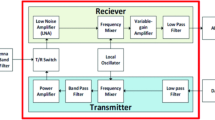
Abstract
A novel approach to survivor memory unit of Decision Feedback Sequence Estimator (DFSE) for 1000BASE-T transceiver based on hybrid architecture of the classical register-exchange and trace-back methods is proposed. The proposed architecture is investigated with special emphasis on low power and small decoder latency, in which a dedicated register-exchange module is designed to provide tentative survivor symbols with zero latency, and a high-speed trace back logic is presented to meet the tight latency budget specified for 1000BASE-T transceiver. Furthermore, clock-gating register banks are constructed for power saving. VLSI implementation reveals that, the proposed architecture provides about 40% savings in power consumption compared to the traditional register-exchange architecture.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Physical Coding Sublayer (PCS), Physical Medium Attachment (PMA) sublayer and baseband medium, type 1000BASE-T. IEEE Standard 802.3, 2008.
A. Duel-Hallen and C. Heegard. Delayed decision-feedback sequence estimation. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 37(1989)5, 428–436.
E. F. Haratsch and K. Azadet. A 1-Gb/s joint equalizer and trellis decoder for 1000BASE-T gigabit ethernet. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 36 (2001)3, 374–384.
D. Ohand and S. Hwang. Design of a Viterbi decoder with low power using minimum-transition trace back scheme. Electronics Letters, 32(1996)24, 2198–2199.
Y. Gang, A. T. Erdogan, and T. Arslan. An efficient pre-traceback architecture for the Viterbi decoder targeting wireless communication applications. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems, 53(2006)9, 1918–1927.
P. Black and T. Meng. Hybrid survivor path architectures for Viterbi decoders. IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 1993, Vol. 1, 433–436.
Chu Yu, Yu-Shan Su, Bor-Shing Lin, et al.. A memoryless Viterbi decoder for LTE systems. 2012 IEEE 1st Global Conference on Consumer Electronics (GCCE), Tokyo, Japan, 2012, 643–644.
Chun-Yuan Chu, Yu-Chuan Huang, and An-Yeu Wu. Power efficient low latency survivor memory architecture for Viterbi decode. IEEE International Symposium on VLSI Design, Automation and Test, (VLSI-DAT 2008), Hsinchu, China, 2008, 228–231.
Sunil P. Joshi and Roy Paily. Low power Viterbi decoder by modified ACSU architecture and clock gating method. 2011 International Conference on Communications and Signal Processing (ICCSP), Calicut, India, 2011, 499–503.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communication author: Qiu Bingsen, male, Ph.D., Principal Research Scientist.
About this article
Cite this article
Qiu, B. Low-power survivor memory architecture for DFSE in 1000BASE-T transceiver. J. Electron.(China) 31, 92–99 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11767-014-3140-8
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11767-014-3140-8
Key words
- Survivor memory unit
- Register exchange
- Trace back
- Decision Feedback Sequence Estimator (DFSE)
- 1000BASE-T