Abstract
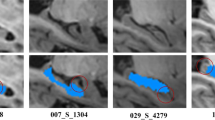
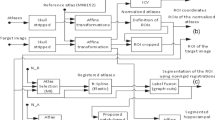
The volume of hippocampal subfields is closely related with early diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease. Due to the anatomical complexity of hippocampal subfields, automatic segmentation merely on the content of MR images is extremely difficult. We presented a method which combines multi-atlas image segmentation with extreme learning machine based bias detection and correction technique to achieve a fully automatic segmentation of hippocampal subfields. Symmetric diffeomorphic registration driven by symmetric mutual information energy was implemented in atlas registration, which allows multi-modal image registration and accelerates execution time. An exponential function based label fusion strategy was proposed for the normalized similarity measure case in segmentation combination, which yields better combination accuracy. The test results show that this method is effective, especially for the larger subfields with an overlap of more than 80%, which is competitive with the current methods and is of potential clinical significance.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
D. L. Collins and J. C. Pruessner. Towards accurate, automatic segmentation of the hippocampus and amygdala from MRI by augmenting ANIMAL with a template library and label fusion. Neuroimage, 52(2010)4, 1355–1366.
Susanne G. Mueller and Micheal W. Weiner. Selective effect of age, Apo e4 and Alzheimer’s disease on hippocampal subfields. Hippocampus, 19(2009)6, 558–564.
John Pluta, Paul Yushkevich, Sandhitsu Das, et al.. In vivo analysis of hippocampal subfield atrophy in mild cognitive impairment via semi-automatic segmentation of T2-weighted MRI. Journal of Alzheimer’s disease, 31(2012)1, 85–99.
Paul A. Yushkevich, Hongzhi Wang, John Pluta, et al.. Nearly automatic segmentation of hippocampal subfields in in vivo focal T2-weighted MRI. NeuroImage, 53(2010)4, 1208–1224.
Xabier Artaechevarria, Arrate Muñoz-Barrutia, and Carlos Ortiz-de-Solórzano. Combination strategies in multi-atlas image segmentation: application to brain MR data. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 28(2009)8, 1266–1277.
Ying Li, Yonggang Shi, Fa Jie, et al.. Multi-modal diffeomorphic demons registration based on mutual information. Proceeding of 4th International Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Informatics, Shanghai, China, 2011, 800–804.
B. B. Avants, C. L. Epstein, M. Grossman, et al.. Symmetric diffeomorphic image registration with cross-correlation: Evaluating automated labeling of elderly and neurodegenerative brain. Medical Image Analysis, 12(2008)1, 26–41.
F. Beg, M. Miller, A. Trouv’e, et al.. Computing large deformation metric mappings via geodesic flows of diffeomorphisms. International Journal of Computer Vision, 61(2005)2, 139–157.
Thévenaz Philippe and Michael Unser. Optimization of mutual information for multiresolution image registration. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 9(2000)12, 2083–2099.
Guang-Bin Huang, Qin-Yu Zhu, and Chee-Kheong Siew. Extreme learning machine: Theory and applications. Neurocomputing, 70(2006)1, 489–501.
Guang-Bin Huang, Hong-Ming Zhou, Xiao-Jian Ding, et al.. Extreme learning machine for regression and multiclass classification. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, 42(2012)2, 513–527.
John Pluta, Susanne Mueller, Caryne Craige, et al.. Hippocampal subfield segmentation protocol at 4T. www.nitrc.org.
A. Klein, J. Andersson, B. A. Ardekani, et al.. Evaluation of 14 nonlinear deformation algorithms applied to human brain MRI registration. Neuroimage, 46(2009)3, 786–802.
Koen Van Leemput, Akram Bakkour, Thomas Benner, et al.. Automated segmentation of hippocampal subfields from ultra-high resolution in vivo MRI. Hippocampus, 19(2009)6, 549–557.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 60971133, 61271112).
Communication author: Shi Yonggang, born in 1969, male, Ph.D., Associate Professor.
About this article
Cite this article
Shi, Y., Zhang, X. & Liu, Z. Automatic segmentation of hippocampal subfields based on multi-atlas image segmentation techniques. J. Electron.(China) 31, 121–128 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11767-014-3183-x
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11767-014-3183-x
Key words
- Hippocampal subfields
- Image segmentation
- Symmetric diffeomorphism
- Mutual information
- Label fusion
- Extreme Learning Machine (ELM)