Abstract
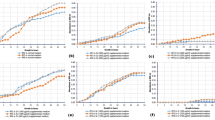
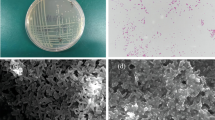
Soil is one of the great reservoirs of microorganisms. A multiple-metal resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain isolated from arable soil was screened for lipase activity since it plays a crucial role in bacterial cellular metabolism. This strain showed higher minimum inhibitory concentrations for the metal Ni, Zn and Cd. The effect of these heavy metals on lipase production was studied by examining qualitative and quantitative aspects of lipase activity in tributyrin agar base medium and lipase production media, respectively. The lipase activity was found to be 304.45 U/L in the control group (without heavy metals), which was higher than in the groups treated with heavy metals. A statistically significant difference was detected in the metal-induced alteration of the lipolytic activity of the studied strain. The inhibitory effect of the heavy metals on lipase production was assessed, with Zn showing the highest inhibition, while Ni exhibited the lowest inhibitory effect among the three metals studied. The lipolytic activity of the strain was altered by the heavy metals, as demonstrated by ATR-FTIR analysis that revealed changes in the functional groups involved in lipase production under heavy metal stress compared to the control. This study is the first attempt to investigate the extracellular lipase activity of a multiple heavy metal-resistant Pseudomonas strain isolated from arable soil of Uttar Dinajpur region of West Bengal, India, which requires further research for future utilization.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this article.
Code availability
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
- FTIR:
-
Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy
- MIC:
-
Minimum inhibitory concentration
- TBA:
-
Tributyrin agar
- ROA:
-
Rhodamine olive oil agar
- PM I:
-
Production medium I
- PM II:
-
Production medium II
- TPH:
-
Thymolphthalein
- MTC:
-
Maximum tolerable concentration
- ATR-FTIR:
-
Attenuated total reflectance - Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy
- ANOVA:
-
Analysis of variance
References
Akhter K, Karim I, Aziz B, Bibi A, Khan J, Akhtar T (2022) Optimization and characterization of alkaliphilic lipase from a novel Bacillus cereus NC7401 strain isolated from diesel fuel polluted soil. PLoS ONE 17(8):e0273368. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0273368
Al-Dhabi NA, Esmail GA, Ghilan A-KM, Arasu MV (2020) Isolation and screening of Streptomyces sp. Al-Dhabi-49 from the environment of Saudi Arabia with concomitant production of lipase and protease in submerged fermentation. Saudi J Biol Sci 27(1):474–479. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sjbs.2019.11.011
Anbu P, Hur BK (2014) Isolation of an organic solvent-tolerant bacterium Bacillus licheniformis PAL05 that is able to secrete solvent-stable lipase. Biotechnol Appl Biochem 61(5):528–534. https://doi.org/10.1002/bab.1202
Beech I, Hanjagsit L, Kalaji M, Neal AL, Zinkevich V (1999) Chemical and structural characterization of exopolymers produced by Pseudomonas sp. NCIMB 2021 in continuous culture. Microbiol (Reading) 145(6):1491–1497. https://doi.org/10.1099/13500872-145-6-1491
Carrazco-Palafox J, Rivera-Chavira BE, Ramírez-Baca N, Manzanares-Papayanopoulos LI, Nevárez-Moorillón GV (2018) Improved method for qualitative screening of lipolytic bacterial strains. MethodsX 5:68–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mex.2018.01.004
Chandra P, Enespa, Singh R, Arora PK (2020) Microbial lipases and their industrial applications: a comprehensive review. Microb Cell Fact 19(1):169. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-020-01428-8
Choudhary S, Sar P (2009) Characterization of a metal resistant Pseudomonas sp. isolated from uranium mine for its potential in heavy metal (Ni2+, Co2+, Cu2+, and Cd2+) sequestration. Bioresour Technol 100(9):2482–2492. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2008.12.015
Dandavate V, Jinjala J, Keharia H, Madamwar D (2009) Production, partial purification and characterization of organic solvent tolerant lipase from Burkholderia multivorans V2 and its application for ester synthesis. Bioresour Technol 100(13):3374–3381. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2009.02.011
Daniel WW (1990) Applied nonparametric statistics. PWS-Kent Publ
de Bruijn FJ (1992) Use of repetitive (repetitive extragenic palindromic and enterobacterial repetitive intergeneric consensus) sequences and the polymerase chain reaction to fingerprint the genomes of Rhizobium meliloti isolates and other soil bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 58(7):2180–2187. https://doi.org/10.1128/aem.58.7.2180-2187.1992
Devi R, Madhavan Nampoothiri K, Sukumaran RK, Sindhu R, Arumugam M (2020) Lipase of Pseudomonas guariconesis as an additive in laundry detergents and transesterification biocatalysts. J Basic Microbiol 60(2):112–125. https://doi.org/10.1002/jobm.201900326
Dhevahi B, Gurusamy R (2014) Factors influencing production of lipase under metal supplementation by bacterial strain, Bacillus subtilis BDG-8. J Environ Biol 35(6):1151–1155
Eggert T, Brockmeier U, Dröge MJ, Quax WJ, Jaeger KE (2003) Extracellular lipases from Bacillus subtilis: regulation of gene expression and enzyme activity by amino acid supply and external pH. FEMS Microbiol Lett 225(2):319–324. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0378-1097(03)00536-6
Eltaweel MA, Rahman RNZRA, Salleh AB, Basri M (2005) An organic solvent-stable lipase from Bacillus sp. strain 42. Ann Microbiol 55(3):187–192
Faghihzadeh F, Anaya NM, Schifman LA, Oyanedel-Craver V (2016) Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy to assess molecular-level changes in microorganisms exposed to nanoparticles. Nanotechnol Environ Eng 1(1):1. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41204-016-0001-8
Gupta R, Gupta N, Rathi P (2004) Bacterial lipases: an overview of production, purification and biochemical properties. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 64(6):763–781. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-004-1568-8
Hasan F, Shah A, Hameed A (2006) Industrial applications of microbial lipases. Enzyme Microb Technol 39:235–251. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enzmictec.2005.10.016
Hasan-Beikdashti M, Forootanfar H, Safiarian MS, Ameri A, Ghahremani MH, Khoshayand MR, Faramarzi MA (2012) Optimization of culture conditions for production of lipase by a newly isolated bacterium Stenotrophomonas maltophilia. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 43(5):670–677. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2012.03.005
Hu C, Guo J, Qu J, Hu X (2007) Photocatalytic degradation of pathogenic bacteria with AgI/TiO2 under visible light irradiation. Langmuir 23(9):4982–4987. https://doi.org/10.1021/la063626x
Ilesanmi OI, Adekunle AE, Omolaiye JA, Olorode EM, Ogunkanmi AL (2020) Isolation, optimization and molecular characterization of lipase producing bacteria from contaminated soil. Sci Afr 8:e00279. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sciaf.2020.e00279
Jagdish P, Deepa V, Rohan G (2013) Production of microbial lipases isolated from curd using waste oil as a substrate. Res J Pharm Biol Chem Sci 4:831–839
Javed S, Azeem F, Hussain S, Rasul I, Siddique MH, Riaz M, Afzal M, Kouser A, Nadeem H (2018) Bacterial lipases: a review on purification and characterization. Prog Biophys Mol Biol 132:23–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbiomolbio.2017.07.014
Jette JF, Ziomek E (1994) Determination of lipase activity by a rhodamine-triglyceride-agarose assay. Anal Biochem 219(2):256–260. https://doi.org/10.1006/abio.1994.1265
Joseph B, Shrivastava N, Ramteke PW (2012) Extracellular cold-active lipase of Microbacterium luteolum isolated from Gangotri glacier, western Himalaya: isolation, partial purification and characterization. J Genet Eng Biotechnol 10(1):137–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jgeb.2012.02.001
Kai W, Peisheng Y (2016) Optimization of lipase production from a novel strain Thalassospira permensis M35-15 using response surface methodology. Bioengineered 7(5):298–303. https://doi.org/10.1080/21655979.2016.1197713
Karadzic I, Masui A, Zivkovic LI, Fujiwara N (2006) Purification and characterization of an alkaline lipase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated from putrid mineral cutting oil as component of metalworking fluid. J Biosci Bioeng 102(2):82–89. https://doi.org/10.1263/jbb.102.82
Kazy SK, Sar P, Asthana RK, Singh SP (1999) Copper uptake and its compartmentalization in Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains: Chemical nature of cellular metal. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 15(5):599–605. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008997718811
Kazy SK, Das SK, Sar P (2006) Lanthanum biosorption by a Pseudomonas sp.: equilibrium studies and chemical characterization. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 33(9):773–783. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-006-0108-1
Kepenek ES, Gozen AG, Severcan F (2019) Molecular characterization of acutely and gradually heavy metal acclimated aquatic bacteria by FTIR spectraoscopy. J Biophotonis 12(5):e201800301. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbio.201800301
Kepenek ES, Severcan M, Gozen AG, Severcan F (2020) Discrimination of heavy metal acclimated environmental strains by chemometric analysis of FTIR spectra. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 202:110953. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.110953
Kouker G, Jaeger KE (1987) Specific and sensitive plate assay for bacterial lipases. Appl Environ Microbiol 53(1):211–213. https://doi.org/10.1128/aem.53.1.211-213.1987
Kumar A, Mukhia S, Kumar N, Acharya V, Kumar S, Kumar R (2020) A broad temperature active lipase purified from a psychrotrophic bacterium of Sikkim Himalaya with potential application in detergent formulation. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 8:642. https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2020.00642
Lanka S, Naveena Lavanya Latha J (2015) A short review on various screening methods to isolate potential lipase producers: lipases-the present and future enzymes of biotech industry. Int J Biol Chem 9:207–219. https://doi.org/10.3923/ijbc.2015.207.219
Mackie RI, White BA, Bryant MP (1991) Lipid metabolism in anaerobic ecosystems. Crit Rev Microbiol 17(6):449–479. https://doi.org/10.3109/10408419109115208
Makhzoum A, Knapp JS, Owusu RK (1995) Factors affecting growth and extracelluar lipase production by Pseudomonas fluorescens 2D. Food Microbiol 12:277–290. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0740-0020(95)80108-1
Midway S, Robertson M, Flinn S, Kaller M (2020) Comparing multiple comparisons: practical guidance for choosing the best multiple comparisons test. PeerJ 8:e10387–e10387. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.10387
Mo Q, Liu A, Guo H, Zhang Y, Li M (2016) A novel thermostable and organic solvent-tolerant lipase from Xanthomonas oryzae pv. Oryzae YB103: screening, purification and characterization. Extremophiles 20(2):157–165. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-016-0809-y
Mobarak-Qamsari E, Kasra-Kermanshahi R, Moosavi-Nejad Z (2011) Isolation and identification of a novel, lipase-producing bacterium, Pseudomnas aeruginosa KM110. Iran J Microbiol 3(2):92–98
Motulsky H (2010) Power of Holm’s multiple comparison testing compared to others. Cross Validated. https://stats.stackexchange.com/q/109
Näher G (1974) Lipase Titrimetric Assay. In: Bergmeyer HU (eds) Methods of Enzymatic Analysis (Second Edition), Academic Press, New York, pp 814–818
Pham VHT, Kim J, Chang S, Chung W (2021) Investigation of lipolytic-secreting bacteria from an artificially polluted soil using a modified culture method and optimization of their lipase production. Microorganisms 9(12):2590. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9122590
Plou FJ, Ferrer M, Nuero OM, Calvo MV, Alcalde M, Reyes F, Ballesteros A (1998) Analysis of tween 80 as an esterase/ lipase substrate for lipolytic activity assay. Biotechnol Tech 12(3):183–186. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008809105270
Rabbani M, Shafiee F, Shayegh Z, MirMohammadSadeghi H, Samsam Shariat Z, Etemadifar Z, Moazen F (2015) Isolation and characterization of a new thermoalkalophilic lipase from soil bacteria. Iran J Pharm Res 14(3):901–906
Rameshwaram NR, Singh P, Ghosh S, Mukhopadhyay S (2018) Lipid metabolism and intracellular bacterial virulence: key to next-generation therapeutics. Future Microbiol 13:1301–1328. https://doi.org/10.2217/fmb-2018-0013
Rohman A (2017) Infrared spectroscopy for quantitative analysis and oil parameters of olive oil and virgin coconut oil: a review. Int J Food Prop 20(7):1447–1456. https://doi.org/10.1080/10942912.2016.1213742
Ruiz C, Pastor FI, Diaz P (2005) Isolation of lipid- and polysaccharide-degrading micro-organisms from subtropical forest soil, and analysis of lipolytic strain Bacillus sp. CR-179 Lett Appl Microbiol 40(3):218–227. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1472-765X.2005.01660.x
Sachan S, Iqbal MS, Singh A (2018) Extracellular lipase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa JCM5962(T): isolation, identification, and characterization. Int Microbiol 21(4):197–205. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10123-018-0016-z
Saha J, Dey S, Pal A (2022) Whole genome sequencing and comparative genomic analyses of Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain isolated from arable soil reveal novel insights into heavy metal resistance and codon biology. Curr Genet 68(3):481–503. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00294-022-01245-z
Tarhan I, Ismail A, Kara A H (2017) Quantitative determination of free fatty acids in extra virgin olive oils by multivariate methods and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy considering different absorption modes. Int J Food Prop 20:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1080/10942912.2017.1312437
Ugras S, Uzmez S (2016) Characterization of a newly identified lipase from a lipase-producing bacterium. Front Biol 11(4):323–330. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11515-016-1409-z
Velu N, Divakar K, Nandhinidevi G, Gautam P (2012) Lipase from Aeromonas caviae AU04: isolation, purification and protein aggregation. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol 1(1):45–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcab.2011.08.004
Yao W, Liu K, Liu H, Jiang Y, Wang R, Wang W, Wang T (2021) A valuable product of microbial cell factories: microbial lipase. Front Microbiol 12:743377. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2021.743377
Yele VU, Desai K (2015) A new thermostable and organic solvent-tolerant lipase from Staphylococcus warneri; optimization of media and production conditions using statistical methods. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 175(2):855–869. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-014-1331-2
Yu JE, Han SY, Wolfson B, Zhou Q (2018) The role of endothelial lipase in lipid metabolism, inflammation, and cancer. Histol Histopathol 33(1):1–10. https://doi.org/10.14670/hh-11-905
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge DST-SAIF, IIT Madras for their sophisticated analytical services (ATR-FTIR).
Funding
None of the authors has received any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JS: Conceptualization, Methodology, Investigation, Original draft writing, Data acquisition and analysis; MGC: Investigation, experimentation, initial draft writing, Data analysis; SK: Methodology, Investigation, Data collection and manipulation; AC: Conceptualization, Methodology, Review, Visualization; AP: Conceptualization, Supervision, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – Original Draft, Review & Editing, Validation, Visualization, Resources.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest/Competing interests
All the authors declare that they have no.
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
All the authors consented to publish the article.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Saha, J., Chaki, M.G., Karmakar, S. et al. Effect of different heavy metals on lipase production by a multiple heavy metal-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain isolated from arable land. Biologia 78, 2975–2985 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11756-023-01465-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11756-023-01465-9