Abstract
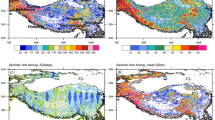
Using the recent compilation of the isotopic composition data of surface snow of Antarctic ice sheet, we proposed an improved interpolation method of δD, which utilizes geographical factors (i.e., latitude and altitude) as the primary predictors and incorporates inverse distance weighting (IDW) technique. The method was applied to a high-resolution digital elevation model (DEM) to produce a grid map of multi-year mean δD values with 1km spatial resolution for Antarctica. The mean absolute deviation between observed and estimated data in the map is about 5.4‰, and the standard deviation is 9‰. The resulting δD pattern resembles well known characteristics such as the depletion of the heavy isotopes with increasing latitude and distance from coast line, but also reveals the complex topographic effects.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bowen G J, Revenaugh J, 2003. Interpolating the isotopic composition of modern meteoric precipitation. Water Resources Research, 39(10): 1299. DOI: 10D1029/2003 WR002086.
Bowen G J, Wilkinson B H, 2002. Spatial distribution of δ18O in meteoric precipitation. Geology, 30(4): 315–318.
Ciais P, Jouzel J, 1994. Deuterium and oxygen 18 in precipitation: Isotopic model, including mixed cloud processes. Journal of Geophysical Research, 99(D8): 16793–16803.
Cuffey K M, Clow G D, Alley R B et al., 1995. Large Arctic temperature change at the Wisconsin-Holocene glacial transition. Science, 270: 455–458.
Dansgaard W, 1964. Stable isotopes in precipitation. Tellus, 16: 436–468.
Ekaykin A A, Lipenkov V Y, Barkov N I et al., 2002. Spatial and temporal variability in isotope composition of recent snow in the vicinity of Vostok Station: implications for ice-core record interpretation. Annals of Glaciology, 35: 181–186.
EPICA (European Project of Ice Cores in Antarctica) Community Members, 2004. Eight glacial cycles from an Antarctic ice core. Nature, 429(6992): 623–628.
Graf W, Oerter, Reinwarth H O et al., 2002. Stable isotope records from Dronning Maud Land, Antarctica. Annals of Glaciology, 35: 195–201.
Fisher D A, 1991. Remarks on the deuterium excess in precipitation in cold regions. Tellus (Series B), 43: 401–407.
GRIP (Greenland Ice-core Project) Members, 1993. Climate instability during the last interglacial period recorded in the GRIP ice core. Nature, 364(6434): 203–207.
Helsen M M, van de Wal R S W, van den Broeke M R, 2007. The isotopic composition of present-day Antarctic snow in a Lagrangian atmospheric simulation. Journal of Climate, 20:739–756.
Johnsen S J, Dahl-Jensen D, Dansgaard W et al., 1995. Greenland palaeotemperatures derived from GRIP bore hole temperature and ice core isotope profiles. Tellus (Series B), 47: 624–629.
Jouzel J, Alley R B, Cuffey C M et al., 1997. Validity of the temperature reconstruction from water isotopes in ice cores. Journal of Geophysical Research, 102(C12): 26471–26487.
Jouzel J, Vimeux F, Caillon N et al., 2003. Magnitude of isotope/temperature scaling for interpretation of central Antarctic ice cores. Journal of Geophysical Research, 108(D12): 4361. DOI: 10.1029/2002JD002677.
Jouzel J, Masson-Delmotte V, Cattani O et al., 2007. Orbital and millennial Antarctic climate variability over the past 800000 years. Science, 317: 793–796.
Lhomme N, Clarke G K C, Ritz C, 2005. Global budget of water isotopes inferred from polar ice sheets. Geophysical Research Letters, 32: L20502. DOI: 10.1029/2003JD004228.
Liu H X, Jezek K C, Li B et al., 2001. Radarsat Antarctic Mapping Project Digital Elevation Model Version 2. Boulder, Colorado: National Snow and Ice Data Center.
Masson-Delmotte V, Delmotte M, Morgan V et al., 2003. Recent southern Indian Ocean climate variability inferred from a Law Dome ice core: New insights for the interpretation of coastal Antarctic isotopic records. Climate Dynamics, 21(2): 153–166.
Masson-Delmotte V, Hou S, Ekaykin A et al., 2008. A review of Antarctic surface snow isotopic composition: observations, atmospheric circulation and isotopic modeling. Journal of Climate, 21: 3359–3387. DOI: 10.1175/2007JCLI2139.1
Masson-Delmotte V, Jouzel J, Landais A et al., 2005. GRIP deuterium excess reveals rapid and orbital-scale changes in Greenland moisture origin. Science, 309: 119–121.
NGICP (North Greenland Ice Core Project) Members, 2004. High-resolution record of Northern Hemisphere climate extending into the last interglacial period. Nature, 431: 147–151.
Noone D, Simmonds I, 2002. Associations between δ18O of water and climate parameters in a simulation of atmospheric circula tion for 1979–95. Journal of Climate, 15: 3150–3169. DOI: 10.1175/1520-0442(2002)015
Noone D, Turner J, Mulvaney R, 1999. Atmospheric signals and characteristics of accumulation on Dronning Maud Land, Antarctica. Journal of Geophysical Research, 104(D16): 19191–19211.
Robin G, 1983. The climatic record from ice cores. In: Robin G (ed). The Climatic Record in Polar Ice Sheets. New York: Cambridge Univ. Press, 180–195
Rozanski K, Araguas-Araguas L, Gonfiantini R, 1993. Isotopic patterns in modern global precipitation. In: Swart P et al. (eds.). Climate Change in Continental Isotopic Records. Washington, DC: American Geophysical Union, 1–36.
Salamatin A N, Ekaykin A A, Lipenkov V Y, 2004. Modelling isotopic composition in precipitation in Central Antarctica. Mater. Glyatsiol. Issled., 97: 24–34.
Schmidt G A, Hoffmann G, Shindell D T et al., 2005. Modeling atmospheric stable water isotopes and the potential for constraining cloud processes and stratosphere-troposphere water exchange. Journal of Geophysical Research, 110: D21314. DOI: 10.1029/2005JD005790.
Schneider D P, Steig E J, Van Ommen T D et al., 2006. Antarctic temperatures over the past two centuries from ice cores. Geophysical Research Letters, 33: L16707. DOI: 10.1029/2006GL 027057.
Schlosser E, Oerter H, 2002. Seasonal variation of accumulation and the isotope record in ice cores: A study with surface snow samples and firn cores from Neumayer station, Antarctica. Annals of Glaciology, 35: 97–101.
Van Lipzig N P M, Van Meijgaard E, Oerlemans J, 2002. The effect of temporal variations in the surface mass balance and temperature inversion strength on the interpretation of ice-core signals. Journal of Glaciology, 48(163): 611–621.
Werner M, Heimann M, 2002. Modeling interannual variability of water isotopes in Greenland and Antarctica. Journal of Geophysical Research, 107: 4001. DOI: 10.1029/2001JD900253.
Yurtsever Y, Gat Jr, 1981. Atmospheric waters. In: Gat Jr et al. (eds.). Stable Isotope Hydrology: Deuterium and Oxygen-18 in the Water Cycle. Vienna: International Atomic Energy Association, 103–139.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: Under the auspices of National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 40825017, 40576001); 100 Talents Project of Chinese Academy of Sciences; National Key Technologies R&D Program of China (No. 2006BAB18B01)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Hou, S., Grigholm, B. et al. An improved method for modeling spatial distribution of δD in surface snow over Antarctic ice sheet. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 19, 120–125 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11769-009-0120-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11769-009-0120-2