Abstract
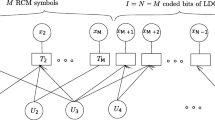
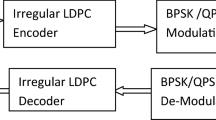
This paper investigates analysis and design of Low-Density Parity-Check (LDPC) coded Bit Interleaved Coded Modulation (BICM) over Additive White Gaussian Noise (AWGN) channel. It focuses on Gray-labeled 8-ary Phase-Shift-Keying (8PSK) modulation and employs a Maximum A Posteriori (MAP) symbol-to-bit metric calculator at the receiver. An equivalent model of a BICM communication channel with ideal interleaving is presented. The probability distribution function of log-likelihood ratio messages from the MAP receiver can be approximated by a mixture of symmetric Gaussian densities. As a result semi-Gaussian approximation can be used to analyze the decoder. Extrinsic information transfer charts are employed to describe the convergence behavior of LDPC decoder. The design of irregular LDPC codes reduces to a linear programming problem on two-dimensional variable edge-degree distribution. This method allows irregular code design in a wider range of rates without any limit on the maximum node degree and can be used to design irregular codes having rates varying from 0.5275 to 0.9099. The designed convergence thresholds are only a few tenths, even a few hundredths of a decibel from the capacity limits. It is shown by Monte Carlo simulations that, when the block length is 30,000, these codes operate about 0.62–0.75 dB from the capacity limit at a bit error rate of 10−8.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
G. Ungerboeck. Channel coding with multilevel/phase signals. IEEE Trans. on Inform. Theory, 28(1982)1, 55–67.
H. Imai, S. Hirakawa. A new multilevel coding method using error correcting codes. IEEE Trans. on Inform. Theory, 23(1977)3, 371–377.
G. Caire, G. Tarrico, E. Biglieri. Bit-interleaved coded modulation. IEEE Trans. on Inform. Theory, 44(1998)3, 927–946.
R. G. Gallager. Low-Density Parity Check Codes. [Ph.D. dissertation], MIT, 1960.
S. Y. Chung, et al. On the design of low-density parity check codes within 0.0045 dB of the Shannon limit. IEEE Commun. Letters, 5(2001)2, 58–60.
T. J. Richardson, R. Urbanke. The capacity of low-density parity check codes under message passing decoding. IEEE Trans. on Inform. Theory, 47(2001)2, 599–618.
T. J. Richardson, A. Shokrollahi, R. Urbanke. Design of capacity approaching irregular low-density parity check codes. IEEE Trans. on Inform. Theory, 47 (2001) 2, 619–637.
S.-Y. Chung, T. J. Richardson, R. L. Urbanke. Analysis of sum-product decoding of low-density parity-check codes using a Gaussian approximation. IEEE Trans. on Inform. Theory, 47(2001)2, 657–670.
M. Tuchler, J. Hagenauer. EXIT charts of irregular codes. in Proc. of Conference on Information Science and Systems, Princeton University, 2002, 20–22.
J. Hou, et al. Multilevel coding with low-density parity-check component codes. Global Telecommunications Conference, San Antonio, Texas, 2001, 1016–1020.
J. Hou, et al. Capacity-approaching bandwidth-efficient coded modulation schemes based on low-density parity-check codes. IEEE Trans. on Inform. Theory, 49(2003)9, 2141–2155.
S. ten Brink. Convergence behavior of iteratively decoded parallel concatenated codes. IEEE Trans. on Commun., 49(2001)10, 1727–1737.
H. Sankar, N. Sindhushayana, K. R. Narayanan. Design of low-density parity-check (LDPC) codes for high order constellations. Globe Telecommunications Conference, Dallas, Texas, 2004, 3113–3117.
Yan Li, W. E. Ryan. Design of LDPC-coded modulation schemes. in Proc. of 3rd International Symp. on Turbo Codes, Brest, France, 2003, 551–554.
M. Ardakani, Frank R. Kschischang. A more accurate one-dimensional analysis and design of irregular LDPC codes. IEEE Trans. on Commun., 52(2004)12, 2106–2114.
Ingmar Land, et al. Bounds on information combining. IEEE Trans. on Inform. Theory, 51(2005)2, 612–619.
F. R. Kschischang, et al. Factor graphs and the sumproduct algorithm. IEEE Trans. on Inform. Theory, 47(2001)2, 498–519.
X. Hu, E. Eleftheriou, D.-M. Arnold, A. Dholakia. Efficient implementations of the sum-product algorithm for decoding LDPC codes. Globe Telecommunications Conference, San Antonio, Texas, 2001, 1036.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, J., Zhang, F. & Zhu, J. Design of LDPC-coded BICM using a semi-Gaussian approximation. J. of Electron.(China) 24, 174–180 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11767-005-0186-7
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11767-005-0186-7
Key words
- Irregular Low-Density Parity-Check (LDPC) codes
- EXtrinsic Information Transfer (EXIT) charts
- Semi-Gaussian assumption