Abstract
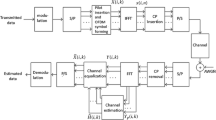
Adaptive modulation can optimize the spectrum efficiency and system performance with the channel state information achieved by the long-range channel prediction. To avoid re-estimating channel correlation function as the channel stationarity varies and to track the channel adaptively, LMS (Least-Mean-Square) based long-range channel prediction is discussed in the existing literature, but it needs long observation interval to reach the convergence. Given that all OFDM (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing) subcarriers have the identical time-domain correlation and stationarity during the same time interval, this paper proposed a 2-D LMS based predictor which updates the filter weights in both time and frequency domain. The proposed scheme can effectively decrease the observation intervals and significantly speed up the convergence than the conventional LMS and Parallel LMS (PLMS). Complexity analysis and simulation results prove that the proposed scheme can improve the BER (Bit Error Rate) performance and spectrum efficiency with negligible complexity increase.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
T. Keller, L. Hanzo. Adaptive multicarrier modulation: a convenient framework for time-frequency processing in wireless communications. Proc. of IEEE, 88(2005)5, 611–640.
M. R. Souryal, R. L. Pickholtz. Adaptive modulation with imperfect channel information in OFDM. IEEE International Conference on Comm. (ICC), Helsinki, Finland, June 2001, vol.6, 1861–1865.
T. Eyceoz, A. Duel-Hallen, H. Hallen. Deterministic channel modeling and long range prediction of fast fading mobile radio channels. Comm. Lett., 2(1998)9, 254–256.
A. Duel-Hallen, S. Hu, H. Hallen. Long-range prediction of fading signals: enabling adapting transmission for mobile radio channels. IEEE Sig. Proc. Mag., 17(2000)3, 62–75.
A. Forenza, R. W. Heath, Jr. Link adaptation and channel prediction in wireless OFDM systems. In Proc. 45th Midwest Symposium on Circuits and Systems, Oklahoma, USA, August 2002, 211–214.
D. Schafhuber, G. Matz, F. Hlawatsch. Adaptive prediction of time-varying channels for coded OFDM systems. IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing (ICASS), Hong Kong, China, May 2002, vol.3, 2459–2452.
I. C. Wong, A. Forenza, R. W. Heath, B. L. Evans. Long range channel prediction for adaptive OFDM systems. Conference Record of the Thirty-Eighth Asilomar Conference on Signal, systems and Computers, Montreal, Canada, Nov. 2004, vol.1, 732–736.
Q. Shen, B. X. Xiu, A. K. Elhakeem. The linear prediction method of fading channel estimation for RAKE receiver with impulsive interference. Wireless Personal Communications, 6(1998), 233–248.
M. Torrance, L. Hanzo. Upper bound performance of adaptive modulation in a slow Rayleigh fading channel. Electronics Letters, 32(1996)8, 718–719.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.60496311).
Communication author: Xu Xiaodong, born in 1975, male, Ph.D. student. National Mobile Communications Research Laboratory, Southeast University, Nanjing 210096, China.
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, X., Jing, Y., Hua, J. et al. Time-frequency 2-D LMS based long-range channel prediction for wireless OFDM systems. J. of Electron.(China) 24, 583–587 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11767-005-0248-x
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11767-005-0248-x
Key words
- Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM)
- Channel prediction
- Least-Mean-Square (LMS)
- Adaptive modulation