Abstract
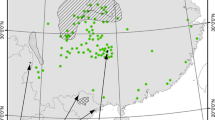
The golden snub-nosed monkey (GSNM), Rhinopithecus roxellana, is an endangered species on the IUCN Red List, and the Yuhe National Nature Reserve in Gansu is one of its principal habitats. The GSNM’s protection and management rely heavily on predicting its probable suitable habitat. The Maxent model was used to examine the habitat suitability of GSNM in the Yuhe Nature Reserve and surrounding areas. Infrared cameras used to monitor GSNM in 2019–2020 provided the model with data. Through analysis and screening, 23 distribution sites of GSNM and five environmental variables were included in the final model. The findings revealed that the Yuhe Nature Reserve’s area of appropriate habitat for GSNM was 248.43 km2, accounting for 52.79 percent of the reserve’s total area and that this was concentrated in the core zone. The Maxent model was optimized using the Kuenm package, and the resulting value reached an exceptional level of 0.948. A Jackknife test revealed that the mean diurnal range was the most important environmental factor affecting the distribution of GSNM (45.84%). Finally, the planning of the reserve was generally in line with the predictions, and the functional zoning could be altered accordingly. We advised extending the reserve southward based on the study’s findings, while strengthening the supervision of marginal areas of the reserve.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data underlying this article will be shared on reasonable request to the corresponding author.
References
Aidoo OF, Souza PGC, da Silva RS et al (2022) Climate-induced range shifts of invasive species (Diaphorina citri Kuwayama). Pest Manag Sci 78(6):2534–2549. https://doi.org/10.1002/ps.6886
Arroyo-Rodríguez V, Fahrig L (2014) Why is a landscape perspective important in studies of primates? Am J Primatol 76(10):901–909. https://doi.org/10.1002/ajp.22282
Babar S, Amarnath G, Reddy CS, Jentsch A, Sudhakar S (2012) Species distribution models: ecological explanation and prediction of an endemic and endangered plant species (Pterocarpus santalinus L.f.). Curr Sci 102(8):1157–1165. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0035867
Cobos ME, Peterson AT, Barve N, Osorio-Olvera L (2019) Kuenm: an R package for detailed development of ecological niche models using Maxent. PeerJ 7:e6281. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.6281
Colwell RK, Brehm G, Cardelús CL, Gilman AC, Longino JT (2008) Global warming, elevational range shifts, and lowland biotic attrition in the wet tropics. Science 322(5899):258–261. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1162547
Dong X, Chu YM, Gu X, Huang Q, Zhang J, Bai W (2019) Suitable habitat prediction of Sichuan snub-nosed monkeys (Rhinopithecus roxellana) and its implications for conservation in Baihe Nature Reserve, Sichuan, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(31):32374–32384. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06369-3
Fahrig L (2003) Effects of habitat fragmentation on biodiversity. Annu Rev Ecol Evol Syst 34(1):487–515. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.ecolsys.34.011802.132419
Fang G, Li M, Liu XJ et al (2018) Preliminary report on Sichuan golden snub-nosed monkeys (Rhinopithecus roxellana roxellana) at Laohegou Nature Reserve, Sichuan, China. Sci Rep 8(1):16183. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-34311-z
Fick SE, Hijmans RJ (2017) WorldClim 2: new 1-km spatial resolution climate surfaces for global land areas. Int J Climatol 37(12):4302–4315. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.5086
Guo S, Ji W, Li B, Li M (2008) Response of a group of Sichuan snub-nosed monkeys to commercial logging in the Qinling Mountains, China. Conserv Biol 22(4):1055–1064. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1523-1739.2008.00975.x
Hanski I (2015) Habitat fragmentation and species richness. J Biogeogr 42(5):989–993. https://doi.org/10.1111/jbi.12478
He H, Zhao H, Qi X et al (2013) Dominance rank of adult females and mating competition in Sichuan snub-nosed monkeys (Rhinopithecus roxellana) in the Qinling Mountains, China. Chin Sci Bull 58(18):2205–2211. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-012-5649-2
He LP, Ma CS, Jin QY et al (2014) Species and protection measures for mammals in Yuhe Provincial Nature Reserve of Gansu. J Gansu For Sci Technol 39(03):41–43+58. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1006-0960.2014.03.012
He L, Ma C, Jin Q et al (2015) Analysis of threatened factors for wild animals in Yuhe Nature Reserve, Gansu. Gansu Sci Technol 31(15):6–8 (CNKI:SUN:GSKJ.0.2015-15-005)
He G, Yang H, Pan R et al (2020) Using unmanned aerial vehicles with thermal-image acquisition cameras for animal surveys: a case study on the Sichuan snub-nosed monkey in the Qinling Mountains. Integr Zool 15(1):79–86. https://doi.org/10.1111/1749-4877.12410
Hou R, He S, Wu F et al (2018) Seasonal variation in diet and nutrition of the northern-most population of Rhinopithecus roxellana. Am J Primatol 80(4):e22755. https://doi.org/10.1002/ajp.22755
Huang P, Bian K, Huang Z et al (2021) Human activities and elevational constraints restrict ranging patterns of snub-nosed monkeys in a mountainous refuge. Integr Zool 16(2):202–213. https://doi.org/10.1111/1749-4877.12490
Jackson CR, Robertson MP (2011) Predicting the potential distribution of an endangered cryptic subterranean mammal from few occurrence records. J Nat Conserv 19(2):87–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnc.2010.06.006
Kufa CA, Bekele A, Atickem A (2022) Impacts of climate change on predicted habitat suitability and distribution of Djaffa Mountains Guereza (Colobus guereza gallarum, Neumann 1902) using MaxEnt algorithm in eastern Ethiopian Highland. Glob Ecol Conserv 35:e02094. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gecco.2022.e02094
Li B, He P, Yang X et al (2001) The present status of the Sichuan snub-nosed monkey in the Qinling Mountains of China, and a proposed conservation strategy for the species. Biosph Conserv Nat Wildl Humans 3(2):107–114. https://doi.org/10.20798/biospherecons.3.2_107
Li B, Pan R, Oxnard CE (2002) Extinction of snub-nosed monkeys in China during the past 400 years. Int J Primatol 23(6):1227–1244. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1021122819845
Li B, Jia Z, Pan R, Ren B (2003) Changes in distribution of the snub-nosed monkey in China. In: Laura KM (ed) Primates in fragments. Springer, Boston, pp 29–51
Li Y, Jiang Z, Li C, Grueter CC (2010) Effects of seasonal folivory and frugivory on ranging patterns in Rhinopithecus roxellana. Int J Primatol 31(4):609–626. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10764-010-9416-4
Li Y, Guo S, Ji W et al (2011) Social play behavior in infant Sichuan snub-nosed monkeys (Rhinopithecus roxellana) in Qinling Mountains, China. Am J Primatol 73(9):845–851. https://doi.org/10.1002/ajp.20944
Li X, Zhao X, Li M (2021) Future effects of climate change and human footprint on the geographical distribution of three snub-nosed monkeys in China. Acta Theriol Sin 41(03):310–320. https://doi.org/10.16829/j.slxb.150513
Liu X, Stanford CB, Yang J, Yao H, Li Y (2013) Foods eaten by the Sichuan snub-nosed monkey (Rhinopithecus roxellana) in Shennongjia National Nature Reserve, China, in relation to nutritional chemistry. Am J Primatol 75(8):860–871. https://doi.org/10.1002/ajp.22149
Luo Z, Zhou S, Yu W et al (2015) Impacts of climate change on the distribution of Sichuan snub-nosed monkeys (Rhinopithecus roxellana) in Shennongjia area, China. Am J Primatol 77(2):135–151. https://doi.org/10.1002/ajp.22317
Margules CR, Pressey RL (2000) Systematic conservation planning. Nature 405(6783):243–253. https://doi.org/10.1038/35012251
Merow C, Smith MJ, Silander JA Jr (2013) A practical guide to MaxEnt for modeling species’ distributions: what it does, and why inputs and settings matter. Ecography 36(10):1058–1069. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0587.2013.07872.x
Muscarella R, Galante PJ, Soley-Guardia M et al (2014) ENMeval: an R package for conducting spatially independent evaluations and estimating optimal model complexity for Maxent ecological niche models. Methods Ecol Evol 5(11):1198–1205. https://doi.org/10.1111/2041-210X.12261
Noss RF, Harris LD (1986) Nodes, network and MUMs: preserving diversity at all scales. Environ Manag 10(3):299–309. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf01867252
Pearce J, Ferrier S (2000) Evaluating the predictive performance of habitat models developed using logistic regression. Ecol Model 133(3):225–245. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-3800(00)00322-7
Phillips SJ, Dudík M (2008) Modeling of species distributions with Maxent: new extensions and a comprehensive evaluation. Ecography 31(2):161–175. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.0906-7590.2008.5203.x
Qi XG, Li BG, Ji WH (2008) Reproductive parameters of wild female Rhinopithecus roxellana. Am J Primatol 70(4):311–319. https://doi.org/10.1002/ajp.20480
Quan G, Xie J (2002) Research on the golden monkeys. Shanghai Scientific & Technological Education Publishing House
Rondinini C, Di Marco M, Chiozza F et al (2011) Global habitat suitability models of terrestrial mammals. Philos Trans R Soc Lond Ser B-Biol Sci 366(1578):2633–2641. https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2011.0113
Şekercioğlu ÇH, Primack RB, Wormworth J (2012) The effects of climate change on tropical birds. Biol Conserv 148(1):1–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocon.2011.10.019
Songer M, Delion M, Biggs A, Huang Q (2012) Modeling impacts of climate change on giant panda habitat. Int J Ecol 108752. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/108752
Su H, Bista M, Li M (2021) Mapping habitat suitability for Asiatic black bear and red panda in Makalu Barun National Park of Nepal from Maxent and GARP models. Sci Rep 11(1):14135. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-93540-x
Sun RY (2001) Principles of animal ecology, 3rd edn. Beijing Normal University Publishing House
Sun X, Long Z, Jia J (2021) A multi-scale Maxent approach to model habitat suitability for the giant pandas in the Qionglai Mountain, China. Glob Ecol Conserv 30:e01766. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gecco.2021.e01766
Tan CL, Guo S, Li B (2007) Population structure and ranging patterns of Rhinopithecus roxellana in Zhouzhi National Nature Reserve, Shaanxi, China. Int J Primatol 28(3):577–591. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10764-007-9147-3
Tirira DG, Sánchez-Sánchez L, Álvarez-Solas S (2021) An update of the geographic distribution of the red-mantled saddle-back tamarin, Leontocebus lagonotus (Callitrichidae), in Ecuador. Int J Primatol 42(4):600–617. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10764-021-00221-7
Wang X, Wang C, Qi X, Guo S, Zhao H, Li B (2013) A newly-found pattern of social relationships among adults within one-male units of golden snub-nosed monkeys (Rhinopithecus roxenalla) in the Qinling Mountains, China. Integr Zool 8(4):400–409. https://doi.org/10.1111/1749-4877.12026
Wang Z, Bai Y, Gao Y, Ma X (2017) Research on vascular plant diversity of Yuhe Reserve in Gansu Province. Genomics Appl Biol 36(11):4829–4835. https://doi.org/10.13417/j.gab.036.004829
Wang P, Teng M, He W, Tang C, Yang J, Yan Z (2018) Using habitat selection index for reserve planning and management for snub-nosed golden monkeys at landscape scale. Ecol Indic 93:838–846. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2018.05.070
Warren DL, Seifert SN (2011) Ecological niche modeling in Maxent: the importance of model complexity and the performance of model selection criteria. Ecol Appl 21(2):335–342. https://doi.org/10.1890/10-1171.1
Wiederholt R, Post E (2011) Birth seasonality and offspring production in threatened Neotropical primates related to climate. Global Change Biol 17(10):3035–3045. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2486.2011.02427.x
Wilson MC, Chen XY, Corlett RT et al (2016) Habitat fragmentation and biodiversity conservation: key findings and future challenges. Landsc Ecol 31(2):219–227. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10980-015-0312-3
Wu Q, Wang L, Zhu R, Yang Y, Jin H, Zou H (2016) Nesting habitat suitability analysis of red-crowned crane in Zhalong Nature Reserve based on MAXENT modeling. Acta Ecol Sin 36(12):3758–3764
Yiming L, Stanford CB, Yuhui Y (2002) Winter feeding tree choice in Sichuan snub-nosed monkeys (Rhinopithecus roxellanae) in Shennongjia Nature Reserve, China. Int J Primatol 23(3):657–675. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1014981919762
Zhang T (1995) Population and conservation of the snub-nosed monkey on the northern slope of the Qin Rause, Gansu, China. In: Xia W, Zhang Y (eds) Primate research and conservation. China Forestry Publishing House, Beijing, pp 138–142
Zhang P, Hu K, Yang B, Yang D (2016) Snub-nosed monkeys (Rhinopithecus spp.): conservation challenges in the face of environmental uncertainty. Sci Bull 61(5):345–348. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-016-1008-z
Zhang J, Wu L, Jiang Z, Lu M, Wang L (2021) Evaluation on the stability of three main forest communities in Yuhe Nature Reserve. J Gansu Agric Univ 56(03):149–158. https://doi.org/10.13432/j.cnki.jgsau.2021.03.019
Zhao D, Li B, Watanabe K (2011) Impact of group size on female reproductive success of free-ranging Rhinopithecus roxellana in the Qinling Mountains, China. Int J Primatol 82(1):1–12. https://doi.org/10.1159/000326058
Zhao H, Wang X, Li J et al (2016) Postconflict behavior among Rhinopithecus roxellana leader males in the Qinling Mountains, China. Curr Zool 62(1):33–37. https://doi.org/10.1093/cz/zov002
Zhao X, Ren B, Garber PA, Li X, Li M (2018) Impacts of human activity and climate change on the distribution of snub-nosed monkeys in China during the past 2000 years. Divers Distrib 24(1):92–102. https://doi.org/10.1111/ddi.12657
Zhao X, Ren B, Li D et al (2019) Climate change, grazing, and collecting accelerate habitat contraction in an endangered primate. Biol Conserv 231:88–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocon.2019.01.007
Zhao H, Li J, Wang X et al (2020) Nutrient strategies of the Sichuan snub-nosed monkey (Rhinopithecus roxellana) when confronted with a shortage of food resources in the Qinling Mountains, China. Glob Ecol Conserv 22:e00963. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gecco.2020.e00963
Acknowledgements
We thank the workers of Yuhe National Nature Reserve for their assistance and support in the field work, Jicheng Liao and Wei Zhao, School of Life Sciences, Lanzhou University, for the guidance on the experiment, and Master Jie Hu of Lanzhou University for her manuscript writing comments. Furthermore, we express our gratitude to the anonymous reviewers for their valuable contributions to improving the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China [31301889], the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities [lzujbky-2021-sp03] and the Natural Science Foundation of Gansu Province, China [22JR5RA468].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SS originally formulated the idea and designed the experiments to guide the fieldwork. CZ, ZJ, DX, CS, BX placed the infrared camera and watched the video. CZ performed data analysis and collaborated with SY on image production, and SY wrote the manuscript. BX made several constructive suggestions on the optimization of the method in the process of revision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical standards
The research employed an ecological analysis based on the geographic location of the study region, life history characteristic data, and environmental variables. There was no field specimen collection in this study, and all experimental data came from video viewing. All experimental protocols were approved by the Institute of Animal Ecology, Lanzhou University.
Conflict of interest
There are no conflicts of interest to declare.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Shi, Y., Cheng, Z., Zeng, J. et al. Prediction of the potential geographic distribution of golden snub-nosed monkey (Rhinopithecus roxellana) in Yuhe National Nature Reserve by Maxent. Biologia 78, 3579–3589 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11756-023-01497-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11756-023-01497-1