Abstract
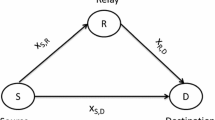
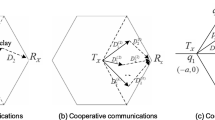
Complex networks have been widely studied. Recently, many results show that the degree distributions of some large networks follow the form of power-law and these networks possess better robustness against random nodes failure. As an effective technology on combating the channel fading, wireless cooperative communication is becoming one of the most important methods to improve the wireless communication performances. In this paper, the complex network models based on cooperative communication and non-cooperative communication are established; and the degree distribution properties for them are studied. The simulation results show that the degree distributions of these networks also follow the form of power-law, which means that the addition of cooperative communication links will not change the property of degree distribution and then these networks will possess better robustness against random nodes failure as well.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. Albert and A. Barabasi. Statistical mechanics of complex networks. Reviews of Modern Physics, 74 (2002)1, 47–97.
X. Li and G. Chen. A local-world evolving network model. Physica A, 328(2003), 274–286.
L. Y. Song, X. Li, and X. F. Wang. Modeling the evolving Internet topology. WCICA, Dalian, 2006, Vol. 1, 16–20.
N. Sarshar and V. Roychowdhury. Scale-free and stable structure in complex Ad hoc networks. Physics Review, E69(026101)2004.
J. M. Zhang, Q. Zhang, C. J. Shao, Y. Wang, P. Zhang, and Z. Zhang. Adaptive optimal transmit power allocation for two-hop non-regenerative wireless relaying system. VTC’ 2004, Milan, Italy, May 17–19, 2004, Vol. 2, 1213–1217.
T. E. Hunter and N. Aria. Diversity through coded cooperation. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 5(2006)2, 283–289.
Y. Wang and X. C. Qu. Power allocation and subcarrier pairing algorithm for regenerative OFDM relay system. IEEE 65th VTC’ 2007, Dublin, Ireland, 2007, 2727–2731.
A. Nosratinia and T. E. Hunter. Cooperative communication in wireless networks. IEEE Communications Magazine, 42(2004)10, 74–80.
L. Long and E. Hossain. Multihop cellular networks: potential gains, research challenges, and a resource allocation framework. IEEE Communications Magazine, 45(2007)9, 66–73.
H. Y. Luo, X. Q. Meng, R. Ramjee, P. Sinha, and L. Li. The design and evaluation of unified cellular and Ad-Hoc networks. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 6(2007)9, 1060–1074.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by Shanghai Leading Academic Discipline Project under Grant T0102, Fund of Innovation for Graduate Student of Shanghai University (No. shucx080151) and Youth Innovation Foundation of SIMIT, CAS (No. 2008QNCX03).
Communication author: Chen Huimin, born in 1946, male, Professor.
About this article
Cite this article
Xie, W., Chen, H., Yang, X. et al. The study on degree distribution property of complex network based on cooperative communication. J. Electron.(China) 27, 224–229 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11767-010-0302-1
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11767-010-0302-1