Abstract
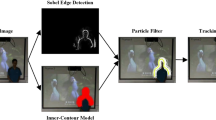
This paper presents a robust object tracking approach via a spatially constrained colour model. Local image patches of the object and spatial relation between these patches are informative and stable during object tracking. So, we propose to partition an object into patches and develop a Spatially Constrained Colour Model (SCCM) by combining the colour distributions and spatial configuration of these patches. The likelihood of the candidate object is given by estimating the confidences of the pixels in the candidate object region. The appearance model is learnt from the first frame and the tracking is carried out by particle filter. The experimental results show that the proposed tracking approach can accurately track the object with scale changes, pose variance and partial occlusion.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. S. Arulampalam, S. Maskell, N. Gordon, and T. Clapp. A tutorial on particle filters for online nonlinear/non-Gaussian Bayesian tracking. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 50(2002)2, 174–188.
M. Isard and A. Blake. CONDENSATION-conditional density propagation for visual tracking. International Journal of Computer Vision, 29(1998)1, 5–28.
C. Chang and R. Ansari. Kernel particle filter for visual tracking. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 12(2005)3, 242–245.
D. Comaniciu, V. Ramesh, and P. Meer. Kernel-based object tracking. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 25(2003)5, 564–577.
A. Adam, E. Rivlin, and I. Shimshoni. Robust fragments-based tracking using the integral histogram. IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New York, USA, June 17–22, 2006, 798–805.
T. Yu and Y. Wu. Differential tracking based on spatial-appearance model (SAM). IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New York, USA, June 17–22, 2006, 720–727.
H. Wang, D. Suter, K. Schindler, and C. Shen. Adaptive object tracking based on an effective appearance filter. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 29(2007)9, 1661–1667.
A. K. Jain and R. C. Dubes, Algorithms for Clus tering Data. NJ, Prentice Hall, 1988, 55–141.
The EC Funded CAVIAR project/IST. URL: http://homepages.inf.ed.ac.uk/rbf/CAVIAR/, 2006.
Test image sequences by Stan Birchfield. URL: http://vision.stanford.edu/birch/headtracker/seq/, 2006.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 60677040).
Communication author: Wang Shupeng, born in 1975, male, Ph.D. candidate.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, S., Ji, H. Effective appearance model for probabilistic object tracking. J. Electron.(China) 26, 503–508 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11767-008-0058-z
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11767-008-0058-z