Abstract
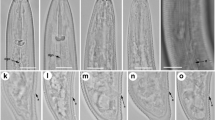
The populations of ectoparasitic nematodes belonging to the family Hoplolaimidae viz., Helicotylencshus dihystera, H. exallus, H. pseudorobustus, and Hoplolaimus seinhorsti were recovered from the soil surrounding the roots of khejri tree (Prosopis cineraria) and Leptadenia pyrotechnica during summer at high temperature (max 50 °C) from the Thar Desert, near Umerkot, Sindh, Pakistan. The species were identified on the basis of morphological and molecular characteristics. According to morphology and morphometrics, these species agree with those of the type species and topotype specimens. The phylogenetic analysis of Helicotylenchus species based on the 18S rDNA placed the studied population in the same clade with other Helicotylenchus with a 1.00 posterior probability. Additionally, phylogenetic analysis of H. seinhorsti using 18S rDNA and cox1 mtDNA sequences placed the Pakistani population close to H. columbus and H. indicus, however, in a different clade with 1.00 posterior probability support value. Measurements, illustrations, LM pictures, and molecular characters of 18S rDNA, and cox1 mtDNA are given. In conclusion, despite the confirmation of the studied species, their ecological role in the agricultural field of Pakistan should be investigated.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmadi MM, Ghaderi R, Kashi L, Karegar A (2016) Observations on Hoplolaimus indicus Sher, 1963 and Hoplolaimus serinhorsti Luc, 1958 (Nematoda: Hoplolaimidae) from Southern Iran. J Crop Protec 5:189–201
Ali SS, Shaheen A, Pervez R (2009) A new species of Hoplolaimus (Basirolaimus) (Hoplolaiminae: Tylenchida) from pigeon pea ecosystem of Bumdel-khand region. Trends Biosci 2:36–48. https://doi.org/10.21307/jofnem-2020-124
Andrássy I (2007) Free-living nematodes of Hungary, II (Nematoda errantia). Budapest, Hungary, Hungarian Natural History Museum and Systematic Zoology Research Group of the Hungarian Academy of Sciences, 496 pp
Ashfaque A, Shahina F, Dawar, Dawar S (2020) Diversity of nematode fauna associated with cotton fields of high temperature areas of Sindh, Pakistan. Pakistan J Nematol 38(1): 25–35. https://doi.org/10.18681/pjn.v38.i01.p25-35
Baermann G (1917) Eine einfache Methode zur Auffindung von Ankylostomum (Nematoden) Larven in Erdproben. Geneeskunding Tijdschrift Voor Nederlandsch-Indië 57:131–137
Boag B, Jairajpuri MS (1985) Helicotylenchus scoticus n. sp. and a conspectus of the genus Helicotylenchus Steiner, 1945 (Tylenchida: Nematoda). Syst Parasitol 7:47–58. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00010161
Bohra P, Sanyal AK, Hussain A, Mitra B (2010) Five new records of nematodes from East Antarctica. J Threat Taxa 2(6):974–977. https://doi.org/10.11609/JoTT.o2342.974-7
Catarina SR, Maria CV, Mariette M, Maria SS, Henk D, Helena F, Wim VDP, Isabel Maria A (2010) First record of Helicotylenchus varicaudatus Yuen, 1964 (Nematoda: Hoplolaimidae) parasitizing Ammophila arenaria (L). Links in Portuguese coastal sand dunes. Phytopathol Medit 49:212–226. https://doi.org/10.14601/Phytopathol_Mediterr-3257
Cobb NA (1893) Nematodes, mostly Australian and Fijian. Linnean Society of New South Wales, Australia, pp 252–308
Cobb NA (1913) New nematode genera found inhabiting fresh water and non-brackish soils. J Wash Acad Sci 3:432–444. https://doi.org/10.5962/bhl.part.20323
Courtney WD, Polley D, Miller VL (1955) TAF, an improved fixative in nematode technique. Plant Dis Rep 39:570–571
Darriba D, Taboada GL, Doallo R, Posada D (2012) jModel Test 2: more models, new heuristics and parallel computing. Nat Methods 9:772. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.2109
De Ley P, Blaxter M (2004) A new system for Nematoda: combining morphological characters with molecular trees, and translating clades into ranks and taxa. In: Proceedings of the fourth international congress of nematology, 8-13 June 2002. Tenerife, Spain, pp 633–653. https://doi.org/10.1163/9789004475236_061
De Man JG (1884) Die frei in der reinen Erde und im süssen Wasser lebenden Nematoden der Niederlandischen Fauna. Eine Systematische Faunistische Monographie, E. J. Brill, Leiden, p 206
Decraemer W, Hunt DJ (2006) Structure and classification. In: Perry RN, Moens M (eds) Plant nematology. CABI Publishing, Wallingford. https://doi.org/10.1079/9781845930561.0003
Derycke S, Remerie T, Vierstraete A, Backeljau T, Vanfleteren J, Vincx M, Moens T (2005) Mitochondrial DNA variation and cryptic speciation within the free-living marine nematode Pellioditis marina. Marine Ecol Progress Ser 300:91–103. https://doi.org/10.3354/meps300091
Divsalar N, Shokoohi E, Marais M, Mashela PW (2020) Molecular and morphological characters of Helicotylenchus Steiner, 1945 species from Iran with a note on the identity of H. pseudorobustus (Steiner, 1914) Golden, 1956. Zootaxa 4789(1):266–280. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4789.1.10
Eroshenko AS, Nguen VT (1981) New species of soil nematodes from Vietnam. Zool Zh 60:1882–1886
Fateh T, Lieven W, Nicole V, Amer D, Julie MN, Francis O, Maurice M (2013) Development of two species-specific primer sets to detect the cereal cyst nematodes Heterodera avenae and Heterodera filipjevi. Eur J Plant Pathol 136(3):613–624. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-013-0192-9
Firoza K, Maqbool MA (1996) Description of Helicotylenchus lemoni n. sp. (Nematoda: Hoplolaimidae) with a key to the species of Pakistan. Pakistan J Nematol 14:83–88
Fortuner R (1984) Morphometrical variability in Helicolylenchus Steiner, 1945. 6: value of the characters used for specific identification. Revue Nématol 7:245–264
Golden AM (1956) Taxonomy of the spiral nematodes (Rotylenchus and Helicotylenchus), and the developmental stages and host-parasitic relationships of R. buxophilus n. sp., attacking boxwood. Maryland Agricultural Experiment Station Bulletin A-85, p 28
Golden AM, Minton NA (1970) Description and larval heteromorphism of Hoplolaimus concaudajuvencus n. sp. (Nematoda: Hoplolaimidae). J Nematol 2:161–166
Guindon S, Gascuel O (2003) A simple, fast and accurate method to estimate large phylogenies by maximum-likelihood. Syst Biol 52:696–704. https://doi.org/10.1080/10635150390235520
Hall TA (1999) BioEdit: a user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucl Acids Symp Ser 41:95–98
Handoo ZA, Golden AM (1992) A key and diagnostic compendium to the species of the genus Hoplolaimus Daday. J Nematol 24(1):45–53
Holterman M, van der Wurff A, van den Elsen ES, van Megen H, Bongers T, Holovachov O, Bakker J, Helder J (2006) Phylum-wide analysis of SSU rDNA reveals deep phylogenetic relationships among nematodes and accelerated evolution toward crown Clades. Mol Biol Evol 23(9):1792–1800. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msl044
Ichinohe M (1952) On the soybean nematode, Heterodera glycines n. sp., from Japan (trans.). Oyo-Dobutsugaku-Zasshi 17:1–4
Ivanova TS (1967) Parasitic nematodes of the subfamily Hoplolaiminae in Tadzhikistan. Izestuya. Akademii Nauk Tadzhikskoi SSR 1: 97–100. [Original in Russian]
Kornobis S, Dobosz R (1966) Some species of Tylenchida (Nemata) from North Korea. J Plant Prot Res 39(2):113–116
Lewis SA, Smith FH, Powell WM (1976) Host-parasite relationships of Hoplolaimus columbus on cotton and soybean. J Nematol 8(2):142–145
Li HM, Gandarilla B, Hortensia YRL, Lamberto, (2011) Phytonematodes associated to Arecaceae plants in antient Havana Province. Fitosanidad 15:36–46
Luc M (1958) Nematodes and wilting in cotton in Southwestern Madagascar. Cot Et Fibr Trap 13:239–256
Ma X, Robbins R, Bernard E, Holguin C, Agudelo P (2019) Morphological and molecular characterisation of Hoplolaimus smokyensis n. sp. (Nematoda: Hoplolaimidae), a lance nematode from Great Smoky Mountains National Park, USA. Nematology 21(9):923–935. https://doi.org/10.1163/15685411-00003266
Maqbool MA, Shahina F (2001) Systematics and distribution. Biodiversity of nematode fauna in Pakistan. National Nematological Research Centre, University of Karachi, Karachi, Pakistan
Marais M (2001) A monograph of the genus Helicotylenchus Steiner, 1945 (Nemata: Hoplolaimidae). Ph.D. Dissertation, University of Stellenbosch, Stellenbosch, South Africa
Nguyen TH, Bui QD, Trinh PQ (2015) Description of Hoplolaimus bachlongviensis sp. n. (Nematoda: Hoplolaimidae) from banana soil in Vietnam. Biodiversity Data Journal 3:e6523. https://doi.org/10.3897/BDJ.3.e6523
Palomares-Rius JE, Cantalapiedra-Navarrete C, Archidona-Yuste A, Vovlas N, Tzortzakakis EA, Castillo P (2018) Molecular and morophological characterization of the spiral nematode Helicotylenchus oleae Inserra, Vovlas & Golden, 1979 (Nematoda: Hoplolaimidae) in the Mediterranean Basin. Eur J Plant Pathol 150:881–891. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-017-1330-6
Perry VG, Darling MH, Throne G (1959) Anatomy, taxonomy and control of certain spiral nematodes attacking blue grass in Wisconsin. Univ Wisconsin Res Bull 207:1–24
Robbins RT (1982) Description of Hoplolaimus magnistylus n. sp. (Nematoda: Hoplolaimidae). J Nematol 14:500–506
Ronquist F, Huelsenbeck J (2003) Mr Bayes 3: Bayesian phylogenetic inference under mixed models. Bioinformatics 19:1572–1574. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btg180
Rybarczyk-Mydłowska K, van Megen H, van den Elsen S, Mooijman P, Karssen G, Bakker J, Helder J (2014) Both SSU rDNA and RNA polymerase II data recognize that root-knot nematodes arose from migratory Pratylenchidae, but probably not from one of the economically high-impact lesion nematodes. Nematology 16:125–136. https://doi.org/10.1163/15685411-00002750
Seinhorst JW (1959) A rapid method for the transfer of nematodes from fixative to anhydrous glycerine. Nematologica 4:67–69
Shahina F, Nasira K, Firoza K, Erum YI (2019) Overview of the nematode fauna of Pakistan. Pakistan J Nematol 37:171–243. https://doi.org/10.18681/pjn.v37.i02.p171-243
Sher SA (1961) Revision of the Hoplolaiminae (Nematoda). I. Classification of nominal genera and nominal species. Nematologica 6:155–169. https://doi.org/10.1163/187529261X00414
Sher SA (1963) Revision of the Hoplolaiminae (Nematoda) II. Hoplolaimus Daday, 1905 and Aorolaimus n. gen. Nematologica 9:267–295. https://doi.org/10.1163/187529263X00476
Sher SA (1966) Revision of the Hoplolaiminae (Nematoda) VI. Helicotylenchus Steiner, 1945. Nematologica 12:1–56. https://doi.org/10.1163/187529266X00013
Shokoohi E (2022) Observation on Hemicriconemoides brachyurus (Loof, 1949) Chitwood & Birchfield, 1957 Associated with grass in South Africa. Helminthologia 59(2):210–216. https://doi.org/10.2478/helm-2022-0019
Shokoohi E, Abolafia J, Mashela PW (2022) Redescription of Hoplolaimus indicus Sher, 1963 (Rhabditida, Hoplolaimidae) from Iran, including the first SEM study of the species. Biologia 77:2161–2172. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11756-022-01104-9
Shokoohi E, Marais M, Fourie H, Panahi H (2018) Morphological and molecular characterization of three Helicotylenchus species from Iran. Zootaxa 4388 (2):207–220. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4388.2.4
Shokoohi E, Marais M, Mashela PW, Divsalar N (2021) Morphological and molecular variations within Helicotylenchus vulgaris. Biologia 76:549–563. https://doi.org/10.2478/s11756-020-00551-6
Shokoohi E, Swart A, Marais M (2023) Characterization of Acrobeloides longiuterus (Rashid & Heyns, 1990) Siddiqi, De Ley & Khan, 1992 (Rhabditida: Cephalobidae) from South Africa including the SEM study of the species. Zoomorphol 142:13–25. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00435-022-00583-3
Siddiqi MR (1963) Two new species of the genus Helicotylenchus Steiner, 1945 (Nematoda: Hoplolaiminae). Z Parasitenkd 23:238–244. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf00259374
Siddiqi MR (2000) Tylenchida parasites of plants and insects, 2nd edn. CABI Publishing, Wallingford
Steiner G (1914) Freilebende Nematodes aus der Schweiz. 1. Teil einer vorlaufigen Mitteilung. Arch Hydrobiol Planktonkd 9:259–276
Steiner G (1945) Helicotylenchus, a new genus of plant-parasitic nematodes and its relationship to Rotylenchus Filipjev. Proc Helminthol Soc Wash 12:34–38
Subbotin SA, Inserra RN, Marais M, Mullin P, Powers TO, Roberts PA, Van Den Berg E, Yeates GW, Baldwin JG (2011) Diversity and phylogenetic relationships within the spiral nematodes of Helicotylenchus Steiner, 1945 (Tylenchida: Hoplolaimidae) as inferred from analysis of the D2–D3 expansion segments of 28S rRNA gene sequences. Nematology 13:333–345. https://doi.org/10.1163/138855410X520936
Subbotin SA, Vovlas O, Yeates GW, Hallmann J, Kiewnick S, Chizhov VN, Manzanilla-López RH, Inserra RN, Castillo P (2015) Morphological and molecular characterization of Helicotylenchus pseudorobustus (Steiner, 1914) Golden, 1956 and related species (Tylenchida: Hoplolaimidae) with a phylogeny of the genus. Nematology 17:27–52. https://doi.org/10.1163/15685411-00002850
Szczygiel A (1970) Tylenchorhynchus polonicus sp. n. and Helicotylenchus pseudodigonicus sp. n. (Nematoda, Tylenchoidea) from Poland. Bull Acad Polonaise Des Sci Warszawa 17:295–690
Thompson JD, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ (1994) CLUSTAL W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucl Acids Res 22:4673–4680
Thorne G (1935) Notes on free-living and plant parasitic nematodes. II. Proc Helminth Soc Wash 2:96–98
Tiwari AK, Misra SL, Malhotra SK (2001) Bioecology of nematodes in soil of a sub-humid region. I. Hoplolaimus johani sp. nov. and Hoplolaimus caudifurcatus sp. nov. around fruit crops. Bulgarian Acad Sci Exp Pathol Parasitol 4:8–19
Uzma I, Nasira K, Firoza K, Shahina F (2015) Review of the genus Helicotylenchus Steiner, 1945 (Nematoda: Hoplolaimidae) with updated diagnostic compendium. Pakistan J Nematol 33: 115–160. https://doi.org/10.18681/2015.v33.i02.p01201507310001
Van Den Berg E, Heyns J (1975) South African Hoplolaiminae. 4. The genus Helicotylenchus Steiner, 1945. Phytophylactica 7:35–52
Vovlas N, Troccoli A, Rodrigues C (1995) Supplemental female morphology and male description of Helicotylenchus variocaudatus from banana roots. Nematol Medit 23:93–99
Waseem M (1961) Two new species of the genus Helicotylenchus Steiner, 1945 (Nematoda: Hoplolaiminae). Can J Zool 39:505–509. https://doi.org/10.1139/z61-054
Yeates GW, Wouts WM (1992) Helicotylenchus spp (Nematoda, Tylenchida) from managed soils in New-Zealand. New Zealand J Zool 19(1–2):13–23
Yuen PH (1964) Four new species of Helicotylenchus Steiner (Hoplolaimidae: Tylenchida) and a redescription of H. canadensis Waseem, 1961. Nematologica 10:373–387. https://doi.org/10.1163/187529264X00385
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Dr. Firoza Kazi for providing literature.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ali, R., Shokoohi, E., Iqbal, E. et al. Morphological and molecular observations of nematodes belonging to the family Hoplolaimidae from the Thar Desert, Pakistan. Biologia 78, 3463–3477 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11756-023-01483-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11756-023-01483-7