Abstract
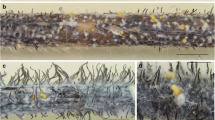
Seed health plays a pivotal role in profitable crop production. However, seed-borne pathogens deteriorate seed health and reduce the market value of crops. Curvularia lunata is an important fungus associated with seeds of several crops. In the present study, broken, discolored and unhealthy seeds were observed during the inspection of soybean germplasm entries indicative of a fungal disease. The suspected fungus was isolated from these seeds using blotter paper and potato dextrose agar. Purified growth of fungus on nutrient media was smooth, regular and conidia were curved which appeared to be C. lunata. DNA was isolated and Internal transcribed spacer (ITS) region was amplified. The amplicon (550 bp) of three isolates NBGCLI-III were sequenced. NCBI BLASTn confirmed assembled sequences as C. lunata. These sequences were submitted to NCBI GenBank with accession numbers OP093623-25. Soybean seeds were also subjected to culture filtrate of these isolates. Inoculated seeds showed reduced germination and the seedlings produced were abnormal as observed earlier when compared to untreated control. From infected seeds fungal DNA was isolated and ITS region was amplified and sequenced. The sequence results confirmed the presence of C. lunata. Hence, the present study has shown the deleterious effects of C. lunata on seed health in soybean and suggests the use of diseased-free seeds for better germination and vigorous crop.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets used in this study are available in the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) database under accession numbers OP093623, OP093624, OP093625, respectively.
References
Anwar SA, Riaz S, Ahmad C, Subhani M, Chattha M (2013) Mycoflora associated with stored seeds of soybean. Mycopath 11(2):85–90
Aslam S, Tahir A, Aslam MF, Alam MW, Shedayi AA, Sadia S (2017) Recent advances in molecular techniques for the identification of phytopathogenic fungi–a mini review. J Plant Interact 12(1):493–504. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcimb.2020.600234
Azizi MMF, Mardhiah NH, Yih LH (2022) Current and emerging molecular technologies for the diagnosis of plant diseases–An overview. J Experim Biol 2294–305. https://doi.org/10.18006/2022.10(2).294.305
Bishaw Z, Struik P, Van Gastelc A (2013) Farmer’s seed sources and seed quality: 2. Seed health. Int J Plant Prod 7(4):637–658. https://doi.org/10.22069/IJPP.2013.1261
Carneiro GA, Matic S, Ortu G, Garibaldi A, Spadaro D, Gullino ML (2017) Development and validation of a TaqMan real-time PCR assay for the specific detection and quantification of Fusarium fujikuroi in rice plants and seeds. Phytopathol 107(7):885–892. https://doi.org/10.1094/PHYTO-10-16-0371-R
Chang JY, Liu SS, Jie SH, Ning GU, Zhang HJ, Jie CH (2020) A new Curvularia lunata variety discovered in Huanghuaihai Region in China. J Integr Agricul 19(2):551–560. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2095-3119(19)62655-9
Cheng Y, Tang X, Gao C, Li Z, Chen J, Guo L, Wang T, Xu J (2020) Molecular diagnostics and pathogenesis of fungal pathogens on bast fiber crops. Pathogens 9(3):223. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9030223
Doyle JJ (1990) Isolation of plant DNA from fresh tissue. Focus 12:13–15
El-Zayat M, Mansour I, Moursy M, Abdel-Fattah M, El-Sayed F (1990) Stalk and root rots of certain cereal forage crops in Egypt. Ann Agric Sci Moshtohor 28(3):1525–1537
Franke J, Geary B, Meyer SE (2014) Identification of the infection route of a Fusarium seed pathogen into nondormant Bromus tectorum seeds. Phytopathology 104(12):1306–1313. https://doi.org/10.1094/PHYTO-03-14-0077-R
Garibyan L, Avashia N (2013) Research techniques made simple: polymerase chain reaction (PCR). The J Invest Dermatol 133(3):e6. https://doi.org/10.1038/jid.2013.1
Gebeyaw M (2020) Review on: impact of seed-borne pathogens on seed quality. Am J Plant Biol 5:77–81. https://doi.org/10.11648/j.ajpb.20200504.11
Gupta S, Dubey A, Singh T (2017) Curvularia lunata as, a dominant seed-borne pathogen in Dalbergia sissoo Roxb: its location in seed and its phytopathological effects. Afr J Plant Sci 11(6):203–208. https://doi.org/10.5897/AJPS2017.1529
Hou J, Ma B, Zuo Y, Guo L, Gao S, Wang Y, Liu T (2013) Rapid and sensitive detection of C urvularia lunata associated with maize leaf spot based on its C lg2p gene using semi-nested PCR. Lett Appl Microbiol 56(4):245–250. https://doi.org/10.1111/lam.12040
Innis MA, Gelfand DH, Sninsky JJ, White TJ (2012) PCR protocols: A guide to methods and applications. Academic press. https://doi.org/10.1016/0307-4412(91)90165-5
Kakde RB, Chavan AM (2011) Extracellular lipase enzyme production by seed-borne fungi under the influence of physical factors. Int J Biol 3(1):94. https://doi.org/10.5539/ijb.v3n1p94
Keinath A, Farnham M, Zitter T (1995) Morphological, pathological, and genetic differentiation of Didymella bryoniae and Phoma spp. isolated from cucurbits. Phytopathol 65(3):364–369. https://doi.org/10.1094/Phyto-85-364
Kumar S, Stecher G, Li M, Knyaz C, Tamura K (2018) MEGA X: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms. Mol Biol Evol 35(6):1547. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msy096
Kusai NA, Mior Zakuan Azmi M, Zulkifly S, Yusof MT, Mohd Zainudin NAI (2016) Morphological and molecular characterization of Curvularia and related species associated with leaf spot disease of rice in Peninsular Malaysia. Rend lincei 27(2):205–214. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12210-015-0458-6
Manamgoda DS, Rossman AY, Castlebury LA, Chukeatirote E, Hyde K (2015) A taxonomic and phylogenetic re-appraisal of the genus Curvularia (Pleosporaceae): human and plant pathogens. Phytotaxa 212(3):175–198. https://doi.org/10.11646/phytotaxa.212.3.1
Marin FY, Hernandez RM, Crous PW (2020) Multi-locus phylogeny of the genus Curvularia and description of ten new species. Mycol Prog 19:559–588. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11557-020-01576-6
Martin RR, James D, Lévesque CA (2000) Impacts of molecular diagnostic technologies on plant disease management. Ann Rev Phytopathol 38(1):207–239. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.phyto.38.1.207
McCartney HA, Foster SJ, Fraaije BA, Ward E (2003) Molecular diagnostics for fungal plant pathogens. Pest Manage Science: Former Pesticide Sci 59(2):129–142. https://doi.org/10.1002/ps.575
Milner H, Ji P, Sabula M, Wu T (2019) Quantitative polymerase chain reaction (Q-PCR) and fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH) detection of soilborne pathogen Sclerotium rolfsii. Appl Soil Ecol 136:86–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2019.01.002
Mohammad S, Mukesh S, Antima S, Anuradha S, Sonika P, Vipul K, Neelam P, Smita R (2013) Molecular characterization of Trichoderma longibrachiatum 21PP isolated from rhizospheric soil based on universal ITS primers. Afr J of Microbiol Res 7(41):4902–4906. https://doi.org/10.5897/AJMR2013.5761
Muhammad I, Anwar S, Azar I, Nazir A, Arain M (2012) Seed-borne fungi associated with cauliflower seeds and their role in seed germination. Pak J Phytopathol 24(1):26–31
Prom LK (2004) The effects of Fusarium thapsinum, Curvularia lunata, and their combination on sorghum germination and seed mycoflora. J New Seeds 6(1):39–49. https://doi.org/10.1300/J153v06n01_03
Rahman SU, Raza G, Zubair M, Ahmed N, Domier LL, Jamil N, Mansoor S, Amin I (2023) Multiple begomoviruses infecting soybean; a case study in Faisalabad. Pakistan Biol 78(2):609–620
Rajput NA, Pathan M, Rajput AQ, Jiskani M, Lodhi AM, Rajput SA, Khaskhali M (2010) Isolation of fungi associated with shisham trees and their effect on seed germination and seedling mortality. Pak J Bot 42(1):369–374
Santos PRRd, Leão EU, Aguiar RWdS, MPd M, Santos GRd (2018) Morphological and molecular characterization of Curvularia lunata pathogenic to Andropogon grass. Bragantia 77:326–332. https://doi.org/10.1590/1678-4499.2017258
Shabana YM, Rashad YM, Ghoneem KM, Arafat NS, Aseel DG, Qi A, Richard B, Fitt BD (2021) Biodiversity of pathogenic and toxigenic seed-borne mycoflora of wheat in Egypt and their correlations with Weather variables. Biol 10(10):1025. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10101025
Sharma K, Goss EM, Dickstein ER, Smith ME, Johnson JA, Southwick FS, van Bruggen AH (2014) Exserohilum rostratum: characterization of a cross-kingdom pathogen of plants and humans. PLoS ONE 9(10):e108691. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0108691
Sheppard J (1998) Seed-borne pathogens of vegetable and flower seeds: their devastation, identification and control.Seed Technol:187–197
Singh R (2002) Seed and Seedling Diseases of Pearl Millet and their Control. Ph. D. Thesis, University of Rajasthan, Jaipur
Tufail AS, Muhammad I, Safdar AA, Raza MM, Zubair AN (2020) Effect of Alternaria sp on seed germination in rapeseed, and its control with seed treatment. J Cereals Oilseeds 11(1):1–6
Ustun R, Ahmet Ç, ÇATAL M, Bülent U (2021) Identification of Seedborne Fungi on soybean (Glycine max L.) seeds grown in Mediterranean Region of Turkey. Türkiye Tarım Araşt Derg 8(3):367–373. https://doi.org/10.19159/tutad.1014598
White TJ, Bruns T, Lee S, Taylor J (1990) Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics. PCR protocols: A guide to methods and applications 18(1):315–322
Wu D, Turgeon BG (2013) Setosphaeria rostrata: insights from the sequenced genome of Setosphaeria turcica. Fungal Genet Biol 61:158–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fgb.2013.08.015
Zhang D, Wang F, Zhao J, Sun J, Fu D, Liu K, Chen N, Li G, Xiao S, Xue C (2019) Virulence, molecular diversity, and mating type of Curvularia lunata in China. Plant Dis 103(7):1728–1737. https://doi.org/10.1094/PDIS-10-18-1857-RE
Acknowledgements
We are thankful to the National Agriculture Research Center (NARC), Islamabad, Pakistan, and USDA, the USA for providing soybean genotypes for the trials.
Funding
This material is based upon work supported by Higher Education Commission (HEC) Pakistan under indigenous PhD fellowship Phase-II, Batch-V.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Imran Amin, Shahid Mansoor and Muhammad Ismail Buzdar gave the basic idea. Muhammad Ismail Buzdar collected the samples, performed the Experiment/trial and wrote the initial draft of manuscript. Muhammad Ismail Buzdar and Rubab Zahra analyzed the data. Imran Amin, Muhammad Jawad Akbar Awan and Saleem Ur-Rahman and Ghulam Raza reviewed and edited the final draft. All the authors read and agreed to finalize the paper for publication.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Buzdar, M.I., Awan, M.J.A., Rahman, S.U. et al. Seed-borne Curvularia lunata deteriorating seed health and germination of soybean. Biologia 78, 2575–2582 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11756-023-01400-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11756-023-01400-y