Abstract
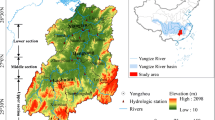
The Huolin River is one of the most important water sources for Xianghai wetland, Horqin wetland, and Chaganhu wetland in the western Songnen Plain of Northeast China. The annual runoff series of 46 years at Baiyun-hushuo Hydrologic Station, which is located in the middle reaches of the Huolin River, were analyzed by using wavelet analysis. Main objective was to discuss the periodic characteristics of the runoff, and examine the temporal patterns of the Huolin River recharging to the floodplain wetlands in the lower reaches of the river, and the corresponding effects of recharging variation on the environmental evolution of the wetlands. The results show that the annual runoff varied mainly at three time scales. The intensities of periodical signals at different time scales were strongly characterized by local distribution in its time frequency domain. The interdecadal variation at a scale of more than 30yr played a leading role in the temporal pattern of runoff variation, and at this scale, the runoff at Baiyunhushuo Hydrologic Station varied in turn of flood, draught and flood. Accordingly, the landscape of the floodplain wetlands presented periodic features, especially prominent before the 1990s. Compared with intense human activities, the runoff periodic pattern at middle (10–20yr) and small (1–10yr) scales, which has relatively low energy, exerted unobvious effects on the environmental evolution of the floodplain wetlands, especially after the 1990s.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bai Junhong, Ouyang Hua, Deng Wei et al., 2004. Modification process of land use/land cover type of wetlands in Huolin River catchment. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 18(1): 172–174. (in Chinese)
Bai Junhong, Yu Guoying, 2001. Environmental problems of wetland resources and their countermeasures in Xianghai Nature Reserve. Rural Eco-Environment, 17(1): 17–20. (in Chinese)
Bradshaw G A, Spies T A, 1992. Characterizing canopy gap structure in forest using wavelet analysis. The Journal of Ecology, 80(2): 205–215.
Daubechies I, 1992. Ten Lecture on Wavelets. SIAM: Philadelphia, PA.
Deng Wei, Song Xinshan, Zhai Jinliang, 2000. Wetland protection and sustainable utilization of water resources in the flooded area. Science and Technology Review, (3): 58–68. (in Chinese)
Foufoula-Georgiou E, Kumar P, 1994. Wavelets in Geophysics: Wavelet Analysis and Its Applications. San Diego: Academic Press, 372.
He Yan, Zhang Mingxiang, 2001. Study on wetland loss and its reasons in China. Chinese Geographical Science, 11(3): 241–245.
Kaiser G, 1994. A Friendly Guide to Wavelets. Boston: Birkhauser.
Li Qingkun, 2003. Study on floodwater utilization and allocation for wetland restoration and protection of Chagan Lake in Jilin Province. Nanjing: Hohai University. (in Chinese)
Lin Zhenshan, Deng Ziwang, 1991. On the Climate Diagnostic Techniques Using Wavelet. Beijing: Meteorological Press, 22–25. (in Chinese)
Liu De, Li Yonghua, Yang Zuoming et al., 2004. A diagnostic analysis of multi-time-scale variations of temperature in Chongqing. Journal of Applied Meteorological Science, 15(2): 251–256. (in Chinese)
Liu Junping, Tian Fengwei, Huang Qiang et al., 2003. Runoff variation of Yellow River based on wavelet analysis. Progress in Natural Science, 13(4): 383–387. (in Chinese)
Lu Xianguo, Liu Hongyu, Yang Qing, 2000. Wetlands in China: feature, value and protection. Chinese Geographical Science, 10(4): 296–3301.
Moortel I, Munday S A, Hood A W, 2004. Wavelet analysis: the effect of varying basic wavelet parameters. Solar Physics, 222(2): 203–228.
Peng Yuhua, 2002. Wavelet Transform and Its Application in Ingineering. Beijing: Science Press. (in Chinese)
Saunders S C, Chen J, Crow T R et al., 1998. Hierarchical relationships between landscape structure and temperature in a managed forest landscape. Landscape Ecology, 13(6): 381–395.
Vitorino M I, Silva Dias P L da, Ferreira N J, 2006. Observational study of the seasonality of the submontyly and intraseasonal signal over the tropics. Meteorology and Atmospheric Physics, 93(1–2): 17–35.
Weng H, Lau KM, 1994. Wavelet, period doubling, and time-frequency localization with application to organization of convection over the tropical western. Journal of the Atomospheric Sciences, 51(17): 2523–2541.
Yang Fusheng, 2001. Analysis and Application of the Wavelet Transform. Beijing: Science Press, 1–16. (in Chinese)
Yang Yong, Yu Youzhong, Zhu Yanfang et al., 2005. Present situation of wetland in Ke’rqin National-level Natural Preserves and its conservation countermeasures. Inner Mongolia Forestry Investigation and Design, 28(2): 3–5. (in Chinese)
Zhai Jinliang, 2002. River-floodplain environmental system research: a case study of the Huolin River. Changchun: Northeast Institute of Geography and Agroecology, Chinese Academy of Sciences. (in Chinese).
Zhang Liping, Zhu Cunwen, Xia Jun, 2004. Analysis on the change of precipitation in multiple temporal scales in North China. Arid Land Geography, 27(4): 548–552. (in Chinese)
Zhang Shaowen, Ding Jing, Liao Jie et al., 2004. Analysis of natural annual runoff time series in the upper reach of the Yellow River based on wavelet transform. Journal of Sichuan University (Engineering Science Edition), 36(3): 32–37. (in Chinese)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: Under the auspices of Knowledge Innovation Program of Chinese Academy of Sciences (No. KZCX3-SW-332-01)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, X., Deng, W. & Zhang, S. Multiple time-scale characteristics of runoff variations in middle reaches of Huolin River and their effects. Chin. Geograph.Sc. 17, 143–150 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11769-007-0143-5
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11769-007-0143-5