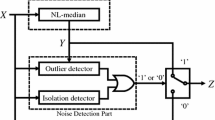
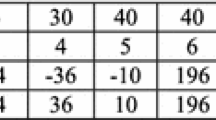
Abstract
We propose an accurate and efficient noise detection algorithm for impulse noise removal, called the boundary discriminative noise detection by elimination (BDNDE), which retains the good characteristics of the BDND filter proposed by Ng and Ma (in IEEE Trans. Image Process. 15(6):1506–1516, 2006) while suppressing noise effectively. In order to determine whether a pixel is corrupted, the algorithm first sets the minimum and maximum boundary (threshold) values based on the localized window centered on the pixel. The thresholding helps in achieving low false-alarm and miss-detection rate (even in random noise), even up to 90% noise densities. Extensive simulation results, conducted on gray scale images under a wide range (from 10 to 90%) of noise corruption, clearly demonstrate that our enhanced switching median filter gives better results compared to existing BDND median-based filters, in terms of suppressing impulse noise while preserving image details. The proposed method is algorithmically simple and faster, compared to existing BDND, and more suitable for real-time implementation and application. The new method has shown superior performance in terms of subjective quality in the filtered image as well as objective quality in the peak signal-to-noise ratio (PSNR) measurement to that of the BDND filter.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bovik A.: Handbook of Image and Video Processing. Academic, New York (2000)
Huang T.S., Yang G.J., Tang G.Y.: Fast two-dimensional medianfiltering algorithm. IEEE Trans. Acoustics Speech Signal Process ASSP-1(1), 13–18 (1979)
Pitas I., Venetsanopoulos A.N.: Order statistics in digital image processing. Proc. IEEE 80(12), 1893–1921 (1992)
Brownrigg D.R.K.: The weighted median filter. Commun. ACM 27(8), 807–818 (1984)
Ko S.-J., Lee Y.H.: Center weighted median filters and their applications to image enhancement. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. 38(9), 984–993 (1991)
Nair, M.S., Revathy, K., Tatavarti, R.: An improved Decision-based algorithm for impulse noise removal In: Proceedings of 2008 International Congress on Image and Signal Processing—CISP 2008, vol. 1, pp. 426–431. IEEE Computer Society Press, Sanya, Hainan, China, May (2008)
Nair, M.S., Revathy, K., Tatavarti, R.: Removal of Salt-and-Pepper noise in images: a new decision-based Algorithm. In: Proceedings of IAENG International Conference on Imaging Engineering—ICIE 2008, vol. 1, pp.611–616. IAENG International Multiconference of Engineers and Computer Scientists—IMECS 2008, Hong Kong, March (2008)
Sun T., Neuvo Y.: Detail-preserving median based filters in image processing. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 15(4), 341–347 (1994)
Florencio, D.A., Schafer, R.W.: Decision-based median filter using local signal statistics. In: Proceedings SPIE Vis. Commun. Image Process., vol. 2308, pp. 268–275, Sep (1994)
Chen T., Ma K.-K., Chen L.-H.: Tri-state median filter for image denoising. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 8(12), 1834–1838 (1999)
Wang Z., Zhang D.: Progressive switching median filter for the removal of impulse noise from highly corrupted images. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II 46(1), 78–80 (1999)
Zhang S., Karim M.A.: A new impulse detector for switching median filters. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 9(4), 360–363 (2002)
Eng H.-L., Ma K.-K.: Noise adaptive soft-switching median filter. IEEE Trans. Image Process 10(2), 242–251 (2001)
Pok G., Liu J.-C., Nair A.S.: Selective removal of impulse noise based on homogeneity level information. IEEE Trans. Image Process 12(1), 85–92 (2003)
Hwang H., Haddad R.A.: Adaptive median filters: new algorithms and results. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 4(4), 499–502 (1995)
Ng P.-E., Ma K.-K.: A switching median filter with boundary discriminative noise detection for extremely corrupted images. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 15(6), 1506–1516 (2006)
Ping, W., Junli, L,, Dongming, L., Gang, C.: A fast and reliable switching median filter for highly corrupted images by impulse noise. In: IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems, ISCAS, pp. 3427–3430, June 2007 (2007)
Dong Y., Xu S.: A new directional weighted median filter for removal of random-valued impulse noise. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 14(3), 193–196 (2007)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nasimudeen, A., Nair, M.S. & Tatavarti, R. Directional switching median filter using boundary discriminative noise detection by elimination. SIViP 6, 613–624 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-010-0189-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-010-0189-1