and Zn and source identification in the area around the Huludao Zinc Plant. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 182(1–3): 743–748. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.06. 097
Ma Jiarui, Shao Mihua, 1994. The heavy metals pollution and dynamical variation in core sediment samples in Jinzhou Bay. China Environmental Science, 14(1): 22–29. (in Chinese)
Mohamed A W, 2005. Geochemistry and sedimentology of core sediment sand the influence of human activities, Qusier, Safaga and Hasighada Harbors, Red sea coast Egypt. Egyptian Journal of Aquaculture Research, 31(1): 92–103.
Nabi-Bidhendi A R, Bayati G H R, 2005. Environmental geochemistry of heavy metals in a sediment core off Bushehr, Persian Gulf. Iranian Journal of Environmental Health Science & Engineering, 2(4): 255–260.
Peng J F, Song Y H, Yuan P et al., 2009. The remediation of heavy metals contaminated sediment. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 161(2-3): 633–640. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.04. 061
Roos P, Valeur J R, 2006. A sediment trap and radioisotope study to determine resuspension of particle reactive substances in the sound between Sweden and Denmark. Continental Shelf Research, 26(4): 474–487. doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2006.01.001
Salomons W, Stigliani W M, 1995. Biogeodynamics of Pollutants in Soils and Sediments: Risk Assessment of Delayed and Non-linear Responses. New York: Springer-Verlag, 331–343.
Sarin M M, Krishnaswami S, Tarun K D et al., 2000. Settling fluxes of U- and Th-series nuclides in the Bay of Bengal: Results from time-series sediment trap studies. Deep-Sea Research I, 47(10): 1961–1985. doi: 10.1016/S0967-0637(00) 00016-9
Shi Xiaoli, Qiu Boqiang, 2008. Study on 137Cs and 210Pb dating an sedimentation rates of Wanghu Lake, Hubei Province. Journal of Ningbo University (NSEE), 21(3): 418–422. (in Chinese)
Su C C, Hu C A, 2002. 210Pb, 137Cs and 239, 240Pu in East China Sea sediments: Sources, pathways and budgets of sediments and radionuclides. Marine Geology, 183(1–4): 163–178. doi: 10.1016/S0025-3227(02)00165-2
Theofanis Z U, Astrid S, Lidia G et al., 2001. Contaminants in sediments: Remobilisation and demobilization. The Science of Total Environment, 266(1–3): 195–202. doi: 10.1016/S0048-9697(00)00740-3
Wan G J, Santschi P H, Sturm M et al., 1987. Natural (210Pb, 7B) and fallout (137Cs, 239, 240Pu, 90Sr) radio nuclides as geochemical tracers of sedimentation in Greifensee. Chemical Geology (Switzerland), 63(3–4): 181–196.
Wan Li, Wang Nianbin, Ding Qian et al., 2009. The Distribution of heavy metal pollution in Jinzhou Bay, Bohai Sea. Fisheries Science, 28(12): 801–804. (in Chinese)
Wang Hong, Jiang Yi, Li Jinfen et al., 2003. 14C, 137Cs and 210Pb dating and accelerated tendency of the present sedimentation rate along the Laolangtuozi coast of the Bohai Bay. Geological Bulletin of China, 22(9): 659–665. (in Chinese)
Yang Chunlin, Ouyang Tong, Zhang Luoping, 2007. Speciations of heavy metals in the surface sediments from Xiamen western Harbor. Journal of Xiamen University (Natural Science), 46(1): 89–93. (in Chinese)
Zhang Yufeng, 2008. Pollution Evaluation on Heavy Metals in Surface Sediments in Jinzhou Bay. Dalian: Dalian Maritime University. (in Chinese)
Zhang Yufeng, Wang Lijun, Huo Chuanlin et al., 2008. Pollution evaluation on heavy metals in surface sediments in Jinzhou Bay. Marine Environmental Science, 27(3): 258–260. (in Chinese)
Zheng Na, Wang Qichao, Liu Jingshuang et al., 2009. Spatial variation of heavy metals contamination in the soil and vegetables of Huludao City. Environmental Science, 30(7): 2071–2076. (in Chinese)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: Under the auspices of National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 40806045), Ocean Public Welfare Scientific Research Project, State Oceanic Administration People’s Republic of China (No. 201105005)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Liu, R., Fan, D. et al. Distribution and accumulation characteristics of heavy metals in sediments in southern sea area of Huludao City, China. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 23, 194–202 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11769-012-0579-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11769-012-0579-0