Abstract
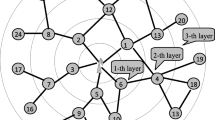
On the basis of complex network theory, the issues of key nodes in Wireless Sensor Networks (WSN) are discussed. A model expression of sub-network fault in WSN is given at first; subsequently, the concepts of average path length and clustering coefficient are introduced. Based on the two concepts, a novel attribute description of key nodes related to sub-networks is proposed. Moreover, in terms of node deployment density and transmission range, the concept of single-point key nodes and generalized key nodes of WSN are defined, and their decision theorems are investigated.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
I. F. Akyildiz, W. Su, Y. Sankarasubramaniam, et al.. Wireless sensor network: a survey. Computer Networks, 38(2002)4, 394–395.
Edgar H. Callaway. Wireless Sensor Networks: Architectures and Protocols. Boca Raton, FL, US, Auerbach Publications, 2004, 67.
Sunil Jardosh and Prabhat Ranjan. A survey: topology control for wireless sensor networks. Proceedings of International Conference on Signal Processing, Communications and Networking, Chennai, India, Jan. 2008, 423–424.
Bela Bollobas. Random Graphs. London, UK, Academic Press, 1985, 18–19.
Yueqing Ren and Lixin Xu. A study on topological characteristics of wireless sensor network based on complex network. Proceedings of 2010 International Conference on Computer Application and System Modeling, Taiyuan, China, Oct. 2010, 486.
A. L. Barabási. The New Science of Networks. Cambridge, UK, Cambridge Prerseus, 2002, 41–42.
Zheng Zhong-tuan. Exploring complex networks by random graph evolution and random walks. [Ph.D. Dissertation]. Shanghai University, 2009, 16 (in Chinese). 郑中团. 基于随机图演化与图上随机游动的复杂网络 研究. [博士论文]. 上海大学, 2009, 16.
A. Helmy. Small worlds in wireless networks. IEEE Communications Letters, 7(2003)10, 491.
G. Sharma and R. R. Mazumdar. Hybrid sensor networks: a small world. Proceedings of the Sixth ACM International Symposium on Mobile Ad-Hoc Networking and Computing, Urbana-Champaign, IL, USA, May 2005, 5–6.
L. Kleinrock and J. Silvester. Optimum transmission radii for packet radio networks or why six is a magic number. Proceedings of IEEE National Telecommunications Conference, Birmingham, UK, Dec. 1978, 433.
M. D. Penrose. The longest edge of the random minimal spanning tree. The Annals of Applied Probability, 7(1997)2, 343–344.
Christian Bettstetter. On the minimum node degree and connectivity of a wireless multi-hop network. Proceedings of the 3rd ACM International Symposium on Mobile Ad-Hoc Networking and Computing, Lausanne, Switzerland, Jun. 2002, 81–82.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the National High Technology Research and Development Program of China (No. 2008AA01A201) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 60503015).
Communication author: Ma Chuang, born in 1974, male, Ph.D. candidate.
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, C., Liu, H., Zuo, D. et al. Research on key nodes of wireless sensor network based on complex network theory. J. Electron.(China) 28, 396–401 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11767-011-0611-z
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11767-011-0611-z