Abstract
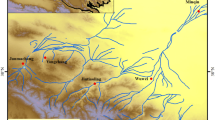
Under the increasing pressure of water shortage and steppe degradation, information on the hydrological cycle in steppe region in Inner Mongolia, China is urgently needed. An intensive investigation of the temporal variations of δD and δ18O in precipitation was conducted in 2007–2008 in the Xilin River Basin, Inner Mongolia in the northern China. The δD and δ18O values for 54 precipitation samples range from +1.1‰ to −34.7‰ and −3.0‰ to −269‰, respectively. This wide range indicates that stable isotopes in precipitation are primarily controlled by different condensation mechanisms as a function of air temperature and varying sources of vapor. The relationship between δD and δ18O defined a well constrained line given by δD = 7.89 δ 18 O + 9.5, which is nearly identical to the Meteoric Water Line in the northern China. The temperature effect is clearly displayed in this area. The results of backward trajectory of each precipitation day show that the vapor of the precipitation in cold season (October to March) mainly originates from the west while the moisture source is more complicated in warm season (April to September). A light precipitation amount effect existes at the precipitation event scale in this area. The vapor source of precipitation with higher d-excesses are mainly from the west wind or neighboring inland area and precipitation with lower d-excesses from a monsoon source from the southeastern China.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aggarwal P, 2002. Isotope hydrology at the International Atomic Energy Agency. Hydrological Processes, 16(11): 2257–2259. doi: 10.1002/hyp.5043
Araguas L, Froehlich K, Rozanski K, 2000. Deuterium and oxygen-18 isotope composition of precipitation and atmospheric moisture. Hydrological Processes, 14(8): 1341–1355. doi: 10.1002/1099-1085(20000615)
Barthold F, Wu J, Vaché K et al., 2010. Identification of geographic runoff sources in a data sparse region: Hydrological processes and the limitations of tracer-based approaches. Hydrological Processes, 24(16): 2313–2327. doi: 10.1002/hyp.7678
Chen Z, 1988. Topography and climate of the Xilin River basin. In: Research on Grassland Ecosystem, Inner Mongolia. Beijing: Science Press, 13–22. (in Chinese)
Clark I, Fritz P, 1997. Environmental Isotopes in Hydrogeology. Boca Raton: Lewis Publishers.
Craig H, 1961. Isotopic variation in meteoric waters. Science, 133(3465): 1702–1703. doi: 10.1126/science.133.3465.1702
Dansgaard W, 1964. Stable isotopes in precipitation. Tellus, 16(4): 436–468. doi: 10.1111/j.2153-3490.1964.tb00181.x
Dinçer T, Davis G, 1984. Application of environmental isotope tracers to modeling in hydrology. Journal of Hydrology, 68(1–4): 95–113. doi: 10.1016/0022-1694(84)90206-3
Dincer T, Al-Mugrin A, Zimmermann U, 1974. Study of the infiltration and recharge through the sand dunes in arid zones with special reference to the stable isotopes and thermonuclear tritium. Journal of Hydrology, 23(1–2): 79–109. doi:10.1016/0022-1694(74)90025-0
Draxler R, Rolph G, 2003. HYSPLIT (HYbrid Single-Particle Lagrangian Integrated Trajectory) Model. Available at: http://www.arl.noaa.gov/ready/hysplit4.html.
Gat J, Bowser C, Kendall C, 1994. The contribution of evaporation from the Great Lakes to the continental atmosphere estimate based on stable isotope data. Geophysics Research Letter, 21(7): 557–560. doi: 10.1029/94GL00069
Gat J, Carmi I, 1970. Evolution of the isotopic composition of atmospheric waters in the Mediterranean Sea area. Journal of Geophysical Research, 75: 3039–3048. doi: 10.1029/JC075i015p03039
Gat J, Dansgaard W, 1972. Stable isotope survey of fresh water occurrence in Israel and the Jordan Rift Valley. Journal of Hydrology, 16: 177–211. doi: 10.1016/0022-1694(72)90052-2
Geyh M, Gu W, 1991. Preliminary isotope hydrological study in the arid Guriani Grassland area, Inner Mongolia. In: Isotope Techniques in Water Resources Development. Vienna: IAEA, 661–662.
Gibson J, Edwards T, Birks S et al., 2005. Progress in isotope tracer hydrology in Canada. Hydrological Processes 19(1): 303–327. doi: 10.1002/hyp.5766
Gibson J, Edwards T, Bursey G, 1993. Estimating evaporation using stable isotopes: Quantitative results and sensitivity analysis for two catchments in northern Canada. Nordic Hydrology, 24: 79–94.
Gourcy L, Groening M, Aggarwal P, 2005. Stable oxygen and hydrogen isotopes in precipitation. In: Aggarwal P et al. (eds.). Isotopes in the Water Cycle: Past, Present and Future of a Developing Science. Amsterdam: Springer, 39–51. doi: 10.1007/1-4020-3023-1_4
IAEA (International Atomic Energy Agency), 1980. Arid zone hydrology: Investigations with isotope techniques. In: Proceedings of an Advisory Group Meeting. Vienna: IAEA.
IAEA, WMO (World Meteorological Organization), 2004. Global Network of Isotopes in Precipitation (GNIP) Database (2004), Vienna, Austria. Available at: http://www.isohis.iaea.org
IAEA. 2001. Environmental isotopes in the hydrological cycle, principles and applications, Volume III: Surface water. In: Mook W (ed.). International Hydrological Programme, Technical Documents in Hydrology 39. Vienna: IAEA.
Ingraham N, Taylor B, 1986. Hydrogen isotope study of large-scale meteoric water transport in Northern California and Nevada. Journal of Hydrology, 85(1–2): 183–197. doi: 10.1016/0022-1694(86)90084-3
Jouzel J, 1986. Isotopes in cloud: multiphase and multistage condensation process. In: Fritz P, Fontes J (eds.). Handbook of Environmental Isotope Geochemistry. NewYork: Elsevier, 61–112.
Jouzel J, Froehkich K, Schotterer U, 1997. Deuterium and oxygen-18 in present-day precipitation: Data and modeling. Hydrological Science, 42(5): 747–763. doi: 10.1080/02626669709492070
Kattan Z, 2006. Characterization of surface water and groundwater in the Damascus Ghotta basin: Hydrochemical and environmental isotopes approaches. Environmental Geology, 51(2): 173–201. doi: 10.1007/s00254-006-0316-z
Kendall C, Coplen T, 2001. Distribution of oxygen-18 and deuterium in river waters across the United States. Hydrological Processes, 15(7): 1363–1393. doi: 10.1002/hyp.217
Kreutz K, Wake C, Aizen V, 2003. Seasonal deuterium excess in a Tien Shan ice core: Influence of moisture transport and recycling in Central Asia. Geophysics Research Letter, 30(18): 19–22. doi: 10.1029/2003GL017896
Lis G, Wassenaar L, Hendry, 2008. High-precision laser spectroscopy D/H and 18O/16O measurements of microliter natural water samples. Analytical Chemistry, 80(1): 287–293. doi: 10.1021/ac701716q
Liu J, Zhao Y, Liu E, Wang D, 1997. Discuss on the stable isotope time-space distribution law of China atmospheric precipitation. Science and Technology on Reconnaissance, 3: 34–39. (in Chinese)
Liu F, Williams M, Caine N, 2004. Sources waters and flow paths in an alpine catchment, Colorado Front Range, USA, Water Resources Research, 40: W09401. doi: 10.1029/2004WR003076
Merlivat L, Jouzel J, 1979. Global climatic interpretation of the deuterium-oxygen-18 relationship for precipitation. Journal of Geophysical Research, 84(C8): 5029–5033. doi: 10.1029/JC084iC08p05029
Schneider K, Ketzer B, Breuer L et al., 2007. Evaluation of evapotranspiration methods for model validation in a semi-arid watershed in northern China. Advances in Geosciences, 11: 37–42.
Song G, Pan J, Wang D et al., 2007. Analysis of the moisture transportation characteristics on summer drought in Inner Mongolia. Meteorological Monthly, 33(6): 75–81. doi: 1000-0526.0.2007-06-010
Song X, Liu X, Xia J et al., 2006. A study of interaction between surface water and groundwater using environmental isotopes in Huaisha River basin. Science in China (Series D), 49(12): 1299–1310. doi: 10.1007/s11430-006-1299-z
Tian L, Masson-Delmotte V, Stievenard M, 2001. Tibetan Plateau summer monsoon northward extent revealed by measurements of water stable isotopes. Journal of Geophysical Research, 106(D22): 28081–28088. doi: 10.1029/2001JD900186
Tong C, Wu J, Yong S et al., 2004. A landscape-scale assessment of steppe degradation in the Xilin River Basin, Inner Mongolia, China. Journal of Arid Environment, 59(1): 133–149. doi: 10.1016/j.jaridenv.2004.01.004
Wang F, 1997. The law of isotopic concentration field on the time-space distribution and environmental effect of atmospheric water in Jilin Province. Jilin Geology, 16(1): 51–56. (in Chinese). doi: 1001-2427.0.1997-01-006
Wu J, Overton C, 2002. Asian ecology: Pressing problems and research challenges. Bulletin of Ecological Society of America, 83(3): 189–194. doi: 10.1890/0012-9623(2002)083
Wu J, Ding Y, Ye B et al., 2010. Spatio-temporal variation of stable isotopes in precipitation in the Heihe River basin, Northwestern China. Environmental Earth Sciences, 61(6): 1123–1134. doi: 10.1007/s12665-009-0432-7
Yakirevich A, Dody A, Adar E et al., 1998. Distribution of stable isotopes in arid storms. II. A double-component kinematic wave flow and transport model. Hydrogeology Journal, 6(1): 66–76. doi: 10.1007/s100400050133
Yao T, Masson V, Jouzel J et al., 1999.Relationship between δ18O in precipitation and surface air temperature in the Urumqi River Basin, East Tianshan Mountain, China. Geophysics Research Letter, 26(23): 3473–3480. doi: 10.1029/1999GL006061
Zhang X, Liu J, Tian L et al., 2004. Variation of δ18O in precipitation along vapor transport paths. Advances in Atmospheric Sciences 21(4): 562–572. doi: 10.1007/BF02915724
Zheng Shuhui, Hou Fagao, Ni Baoling, 1983. The study on deuterium and oxygen-18 in precipitation in China. Chinese Science Bulletin, 28(13): 801–806. (in Chinese)
Zhou S, Nakawo M, Sakai A et al., 2007. Water isotope variations in the snow pack and summer precipitation at July 1 Glacier, Qilian Mountains in northwest China. Chinese Science Bulletin, 52(21): 2963–2972. doi: 10.1007/s11434-007-0401-z
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: Under the auspices of Nation Basic Research Program of China (No. 2007CB411502), German Science Foundation (Research Unit 536), Independent Research Project from State Key Laboratory of Cryospheric Science (No. SKLCS-ZZ-2010-02)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, J., Ding, Y., Ye, B. et al. Stable isotopes in precipitation in Xilin River Basin, northern China and their implications. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 22, 531–540 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11769-012-0543-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11769-012-0543-z